Dex(Dalvik Executable)是Android系统中Java字节码的优化格式,相比传统的class文件,Dex具有更高的执行效率和更小的文件体积。
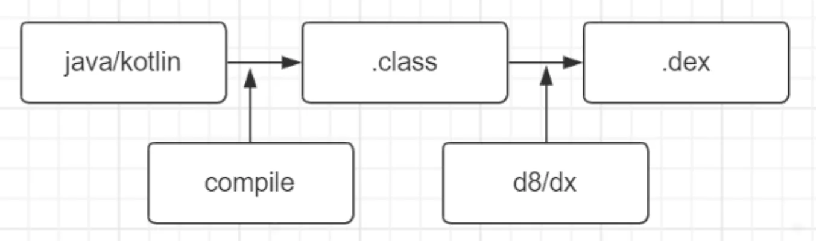
Dex文件整体架构
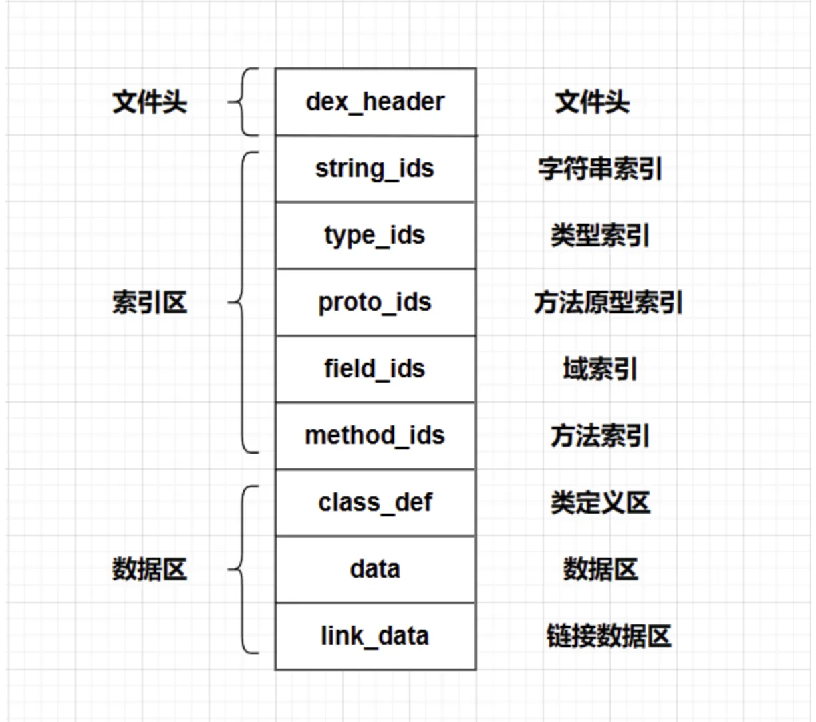
Dex文件采用索引+数据的分离设计,所有索引区在前,实际数据在后。这种设计优化了内存访问和加载速度。
下面是解析Dex结构可能用到的数据类型
Android源码 定义了dex文件用到的数据结构
sleb128、uleb128、uleb128p1是Dex文件中特有的LEB128类型.在下述Android源码位置可以找到LEB128的实现.
sleb128:有符号LEB128
uleb128:无符号LEB128
uleb128p1:uleb128+1
每个LEB128由1-5字节组成,所有字节组合在一起表示一个32位的数据, 每个字节只有低7位为有效位,最高位标识是否需要使用额外字节
如果第1个字节的最高位为1,表示LEB128需要使用第2个字节,如果第2个字节的最高位为1,表示会使用第3个字节,依次类推,直到最后一个字节的最高位为0
uleb128读取代码如下
值得注意的是参数为二级指针,也就是说,调用该函数时会移动一级指针,一级指针的偏移量即为读取到的uleb128的大小
将LEB128编码的字节序列解码为32位无符号整数。
合并两个字节的操作十分巧妙:
encoded_value是Dex文件中用于存储常量值的通用编码格式。它可以表示各种类型的常量数据,如数字、字符串、类型引用等。
头字节解析(1字节)
value_type含义(低五位)
指定数据的类型格式:
value_arg函数(高3位)
根据类型不同,含义不同:
对于数值类型:value_arg = 字节数 - 1
对于布尔类型:value_arg直接表示值
对于索引类型(STRING、TYPE、FIELD、METHOD)
value_arg = 索引字节数 - 1
对于特殊类型(NULL,ARRAY等)
value_arg通常为0或有特殊含义
encoded_array是Dex文件中用于存储数组常量的数据结构,主要用于:
数据结构定义:
由于encoded_array.values数组元素为encoded_value,所以每个元素的大小不固定,不能当作一般的数组解析
encoded_annotation是Dex文件中用于存储注解实例的数据结构,它表示一个具体的注解及其参数值。
该类型主要在DexClassDef的Annotations部分使用,此处仅做介绍
注解是什么?
特点:
官方好像不支持头文件,所以我们需要手搓或者偷一个,这里直接去安卓源码copy一下
d56K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6S2L8X3c8J5L8$3W2V1i4K6u0W2k6$3!0G2k6$3I4W2M7$3!0#2M7X3y4W2i4K6u0W2j5$3!0E0i4K6u0r3M7r3I4S2N6r3k6G2M7X3#2Q4x3V1k6V1j5h3I4$3K9h3E0Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1u0Q4x3V1k6J5k6h3k6K6i4K6u0r3K9r3g2S2k6s2y4Q4x3V1k6E0j5i4y4@1k6i4u0Q4x3V1k6D9K9h3u0V1k6i4S2Q4x3V1k6p5k6i4S2r3K9h3I4W2i4K6u0W2K9l9`.`.
4fbK9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6S2L8X3c8J5L8$3W2V1i4K6u0W2k6$3!0G2k6$3I4W2M7$3!0#2M7X3y4W2i4K6u0W2j5$3!0E0i4K6u0r3M7r3I4S2N6r3k6G2M7X3#2Q4x3V1k6S2M7Y4c8Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1u0Q4x3V1k6J5k6h3k6K6i4K6u0r3K9r3g2S2k6s2y4Q4x3V1k6E0j5i4y4@1k6i4u0Q4x3V1k6D9K9h3u0V1k6i4S2X3K9h3I4W2i4K6u0r3k6r3g2^5i4K6u0r3k6r3g2^5i4K6g2X3k6X3W2D9k6g2)9J5k6h3R3`.
