之前在分析其他安全厂商App的防护策略时,想要设计个风控分析沙盒来实现对于App行为的全面监控,包括
其中很棘手的问题在于如何应对App中越来越常见的内联系统调用,对于内联系统调用的监控我不希望通过ptrace这类进程注入的方式来实现,而是想寻求通过定制系统或者相关的方式来实现以达到无侵入App的目的
另一方面来说,通过定制系统的方式完成相关系统函数的修改确实是一种方式,但是定制系统在生产环境使用中会存在两个问题:
综上,最最贴合真实场景的是一种无侵入App且不阻断内核启动的方案,经过一顿搜索,最终定位到了Linux Kprobe这类内核监控方案
第一次了解到kprobe技术是在evilpan的文章Linux 内核监控在 Android 攻防中的应用
中,在现有的内核监控方案中分为数据、采集、前端三个层级
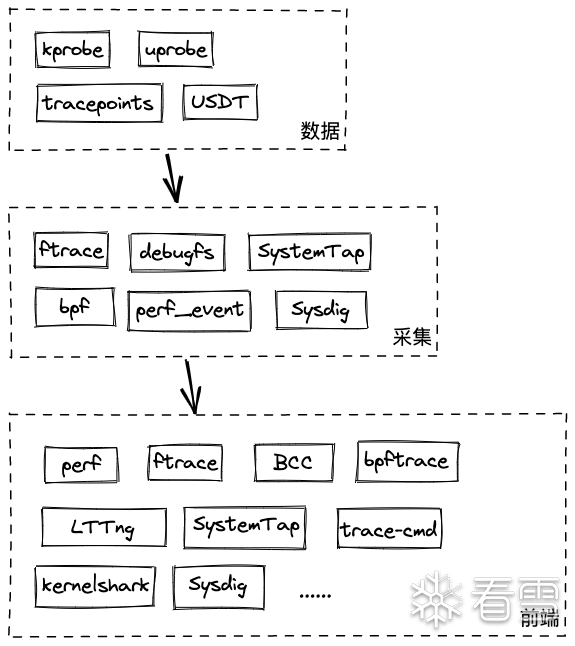
而作为最底层的数据来源,kprobe、uprobe等是我们在做内核监控时需要重点关注的点,相比较于其他几种实现方式,kprobe无论从可扩展性、影响范围上都是最适合做二次开发的,参考作者给出的对比表
因此最终确定了使用Linux Kprobe来作为内核系统函数的监控方案
kprobe可以认为是一种kernel hook手段,它基于内核中断的方式实现,可以想象它是内核层的异常hook(参考SandHook),既然是异常hook,那么它所能hook的范围就没有限制了,可以针对函数、也可以针对单条指令
简单理解就是把指定地址的指令替换成一个可以让cpu进入debug模式的指令(不同架构上指令不同),跳转到probe处理函数上进行数据收集、修改,再跳转回来继续执行
X86中使用的是int3指令,ARM64中使用的是BRK指令进入debug monitor模式
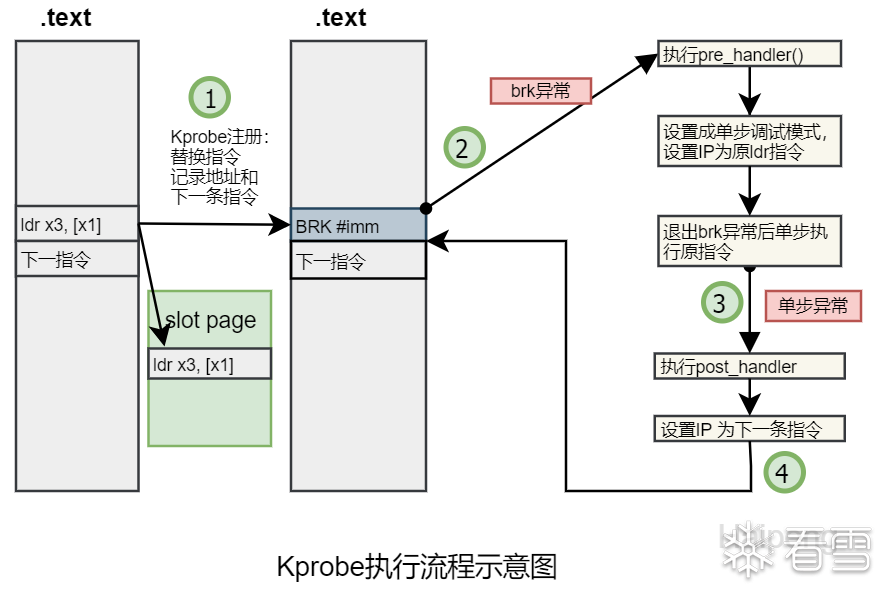
参考HPYU的Kprobe执行流程示意图
kprobe主要有两种使用方法,一是通过模块加载;二是通过debugfs接口。从可扩展性和工程化的角度来看,模块加载是更优的选择,debugfs在某些特殊场景下(快速验证某些函数)可能会适合
首先了解下动态内核模块(Loadable kernel module),LKM可以看出是内核向外提供的一个接口,通常是我们基于已编译好的内核产物+自定义的模块代码编译得到的ko文件,通过insmod的方式来实现动态新增定制功能,这种做法的好处是无需修改内核,需要新增功能时只需要变动相关LKM即可,它的作用域和静态编译的内核其他模块是完全等价的,而缺点是会带来些许性能上的损失,不过相比易用性来说这点可以忽略不计
参考Linux源码下的samples/kprobes,里面包含kprobe、kretprobe等案例
整个案例可以拆分成几个部分来看
这样就完成了对于do_for函数的hook,整体使用流程很清晰简单,初始化kprobes结构体(设置symbol_name、handlder)->注册kprobes->LKM封装
到目前为止,对于kprobe的使用是比较清晰了,下面从其原理角度来探究它是如何实现这套hook机制的
首先我们从kprobe的起始点init_kprobe函数切入,由于各个架构的实现不同,下面以arm64为例
init_kprobes的第一步是初始化哈希表,这里的哈希表指代的就是管理kprobe实例
KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE是64,对于每个槽初始化一个头结点
kprobe table的形式参考下图
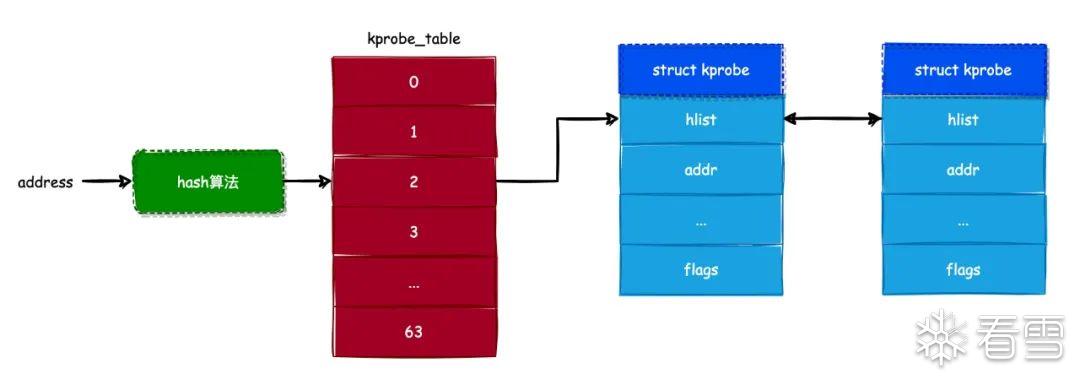
以hook的address为key,将kprobe保存到哈希表中,后续在查找时可以通过address来快速定位到kprobe_table槽,再通过对比hlist_node来确定kprobe
注册了kprobe_exceptions_notify函数作为回调函数,暂时不知道什么时候会出发die链的回调函数,先接着往下看
init_kprobes主要做了5件事
计算待hook点地址,这里分为了两种情况
kallsyms_lookup_name是内核的导出函数,可以通过kallsyms_lookup_name定位符号的真实地址
判断kprobe是否已注册过,注册过会在kprobe_table中查找到
这个过程主要对跟踪指令的内存地址进行合法检测,主要检查几个点:
申请新空间来保存当前地址原有指令,以便后续跳转回来时使用
根据地址计算key,插入kprobe的hlist字段,也就是hlist_node
调用链如下arm_kprobe->__arm_kprobe->arch_arm_kprobe,最终arch_arm_kprobe由各个架构决定,如arm64
将该地址的值替换成brk指令
register_kprobe主要做了件事
到这里为止,已经完成了对应地址的指令替换和原始指令的保存,下面看看是怎么触发自定义handler的处理
kprobe的触发和处理是通过brk exception和single step单步exception执行的,每次的处理函数中会修改被异常中断的上下文(struct pt_regs)的指令寄存器,实现执行流的跳转。ARM64对于异常处理的注册在arch/arm64/kernel/debug-monitors.c, 是arm64的通用debug模块
通过hook_debug_fault_code动态定义了异常处理的钩子函数brk_handler,它将在断点异常处理函数中被调用。hook_debug_fault_code替换了debug_fault_info的值,将原有的异常处理函数变成自定义的异常处理函数
arm64的异常处理都在arch/arm64/kernel/entry.S中