copy之后还需要修改,让ai来即可
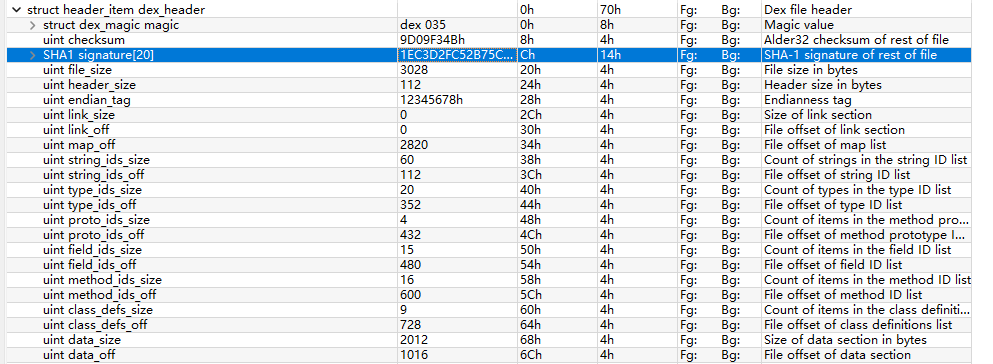
Magic
魔数和版本
作用:标识文件类型和DEX格式版本
格式:
用途:快速识别文件是否为DEX文件,以及使用的格式版本
checksum校验和
作用:验证文件完整性
计算范围:从signature字段开始到文件末尾的所有数据
算法:Adler-32(比CRC32更快但稍弱的校验算法)
用途:检测文件是否被损坏或篡改
signature[20]-sha1签名
作用:文件的唯一标识和完整性验证
计算范围:从file_size字段开始到文件末尾
算法:SHA-1(160位/20字节)
用途:
filesize-文件大小
作用:记录DEX文件的总大小
用途:
Header_size-头部大小
作用:DEX头部结构的大小
固定值:0x70 (112字节)
用途:
endian_tag-字节序标记
作用:标识文件使用的字节序
标准值:0x12345678(小端序,Android标准)
用途:
link_size & link_off 链接段
作用:静态链接数据(很少使用)
通常值:都为0
用途:预留给静态链接的DEX文件使用(实际很少见)
map_off-映射表偏移
作用:指向DEX文件的映射表(map_list)
用途:
映射表具体指的是什么:映射表是Dex文件的完整目录
映射表在文件末尾(例子中在 0x00000b04),它会列出所有数据区:
假设要找字符串"hello world"
方法一:只用Header
方法二:用映射表
解析代码
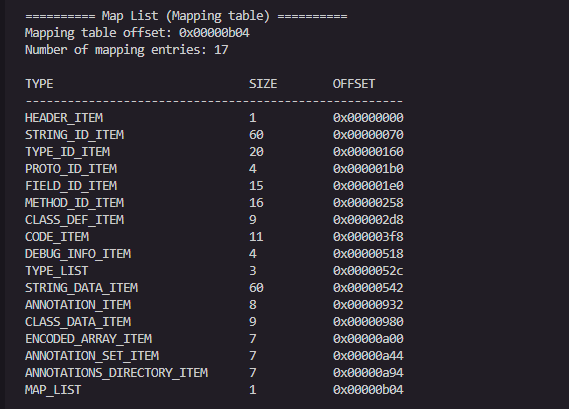
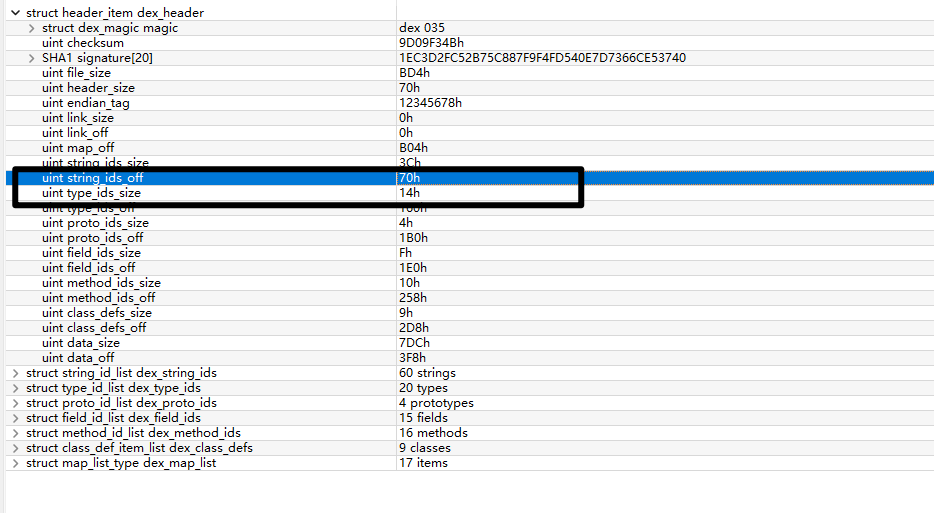
string_ids_size & string_ids_off-字符串索引表
作用:管理DEX中所有的字符串
内容:类名、方法名、字段名、常量字符串等
结构:每个条目4字节,指向实际字符串数据
用途:
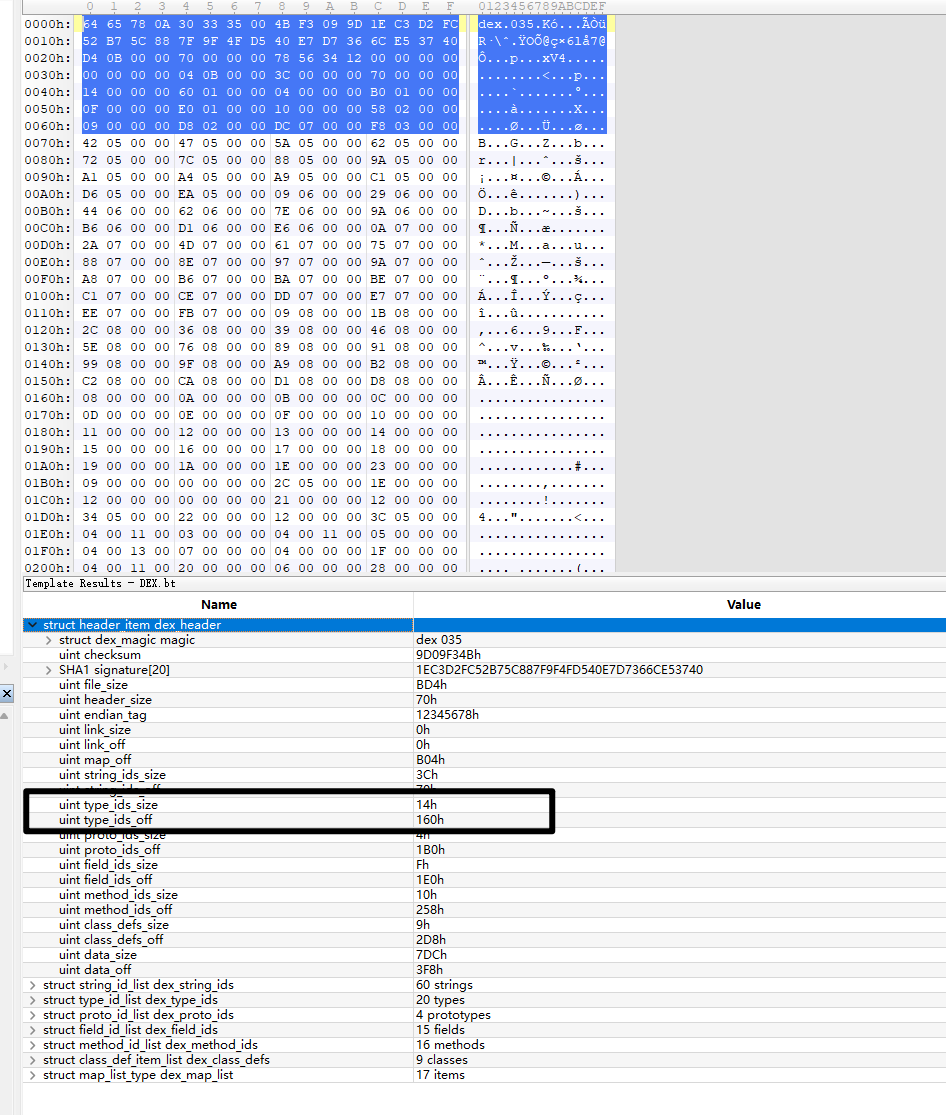
type_ids_size&type_ids_off-类型索引表
作用:存储所有类型描述符
内容:类类型、基本类型、数组类型等
格式:每个条目4字节,指向string_ids中的类型描述符
proto_ids_size & proto_ids_off-方法原型索引表
作用:存储方法签名(参数类型+返回类型)
内容:方法的参数列表和返回类型组合
结构:每个条目12字节
用途:
** field_ids_size & field_ids_off - 字段索引表**
作用:存储所有字段的引用
内容:所属类、字段类型、字段名
结构:每个条目8字节
用途:字段访问和引用
method_ids_size & method_ids_off - 方法索引表
作用:存储所有方法的引用
内容:所属类、方法原型、方法名
结构:每个条目8字节
用途:
class_defs_size & class_defs_off - 类定义表
作用:存储DEX中定义的所有类
内容:类的完整信息(字段、方法、访问标志等)
结构:每个条目32字节
用途:
data_size & data_off - 数据段
作用:存储实际的代码和数据
内容:
特点:通常占DEX文件的大部分空间
直接打印即可
实际字符串数据格式(在data区)
utf16_size:
数据类型:ULEB128变长编码
含义:字符串的UTF-16字符数量(不是字节数)
为什么用UTF-16长度:因为Java内部使用UTF-16编码,这个长度对应Java String的length()方法返回值
举例:字符串"Hello"的utf16_size = 5,中文"你好"的utf16_size = 2
data[]字段:
编码格式:MUTF-8 (Modified UTF-8)
结尾标记:必须以0x00字节结尾
长度:变长,实际字节数取决于字符内容和编码
什么是MUTF-8编码?