会调用到do_debug_exception函数,之所以是在el1这里处理,是因为BRK异常的产生是因为在内核态执行了BRR指令,内核态是执行在EL1的,所以异常等级是EL1
这里根据传入的esr解析得到数组索引,对于BRK,解析出来的索引为6,从而调用到debug_traps_init里注册的BRK exception处理函数brk_handler;对于HWSS exception,解析出来的索引是1,则调用debug_traps_init里注册的BRK exception处理函数single_step_handler
对于brk断点来说,最终会调用brk_handler
在brk异常处理中,首先是调用了自定义的pre_handler完成函数指令调用前的操作,接着调用了setup_singlestep函数,setup_singlestep主要是设置寄存器状态变成单步调试状态并设置pc指令为之前缓存的opcode(缓存的指令就是原始指令),由于之前设置了单步调试,在执行opcode之后会触发HWSS exception从而进入kprobe_single_step_handler
以上就是从源码角度来分析kprobe的实现流程,总结下来就是
可以结合和上文Kprobe执行流程示意图来梳理思路
| 监控方案 |
静态 |
动态 |
内核 |
用户 |
| Kprobes |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
| Uprobes |
✔ |
|
|
✔ |
| Tracepoints |
✔ |
|
✔ |
|
| USDT |
✔ |
|
|
✔ |
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kprobes.h>
static struct kprobe kp = {
.symbol_name = "_do_fork",
};
static int handler_pre(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, ip = %lx,"
" flags = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->ip, regs->flags);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, nip = 0x%lx,"
" msr = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->nip, regs->msr);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MIPS
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, epc = 0x%lx,"
" status = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->cp0_epc, regs->cp0_status);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TILEGX
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, pc = 0x%lx,"
" ex1 = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->pc, regs->ex1);
#endif
return 0;
}
static void handler_post(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs,
unsigned long flags)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, flags = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->flags);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, msr = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->msr);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MIPS
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, status = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->cp0_status);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TILEGX
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, ex1 = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->ex1);
#endif
}
static int handler_fault(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs, int trapnr)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "fault_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, trap #%dn",
p->addr, trapnr);
return 0;
}
static int __init kprobe_init(void)
{
int ret;
kp.pre_handler = handler_pre;
kp.post_handler = handler_post;
kp.fault_handler = handler_fault;
ret = register_kprobe(&kp);
if (ret < 0) {
printk(KERN_INFO "register_kprobe failed, returned %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
printk(KERN_INFO "Planted kprobe at %p\n", kp.addr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit kprobe_exit(void)
{
unregister_kprobe(&kp);
printk(KERN_INFO "kprobe at %p unregistered\n", kp.addr);
}
module_init(kprobe_init)
module_exit(kprobe_exit)
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
struct kprobe {
struct hlist_node hlist;
struct list_head list;
unsigned long nmissed;
kprobe_opcode_t *addr;
const char *symbol_name;
unsigned int offset;
kprobe_pre_handler_t pre_handler;
kprobe_post_handler_t post_handler;
kprobe_opcode_t opcode;
struct arch_specific_insn ainsn;
u32 flags;
};
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kprobes.h>
static struct kprobe kp = {
.symbol_name = "_do_fork",
};
static int handler_pre(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, ip = %lx,"
" flags = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->ip, regs->flags);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, nip = 0x%lx,"
" msr = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->nip, regs->msr);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MIPS
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, epc = 0x%lx,"
" status = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->cp0_epc, regs->cp0_status);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TILEGX
printk(KERN_INFO "pre_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, pc = 0x%lx,"
" ex1 = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->pc, regs->ex1);
#endif
return 0;
}
static void handler_post(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs,
unsigned long flags)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_X86
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, flags = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->flags);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PPC
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, msr = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->msr);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MIPS
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, status = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->cp0_status);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_TILEGX