MUTF-8 (Modified UTF-8) 是Java虚拟机使用的一种UTF-8变体,与标准UTF-8有几个关键区别
需要注意MUTF-8编码和UTF-8编码不同的情况只有:
MUTF-8字符串头部保存的是字符串长度,是uleb128类型
二级索引结构
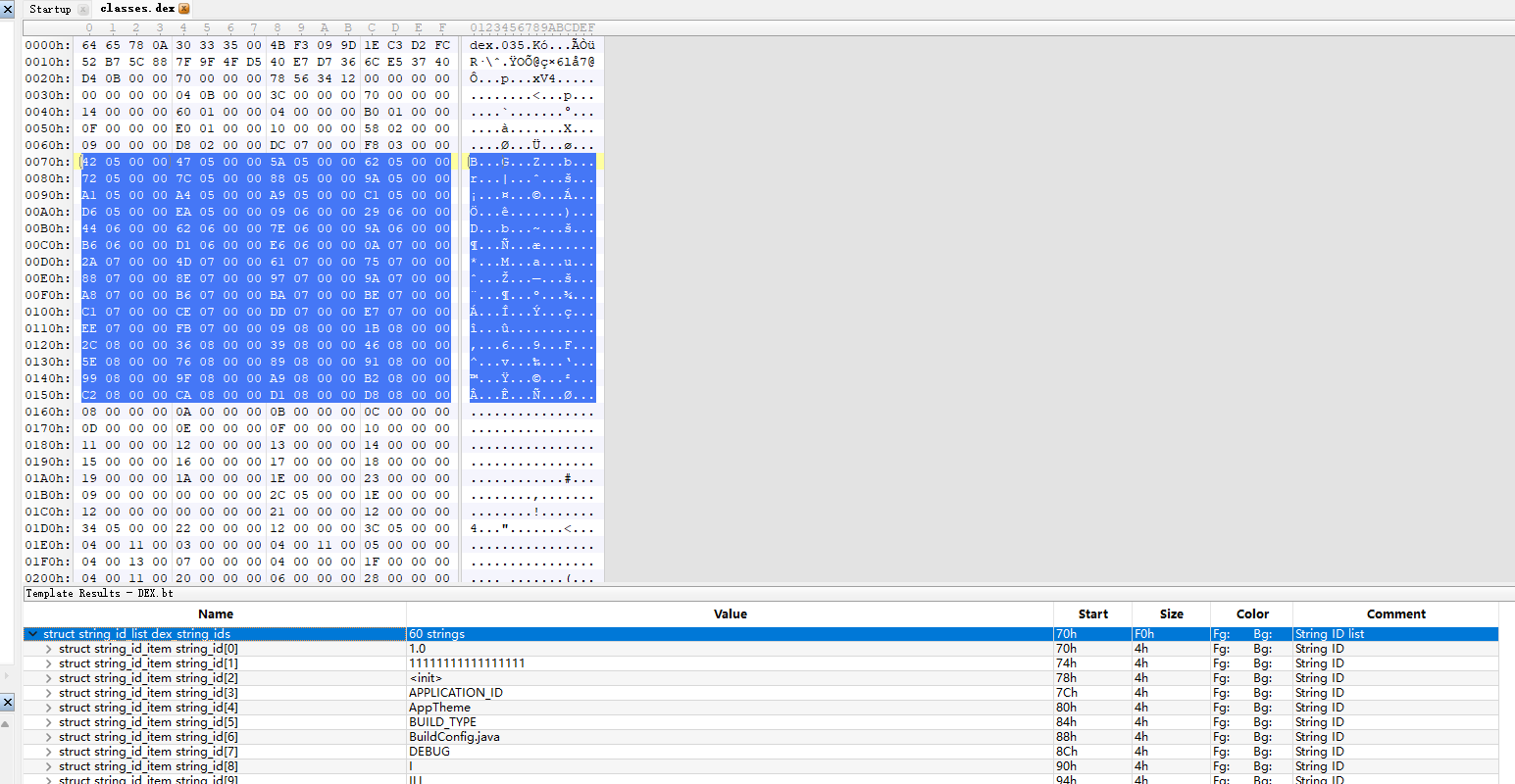
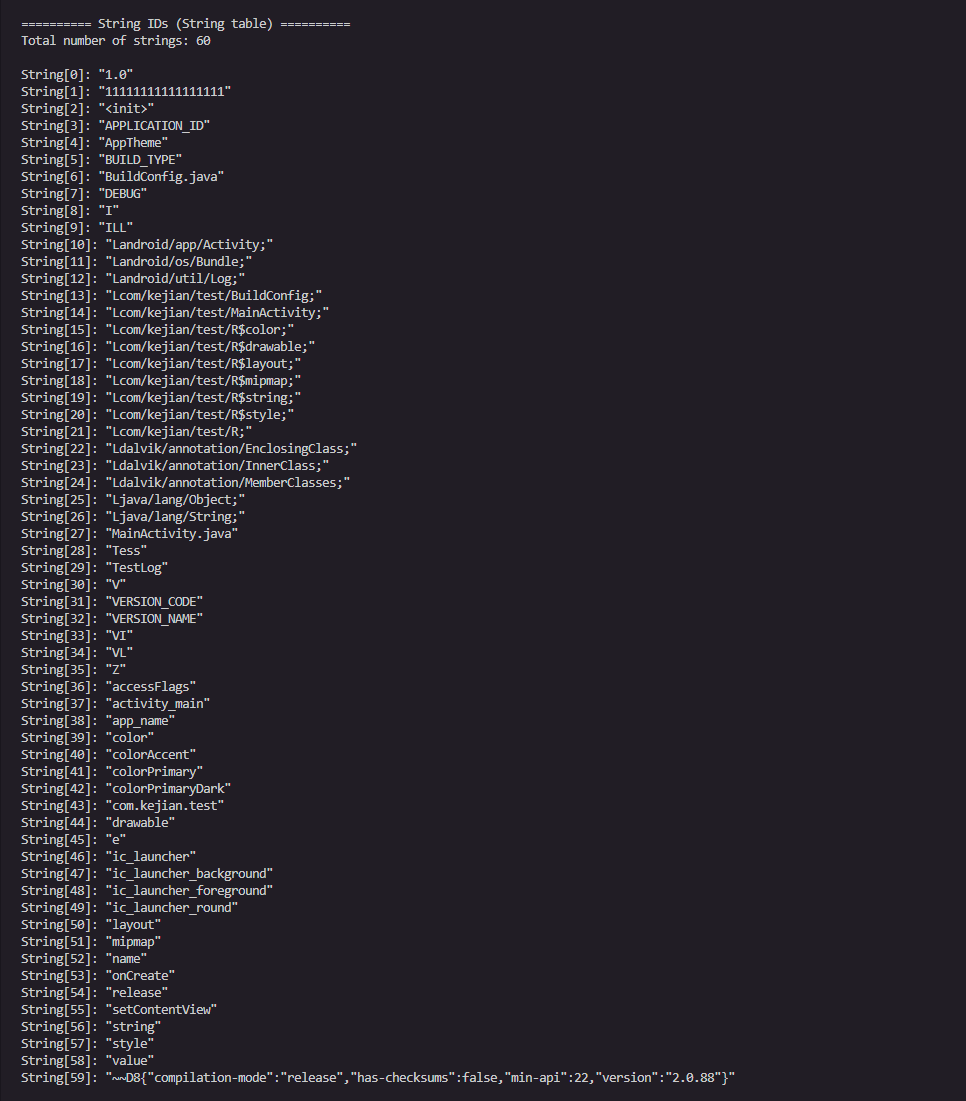
所以0x70就是string_id的起始位置,0x3C转换即为60,也就是string_id的数量
可以看到存储的字符串为"1.0"
我们看一下第一个字符串

可以看到string_data_off为0x542
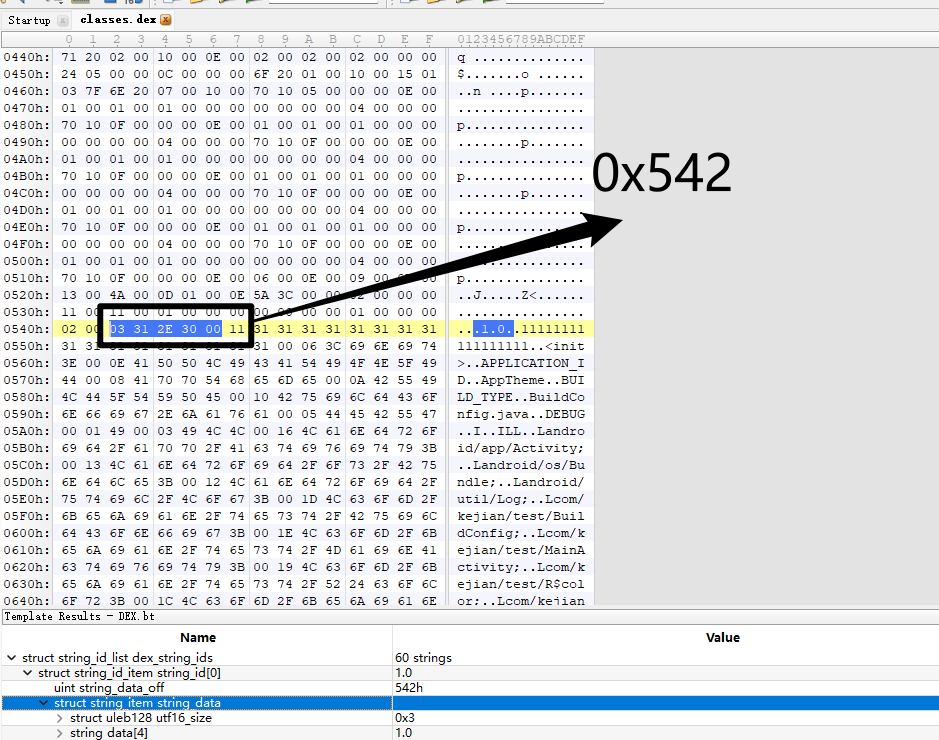
03 31 2E 30 00
0x3表示长度为UTF-16字符长度为3
MUTF-8编码的字符串数据为"1.0"结尾为00
我们再以一个最长的为例子
首先第一个字节0x58即为后面data的长度88,由于结尾还有00,即为89
解析代码
辅助函数为:
辅助函数处理不同长度的data[]利用了c语言字符串以NULL结尾的特性。
作用:类型系统的核心
和string一样,读取的只是索引
所以我们直接读取字符串即可获取类型了
辅助函数
这个辅助函数其实还是调用get_string_by_idx函数,只需要传进去正确的索引即可