printk(KERN_INFO "post_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, ex1 = 0x%lx\n",
p->addr, regs->ex1);
#endif
}
static int handler_fault(struct kprobe *p, struct pt_regs *regs, int trapnr)
{
printk(KERN_INFO "fault_handler: p->addr = 0x%p, trap #%dn",
p->addr, trapnr);
return 0;
}
static int __init kprobe_init(void)
{
int ret;
kp.pre_handler = handler_pre;
kp.post_handler = handler_post;
kp.fault_handler = handler_fault;
ret = register_kprobe(&kp);
if (ret < 0) {
printk(KERN_INFO "register_kprobe failed, returned %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
printk(KERN_INFO "Planted kprobe at %p\n", kp.addr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit kprobe_exit(void)
{
unregister_kprobe(&kp);
printk(KERN_INFO "kprobe at %p unregistered\n", kp.addr);
}
module_init(kprobe_init)
module_exit(kprobe_exit)
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
struct kprobe {
struct hlist_node hlist;
struct list_head list;
unsigned long nmissed;
kprobe_opcode_t *addr;
const char *symbol_name;
unsigned int offset;
kprobe_pre_handler_t pre_handler;
kprobe_post_handler_t post_handler;
kprobe_opcode_t opcode;
struct arch_specific_insn ainsn;
u32 flags;
};
static int __init init_kprobes(void)
{
int i, err = 0;
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kprobe_table[i]);
......
}
......
if (kretprobe_blacklist_size) {
for (i = 0; kretprobe_blacklist[i].name != NULL; i++) {
kretprobe_blacklist[i].addr =
kprobe_lookup_name(kretprobe_blacklist[i].name, 0);
.....
}
}
......
err = arch_init_kprobes();
if (!err)
err = register_die_notifier(&kprobe_exceptions_nb);
if (!err)
err = register_module_notifier(&kprobe_module_nb);
kprobes_initialized = (err == 0);
if (!err)
init_test_probes();
return err;
}
int __init arch_init_kprobes()
{
return 0;
}
static int __init init_kprobes(void)
{
int i, err = 0;
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kprobe_table[i]);
......
}
......
if (kretprobe_blacklist_size) {
for (i = 0; kretprobe_blacklist[i].name != NULL; i++) {
kretprobe_blacklist[i].addr =
kprobe_lookup_name(kretprobe_blacklist[i].name, 0);
.....
}
}
......
err = arch_init_kprobes();
if (!err)
err = register_die_notifier(&kprobe_exceptions_nb);
if (!err)
err = register_module_notifier(&kprobe_module_nb);
kprobes_initialized = (err == 0);
if (!err)
init_test_probes();
return err;
}
int __init arch_init_kprobes()
{
return 0;
}
static struct hlist_head kprobe_table[KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE];
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kprobe_table[i]);
......