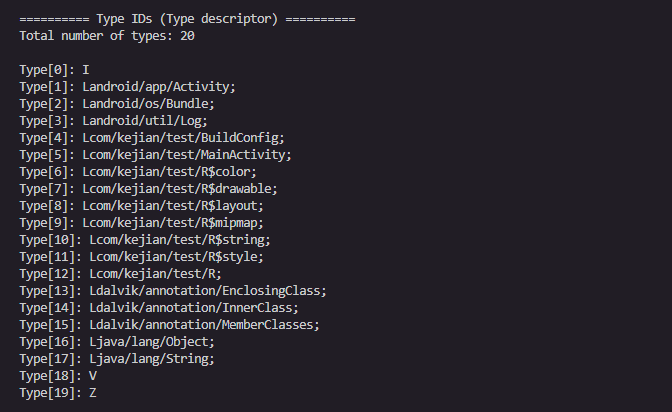
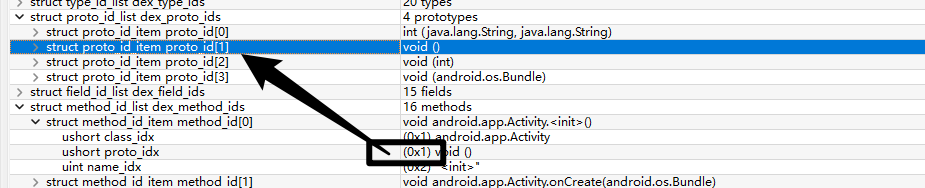
shorty_idx和return_type_idx其实我们已经知道是什么了,那么parameters_off呢?
参数列表结构:
其实这个还是指向type_ids
在我们逆向的时候,ProtoIDs就是我们见到的
对应的type_list

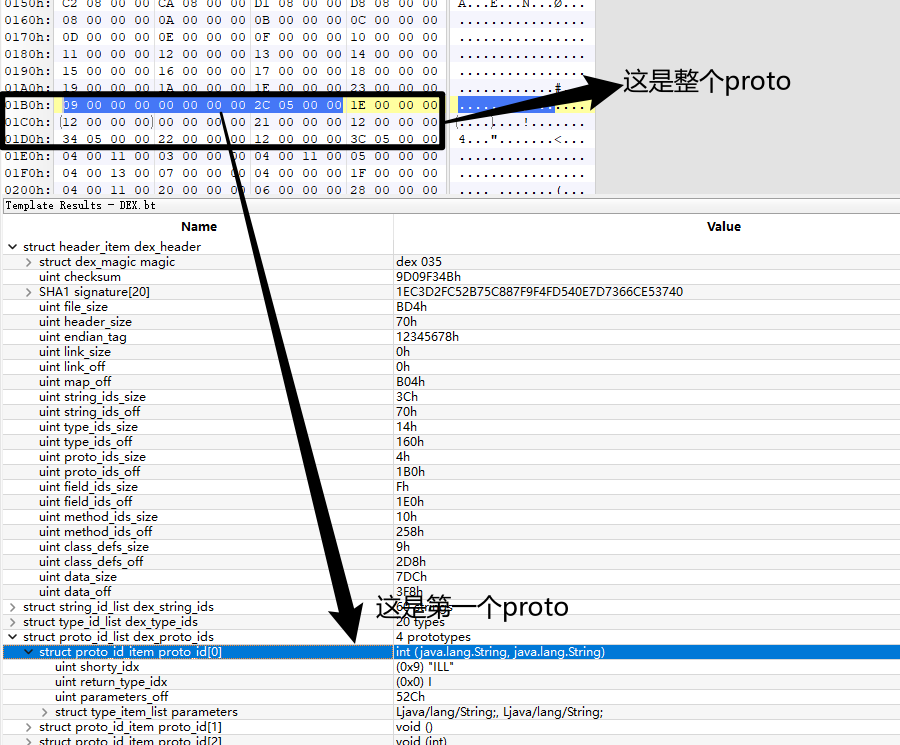

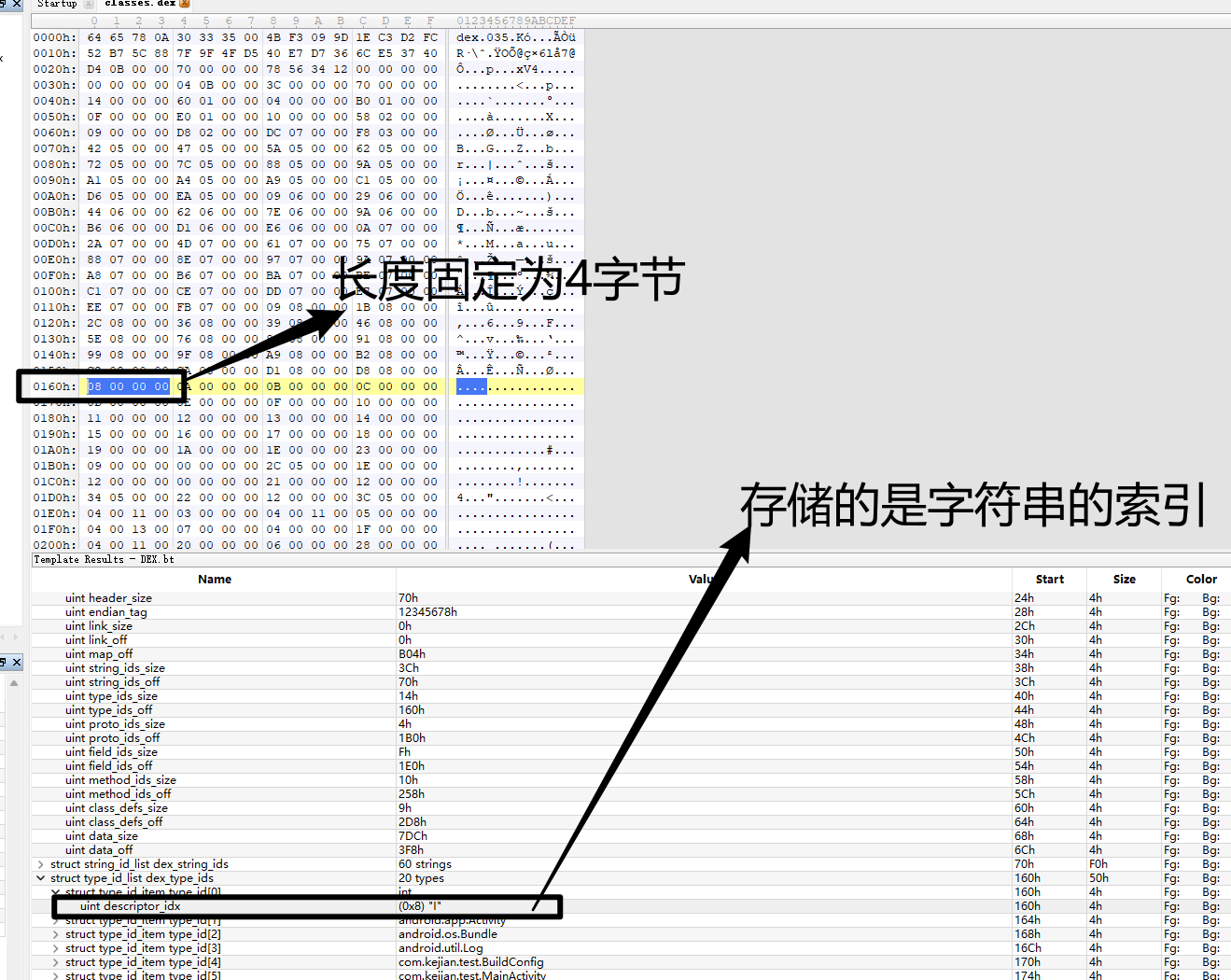
第一个在字符串的索引为9,第二个type_idx为0,那么就按照type_idx的解析方式解析,type_idx为0,对应的string为I
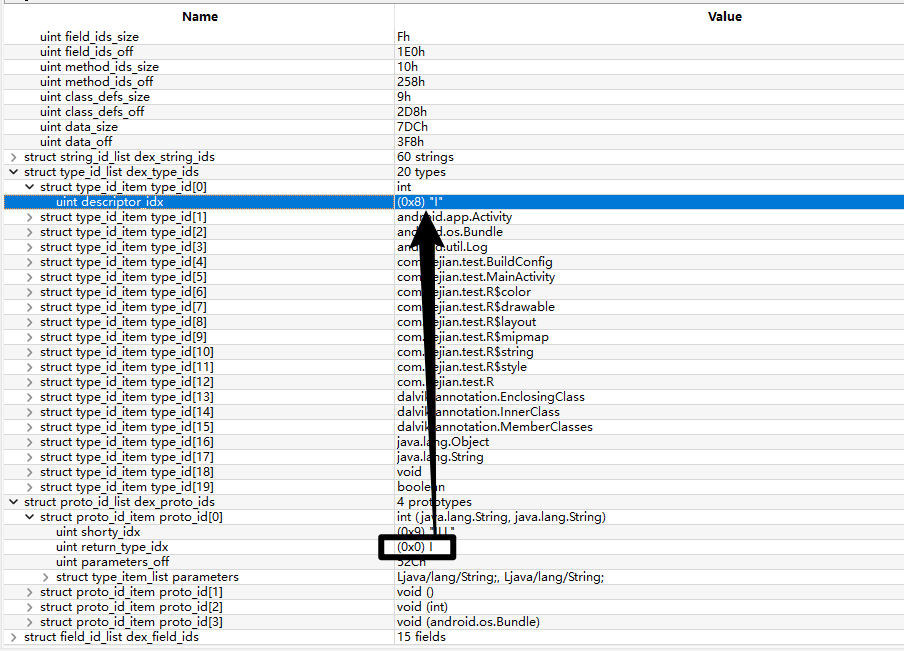
现在我们去找一下uint parameters_off值为0x52C
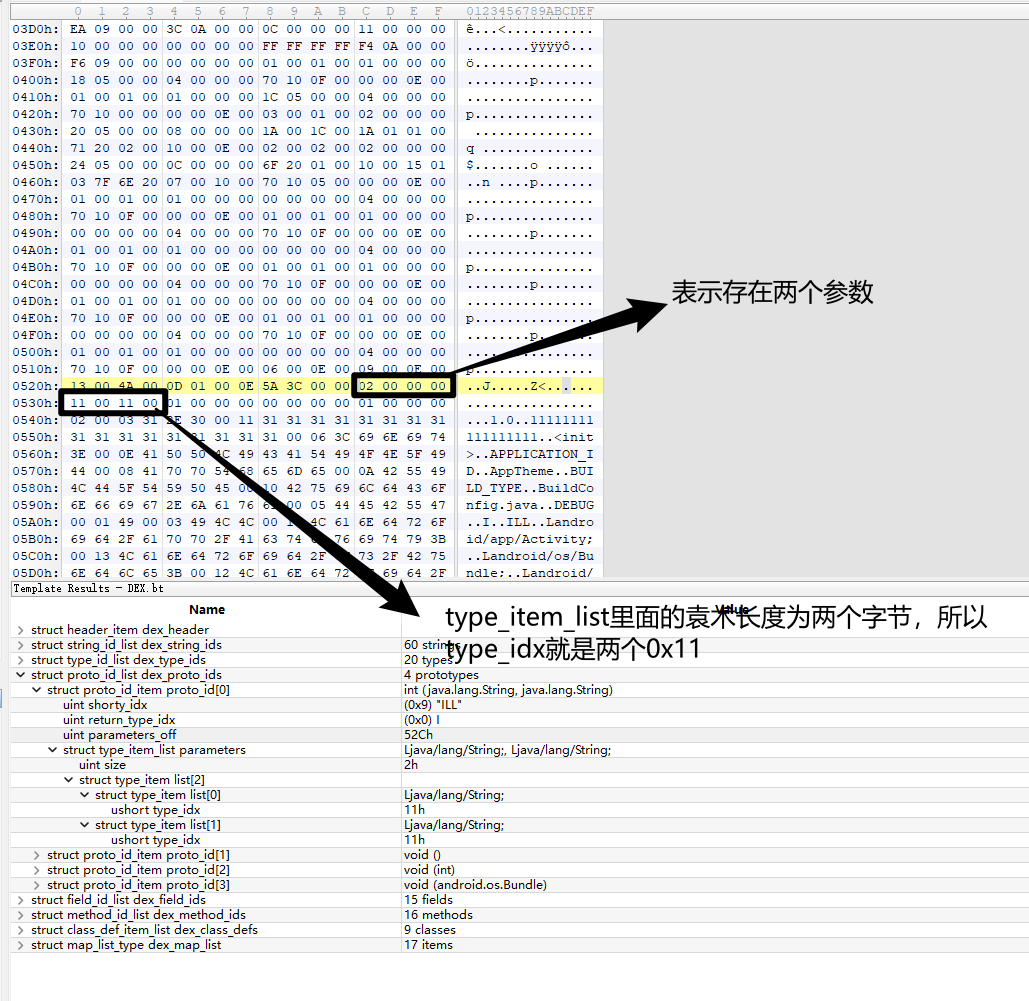
0x11也就是17,即

可以和上图对照验证
解析代码
辅助函数都是原来用过的,就不讲解了
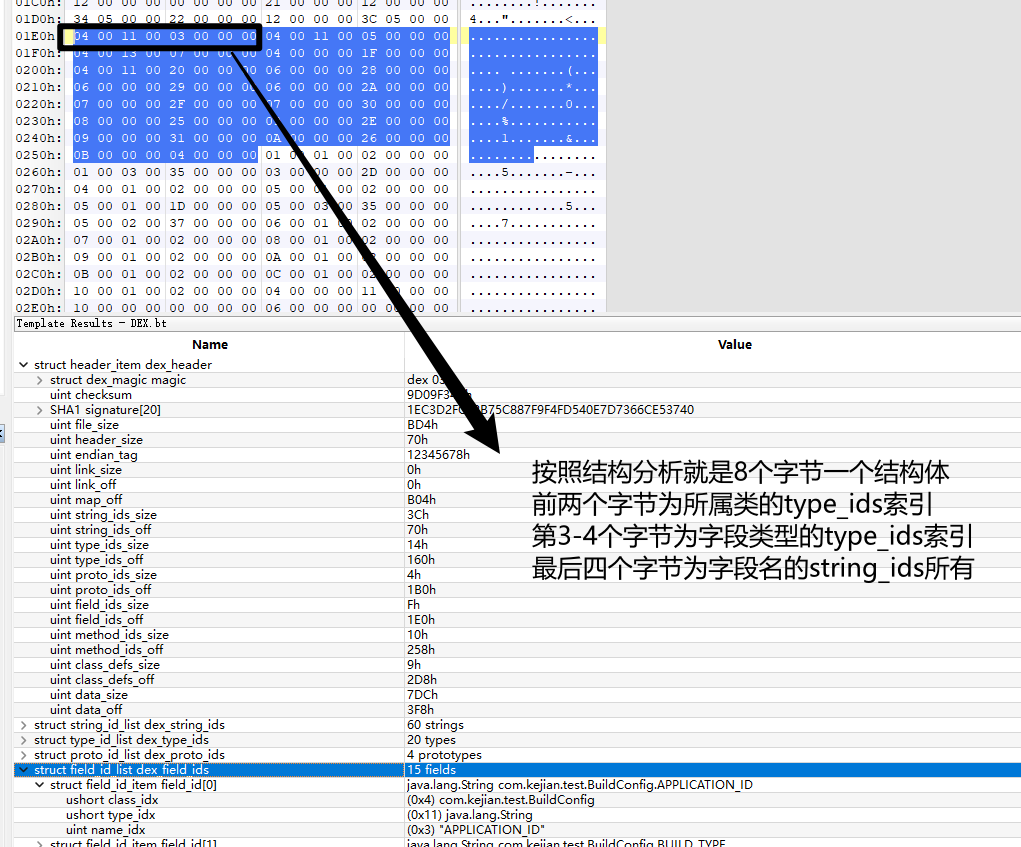
存储所有字段的索引
对应java代码

这个比较简单,都是我们刚才学过的概念