}
struct kprobe *get_kprobe(void *addr)
{
struct hlist_head *head;
struct kprobe *p;
head = &kprobe_table[hash_ptr(addr, KPROBE_HASH_BITS)];
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(p, head, hlist) {
if (p->addr == addr)
return p;
}
return NULL;
}
static struct hlist_head kprobe_table[KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE];
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&kprobe_table[i]);
......
}
struct kprobe *get_kprobe(void *addr)
{
struct hlist_head *head;
struct kprobe *p;
head = &kprobe_table[hash_ptr(addr, KPROBE_HASH_BITS)];
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(p, head, hlist) {
if (p->addr == addr)
return p;
}
return NULL;
}
static struct notifier_block kprobe_exceptions_nb = {
.notifier_call = kprobe_exceptions_notify,
.priority = 0x7fffffff
};
int __kprobes kprobe_exceptions_notify(struct notifier_block *self,
unsigned long val, void *data)
{
struct die_args *args = data;
unsigned long addr = args->err;
int ret = NOTIFY_DONE;
switch (val) {
case DIE_IERR:
if (arc_kprobe_handler(addr, args->regs))
return NOTIFY_STOP;
break;
case DIE_TRAP:
if (arc_post_kprobe_handler(addr, args->regs))
return NOTIFY_STOP;
break;
default:
break;
}
return ret;
}
static struct notifier_block kprobe_exceptions_nb = {
.notifier_call = kprobe_exceptions_notify,
.priority = 0x7fffffff
};
int __kprobes kprobe_exceptions_notify(struct notifier_block *self,
unsigned long val, void *data)
{
struct die_args *args = data;
unsigned long addr = args->err;
int ret = NOTIFY_DONE;
switch (val) {
case DIE_IERR:
if (arc_kprobe_handler(addr, args->regs))
return NOTIFY_STOP;
break;
case DIE_TRAP:
if (arc_post_kprobe_handler(addr, args->regs))
return NOTIFY_STOP;
break;
default:
break;
}
return ret;
}
static struct notifier_block kprobe_module_nb = {
.notifier_call = kprobes_module_callback,
.priority = 0
};
static int kprobes_module_callback(struct notifier_block *nb,
unsigned long val, void *data)
{
struct module *mod = data;
struct hlist_head *head;
struct kprobe *p;
unsigned int i;
int checkcore = (val == MODULE_STATE_GOING);
if (val != MODULE_STATE_GOING && val != MODULE_STATE_LIVE)
return NOTIFY_DONE;
mutex_lock(&kprobe_mutex);
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
head = &kprobe_table[i];
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(p, head, hlist)
if (within_module_init((unsigned long)p->addr, mod) ||
(checkcore &&
within_module_core((unsigned long)p->addr, mod))) {
kill_kprobe(p);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&kprobe_mutex);
return NOTIFY_DONE;
}
static struct notifier_block kprobe_module_nb = {
.notifier_call = kprobes_module_callback,
.priority = 0
};
static int kprobes_module_callback(struct notifier_block *nb,
unsigned long val, void *data)
{
struct module *mod = data;
struct hlist_head *head;
struct kprobe *p;
unsigned int i;
int checkcore = (val == MODULE_STATE_GOING);
if (val != MODULE_STATE_GOING && val != MODULE_STATE_LIVE)
return NOTIFY_DONE;
mutex_lock(&kprobe_mutex);
for (i = 0; i < KPROBE_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
head = &kprobe_table[i];
hlist_for_each_entry_rcu(p, head, hlist)
if (within_module_init((unsigned long)p->addr, mod) ||
(checkcore &&
within_module_core((unsigned long)p->addr, mod))) {
kill_kprobe(p);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&kprobe_mutex);
return NOTIFY_DONE;
}
int register_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
addr = kprobe_addr(p);
p->addr = addr;
ret = check_kprobe_rereg(p);
if (ret)
return ret;
......
ret = check_kprobe_address_safe(p, &probed_mod);
......
old_p = get_kprobe(p->addr);
if (old_p) {
ret = register_aggr_kprobe(old_p, p);
goto out;
}
ret = prepare_kprobe(p);
......