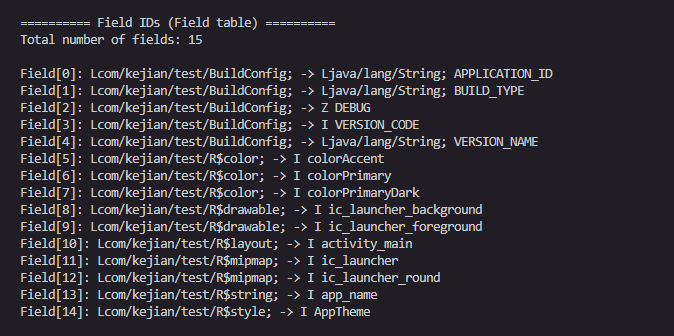
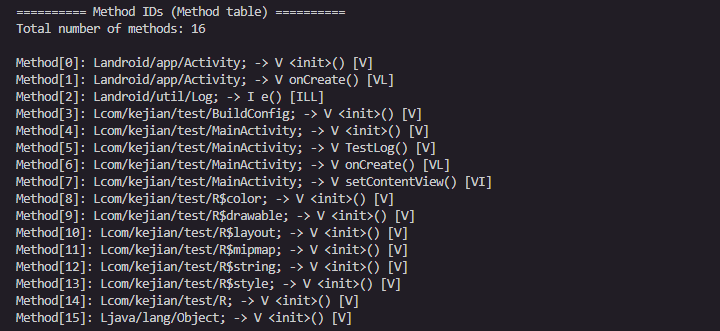
存储所有方法的引用
类似
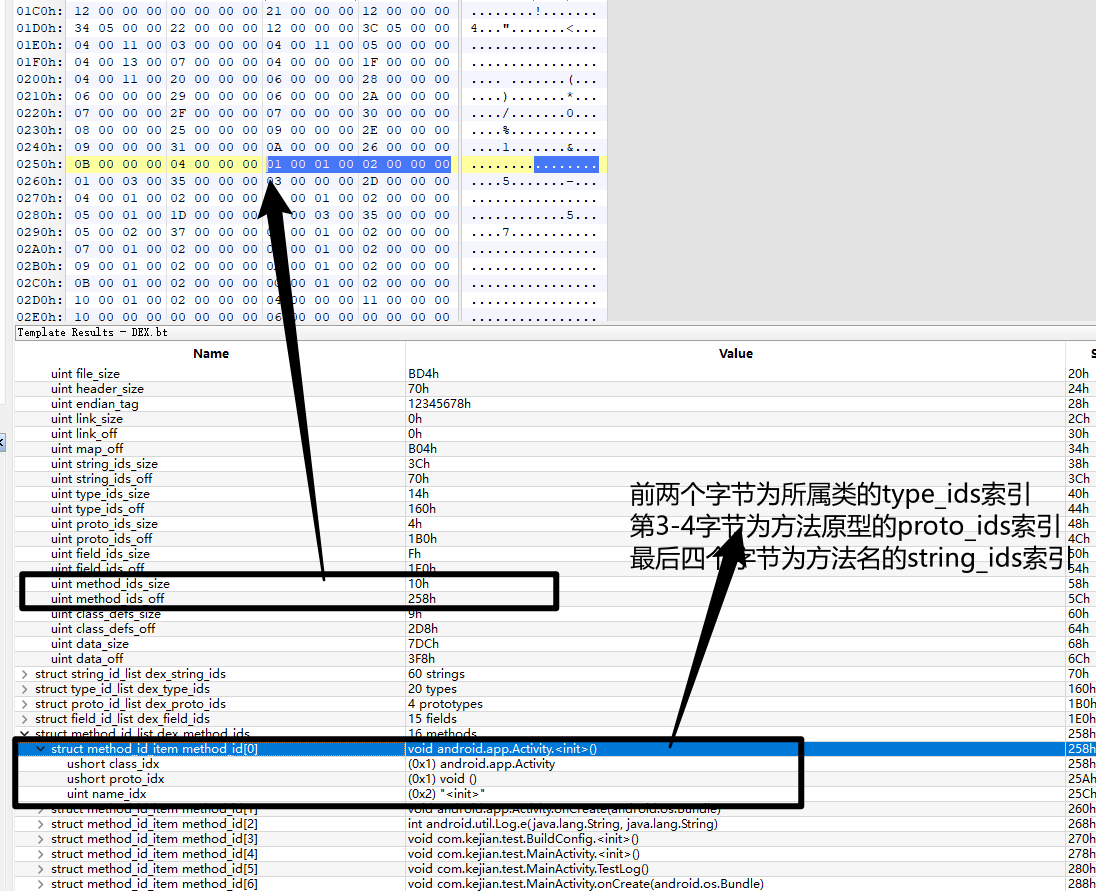
第二个字段proto_idx
解析代码
这是最复杂的部分
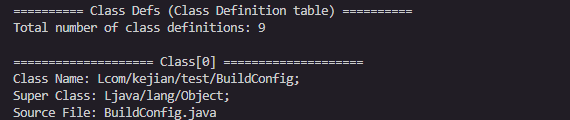
Class Defs(类定义)是DEX文件中本DEX定义的类的完整信息。
含义: 指向type_ids表,标识这个类的类型
示例: type_ids[5] → "Lcom/example/MainActivity;"
用途: 获取类的完整限定名,也就是类名
含义: 指向type_ids表,标识父类
特殊值: 0xFFFFFFFF (DEX_NO_INDEX) 表示没有父类
注意: 只有java.lang.Object没有父类
含义: 指向string_ids表,表示源文件名
示例: "MainActivity.java"
可选:可能为DEX_NO_INDEX(混淆或优化时)
<font style="color:rgb(255, 255, 255);">限定名限定名限定名</font>
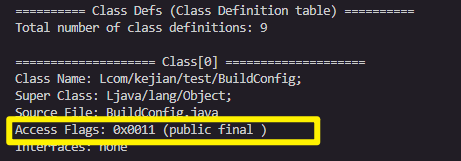
含义: 描述类的访问权限和特性
可能的值为:
解析代码
含义: 指向type_list结构的偏移,包含实现的接口列表
值为0: 表示不实现任何接口
结构: 与方法参数的type_list相同格式
与其他结构的关系
解析代码
含义: 指向class_data_item结构
重要性: 包含类的字段和方法定义
值为0: 表示没有字段和方法(如接口的某些情况)
字段索引差值是什么
encoded_method比encoded_field多了一个code_off
内存布局示意图
解析代码
为什么传递二级指针呢?
C语言是值传递,在c语言中,函数参数都是复制一份副本传入的
一级指针的情况
二级指针
这样我们就正确读取了
static_fields_size,instance_fields_size,direct_methods_size,virtual_methods_size的值,现在可以分析这四个对应的结构了
四个字段但是只有两个结构,因此只需要定义两个函数即可
get_access_flags_string已经介绍过了
解析代码项和调试信息
解析调试信息
含义: 指向 annotations_directory_item 结构的偏移
值为0: 表示没有注解
内容:类级别,字段级别,方法级别的注解信息
这个很复杂,我们需要先了解一下结构
注解是什么?注解就是java中的@标记符,用户给代码添加元数据
注解系统的层级结构:
第一层annotations_directory_item(注解目录)
一个类的所有注解的目录!
类注解不需要索引,因为一个类只有一组注解
参数注解比较特殊,因为一个方法可能多个参数,每个参数可能都有自己的注解
方法注解为:
第二层:annotation_set_item (注解集合)
存储一组注解(一个元素可能有多个注解)
例如一个方法可能同时有 @Override @Deprecated
第三层:annotation_item (注解项)
第4层:encoded_annotation (注解内容)
简化
解析代码,综上分析我们知道了类注解,字段注解,方法注解,可以用一套代码,但是参数注解需要多一步
以解析类注解为例,概括字段注解,方法注解
解析注解集,也就是处理第二层
下面该解析第三层了,也就是注解项
下面第四层,解析注解内容
parse_encoded_value解析
含义: 指向encoded_array_item,包含静态字段的初始值
值为0: 表示没有静态字段初始值
用途: 静态字段的默认值
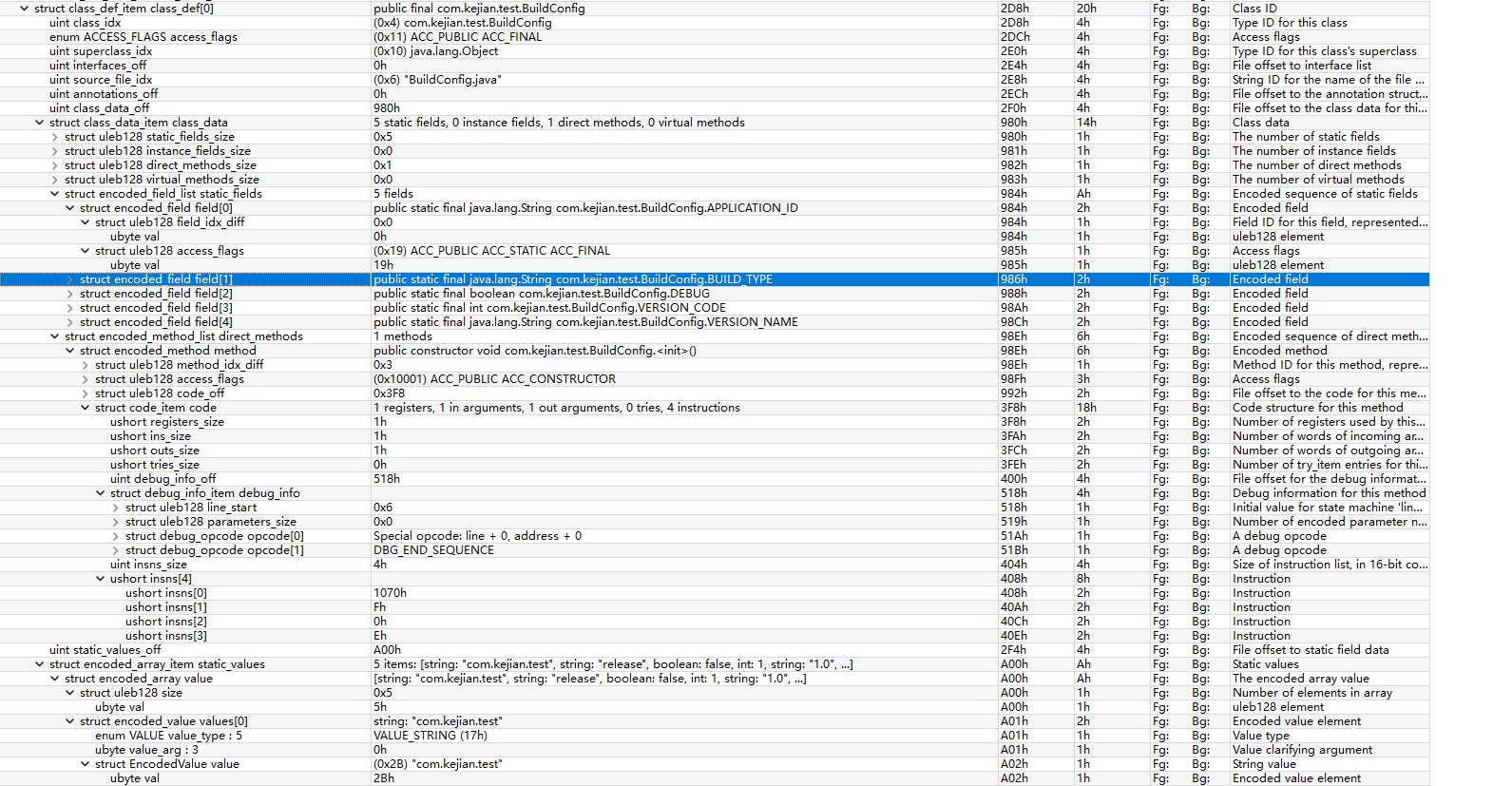
解析静态值
parse_static_values
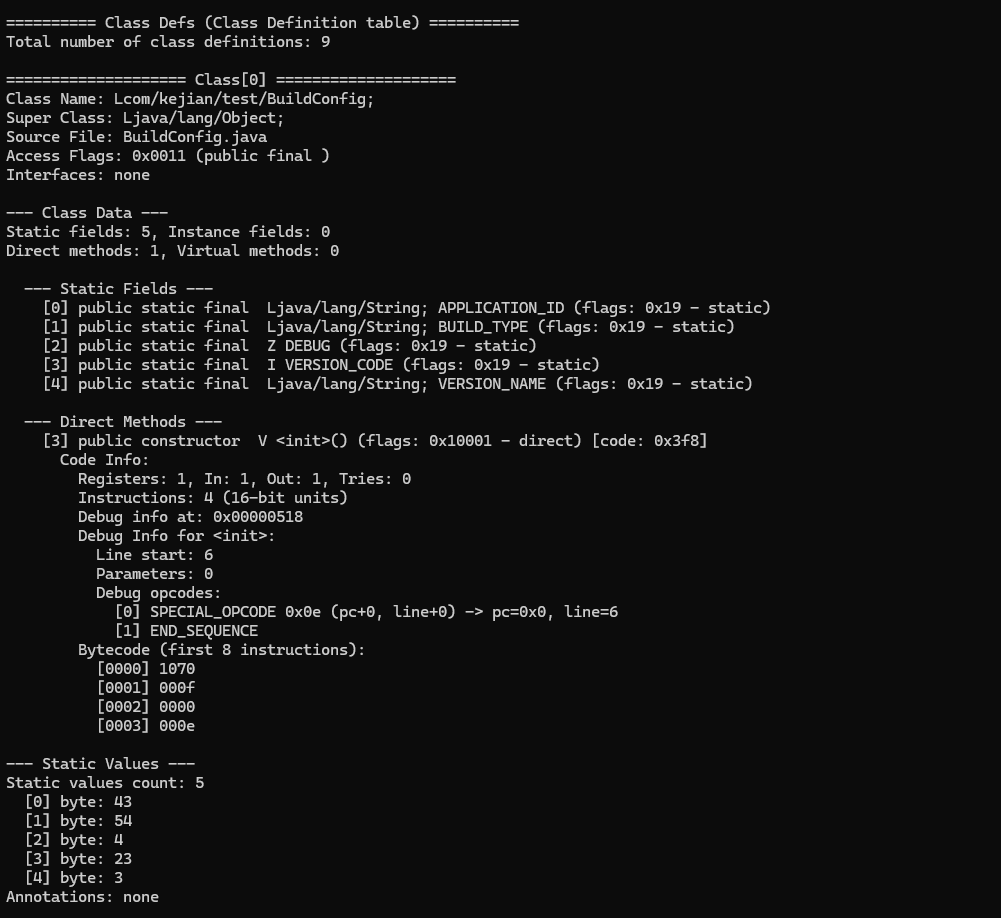
Data区是DEX文件的核心内容区,存储所有实际数据,而前面的索引表只是"目录"
存储静态链接信息,但是通常为空,因为Android使用动态链接,类和方法在运行时解析。link_data是为早期的静态链接优化设计的,现代Android基本不用
参考
文件偏移 区域名称 作用
0x00 dex_header 文件头信息
0x70 string_ids 字符串索引表
... type_ids 类型索引表
... proto_ids 方法原型索引表
... field_ids 字段索引表
... method_ids 方法索引表
... class_defs 类定义表
... call_site_ids 调用点索引表(API 26+)
... method_handles 方法句柄表(API 26+)
... data 实际数据区
... link_data 链接数据(可选)
文件偏移 区域名称 作用
0x00 dex_header 文件头信息
0x70 string_ids 字符串索引表
... type_ids 类型索引表
... proto_ids 方法原型索引表
... field_ids 字段索引表
... method_ids 方法索引表
... class_defs 类定义表
... call_site_ids 调用点索引表(API 26+)
... method_handles 方法句柄表(API 26+)
... data 实际数据区
... link_data 链接数据(可选)
| 自定义类型 |
原类型 |
含义 |
| s1 |
int8_t |
有符号单字节 |
| u1 |
uint8_t |
无符号单字节 |
| s2 |
int16_t |
|
| u2 |
uint16_t |
|
| s4 |
int32_t |
|
| u4 |
uint32_t |
|
| s8 |
int64_t |
|
| u8 |
uint64_t |
|
| sleb128 |
无 |
有符号LEB128,可变长度 |
| uleb128 |
无 |
无符号LEB128,可变长度 |
| uleb128p1 |
无 |
等于ULEB128加1,可变长度 |
int readUnsignedLeb128(const u1** pStream) {
const u1* ptr = *pStream; //初始化
int result = *(ptr++); //获取第一个字节
if (result > 0x7f) { //如果第一个字节大于0x7f,那么就还有第二个字节
int cur = *(ptr++); //第二个字节
result = (result & 0x7f) | ((cur & 0x7f) << 7); //把两个字节合并
if (cur > 0x7f) { //继续处理
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 14;
if (cur > 0x7f) {
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 21;
if (cur > 0x7f) {
/*
* Note: We don't check to see if cur is out of
* range here, meaning we tolerate garbage in the
* high four-order bits.