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&p->hlist);
hlist_add_head_rcu(&p->hlist,
&kprobe_table[hash_ptr(p->addr, KPROBE_HASH_BITS)]);
if (!kprobes_all_disarmed && !kprobe_disabled(p))
arm_kprobe(p);
try_to_optimize_kprobe(p);
out:
mutex_unlock(&kprobe_mutex);
if (probed_mod)
module_put(probed_mod);
return ret;
}
int register_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
addr = kprobe_addr(p);
p->addr = addr;
ret = check_kprobe_rereg(p);
if (ret)
return ret;
......
ret = check_kprobe_address_safe(p, &probed_mod);
......
old_p = get_kprobe(p->addr);
if (old_p) {
ret = register_aggr_kprobe(old_p, p);
goto out;
}
ret = prepare_kprobe(p);
......
INIT_HLIST_NODE(&p->hlist);
hlist_add_head_rcu(&p->hlist,
&kprobe_table[hash_ptr(p->addr, KPROBE_HASH_BITS)]);
if (!kprobes_all_disarmed && !kprobe_disabled(p))
arm_kprobe(p);
try_to_optimize_kprobe(p);
out:
mutex_unlock(&kprobe_mutex);
if (probed_mod)
module_put(probed_mod);
return ret;
}
static struct kprobe *__get_valid_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
struct kprobe *ap, *list_p;
ap = get_kprobe(p->addr);
if (unlikely(!ap))
return NULL;
if (p != ap) {
list_for_each_entry_rcu(list_p, &ap->list, list)
if (list_p == p)
goto valid;
return NULL;
}
valid:
return ap;
}
static struct kprobe *__get_valid_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
struct kprobe *ap, *list_p;
ap = get_kprobe(p->addr);
if (unlikely(!ap))
return NULL;
if (p != ap) {
list_for_each_entry_rcu(list_p, &ap->list, list)
if (list_p == p)
goto valid;
return NULL;
}
valid:
return ap;
}
int __kprobes arch_prepare_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
unsigned long probe_addr = (unsigned long)p->addr;
extern char __start_rodata[];
extern char __end_rodata[];
......
p->opcode = le32_to_cpu(*p->addr);
switch (arm_kprobe_decode_insn(p->addr, &p->ainsn)) {
case INSN_REJECTED:
return -EINVAL;
case INSN_GOOD_NO_SLOT:
p->ainsn.api.insn = NULL;
break;
case INSN_GOOD:
p->ainsn.api.insn = get_insn_slot();
if (!p->ainsn.api.insn)
return -ENOMEM;
break;
};
if (p->ainsn.api.insn)
arch_prepare_ss_slot(p);
else
arch_prepare_simulate(p);
return 0;
}
static void __kprobes arch_prepare_ss_slot(struct kprobe *p)
{
patch_text(p->ainsn.api.insn, p->opcode);
flush_icache_range((uintptr_t) (p->ainsn.api.insn),
(uintptr_t) (p->ainsn.api.insn) +
MAX_INSN_SIZE * sizeof(kprobe_opcode_t));
p->ainsn.api.restore = (unsigned long) p->addr +
sizeof(kprobe_opcode_t);
}
int __kprobes arch_prepare_kprobe(struct kprobe *p)
{
unsigned long probe_addr = (unsigned long)p->addr;
extern char __start_rodata[];
extern char __end_rodata[];
......
p->opcode = le32_to_cpu(*p->addr);
switch (arm_kprobe_decode_insn(p->addr, &p->ainsn)) {
case INSN_REJECTED:
return -EINVAL;
case INSN_GOOD_NO_SLOT:
p->ainsn.api.insn = NULL;
break;
case INSN_GOOD:
p->ainsn.api.insn = get_insn_slot();
if (!p->ainsn.api.insn)
传播安全知识、拓宽行业人脉——看雪讲师团队等你加入!