*/
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= cur << 28;
}
}
}
}
*pStream = ptr;
return result;
}
int readUnsignedLeb128(const u1** pStream) {
const u1* ptr = *pStream; //初始化
int result = *(ptr++); //获取第一个字节
if (result > 0x7f) { //如果第一个字节大于0x7f,那么就还有第二个字节
int cur = *(ptr++); //第二个字节
result = (result & 0x7f) | ((cur & 0x7f) << 7); //把两个字节合并
if (cur > 0x7f) { //继续处理
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 14;
if (cur > 0x7f) {
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= (cur & 0x7f) << 21;
if (cur > 0x7f) {
/*
* Note: We don't check to see if cur is out of
* range here, meaning we tolerate garbage in the
* high four-order bits.
*/
cur = *(ptr++);
result |= cur << 28;
}
}
}
}
*pStream = ptr;
return result;
}
步骤1:result & 0x7f
result = 0xAC = 1010 1100
0x7f = 0x7F = 0111 1111
result & 0x7f = 0010 1100 = 0x2C = 44
作用:去掉第一个字节的继续标志,只保留数据位
步骤2:cur & 0x7f
cur = 0x02 = 0000 0010
0x7f = 0x7F = 0111 1111
cur & 0x7f = 0000 0010 = 0x02 = 2
作用:去掉第二个字节的继续标志(虽然本来就是0)
步骤3:(cur & 0x7f) << 7
(cur & 0x7f) = 2 = 0000 0010
左移7位后 = 0000 0010 0000 0000 = 256
作用:将第二个字节的数据放到正确的位置(bit 7-13)
步骤4:最终合并
(result & 0x7f) = 44 = 0000 0000 0010 1100
((cur & 0x7f) << 7) = 256 = 0000 0001 0000 0000
─────────────────────
最终result = 44 | 256 = 300 = 0000 0001 0010 1100
步骤1:result & 0x7f
result = 0xAC = 1010 1100
0x7f = 0x7F = 0111 1111
result & 0x7f = 0010 1100 = 0x2C = 44
作用:去掉第一个字节的继续标志,只保留数据位
步骤2:cur & 0x7f
cur = 0x02 = 0000 0010
0x7f = 0x7F = 0111 1111
cur & 0x7f = 0000 0010 = 0x02 = 2
作用:去掉第二个字节的继续标志(虽然本来就是0)
步骤3:(cur & 0x7f) << 7
(cur & 0x7f) = 2 = 0000 0010
左移7位后 = 0000 0010 0000 0000 = 256
作用:将第二个字节的数据放到正确的位置(bit 7-13)
步骤4:最终合并
(result & 0x7f) = 44 = 0000 0000 0010 1100
((cur & 0x7f) << 7) = 256 = 0000 0001 0000 0000
─────────────────────
最终result = 44 | 256 = 300 = 0000 0001 0010 1100
// encoded_value不是固定结构体,而是变长的数据格式
// 由头字节 + 可变长度数据组成
struct encoded_value {
u1 type_and_arg; // 头字节:(value_arg << 5) | value_type
u1 data[]; // 可变长度数据,根据类型和参数决定长度
};
// encoded_value不是固定结构体,而是变长的数据格式
// 由头字节 + 可变长度数据组成
struct encoded_value {
u1 type_and_arg; // 头字节:(value_arg << 5) | value_type
u1 data[]; // 可变长度数据,根据类型和参数决定长度
};
// 格式:(value_arg << 5) | value_type
// 位布局:AAA TTTTT
// A = value_arg(高3位,0-7)
// T = value_type(低5位,0-31)
u1 header = (value_arg << 5) | value_type;
// 解析方式
u1 value_type = header & 0x1F; // 提取低5位
u1 value_arg = (header >> 5) & 0x07; // 提取高3位
// 格式:(value_arg << 5) | value_type
// 位布局:AAA TTTTT
// A = value_arg(高3位,0-7)
// T = value_type(低5位,0-31)
u1 header = (value_arg << 5) | value_type;
// 解析方式
u1 value_type = header & 0x1F; // 提取低5位
u1 value_arg = (header >> 5) & 0x07; // 提取高3位
#define VALUE_BYTE 0x00 // 字节值
#define VALUE_SHORT 0x02 // 短整型
#define VALUE_CHAR 0x03 // 字符
#define VALUE_INT 0x04 // 整型
#define VALUE_LONG 0x06 // 长整型
#define VALUE_FLOAT 0x10 // 浮点数
#define VALUE_DOUBLE 0x11 // 双精度浮点数
#define VALUE_METHOD_TYPE 0x15 // 方法类型
#define VALUE_METHOD_HANDLE 0x16 // 方法句柄
#define VALUE_STRING 0x17 // 字符串索引
#define VALUE_TYPE 0x18 // 类型索引
#define VALUE_FIELD 0x19 // 字段索引
#define VALUE_METHOD 0x1A // 方法索引
#define VALUE_ENUM 0x1B // 枚举值
#define VALUE_ARRAY 0x1C // 数组
#define VALUE_ANNOTATION 0x1D // 注解
#define VALUE_NULL 0x1E // null值
#define VALUE_BOOLEAN 0x1F // 布尔值
#define VALUE_BYTE 0x00 // 字节值
#define VALUE_SHORT 0x02 // 短整型
#define VALUE_CHAR 0x03 // 字符
#define VALUE_INT 0x04 // 整型
#define VALUE_LONG 0x06 // 长整型
#define VALUE_FLOAT 0x10 // 浮点数
#define VALUE_DOUBLE 0x11 // 双精度浮点数
#define VALUE_METHOD_TYPE 0x15 // 方法类型
#define VALUE_METHOD_HANDLE 0x16 // 方法句柄
#define VALUE_STRING 0x17 // 字符串索引
#define VALUE_TYPE 0x18 // 类型索引
#define VALUE_FIELD 0x19 // 字段索引
#define VALUE_METHOD 0x1A // 方法索引
#define VALUE_ENUM 0x1B // 枚举值
#define VALUE_ARRAY 0x1C // 数组
#define VALUE_ANNOTATION 0x1D // 注解
#define VALUE_NULL 0x1E // null值
#define VALUE_BOOLEAN 0x1F // 布尔值
// 整数42只需1字节存储
value_arg = 1 - 1 = 0
// 整数65536需要3字节存储
value_arg = 3 - 1 = 2
// 整数42只需1字节存储
value_arg = 1 - 1 = 0
// 整数65536需要3字节存储
value_arg = 3 - 1 = 2
// true: value_arg = 1
// false: value_arg = 0
// true: value_arg = 1
// false: value_arg = 0
// 字符串索引15,需要1字节
value_type = VALUE_STRING (0x17)
value_arg = 1 - 1 = 0
header = (0 << 5) | 0x17 = 0x17
// 字符串索引300,需要2字节
value_type = VALUE_STRING (0x17)
value_arg = 2 - 1 = 1
header = (1 << 5) | 0x17 = 0x37
// 字符串索引15,需要1字节
value_type = VALUE_STRING (0x17)
value_arg = 1 - 1 = 0
header = (0 << 5) | 0x17 = 0x17
// 字符串索引300,需要2字节
value_type = VALUE_STRING (0x17)
value_arg = 2 - 1 = 1
header = (1 << 5) | 0x17 = 0x37
// NULL值
value_type = VALUE_NULL (0x1E)
value_arg = 0 // 固定为0
header = (0 << 5) | 0x1E = 0x1E
// 数组
value_type = VALUE_ARRAY (0x1C)
value_arg = 0 // 固定为0,大小用uleb128单独编码
header = (0 << 5) | 0x1C = 0x1C
// NULL值
value_type = VALUE_NULL (0x1E)
value_arg = 0 // 固定为0
header = (0 << 5) | 0x1E = 0x1E
// 数组
value_type = VALUE_ARRAY (0x1C)
value_arg = 0 // 固定为0,大小用uleb128单独编码
header = (0 << 5) | 0x1C = 0x1C
encoded_array {
uleb128 size; // 数组元素个数
encoded_value values[]; // 数组元素,每个都是encoded_value
}
encoded_array {
uleb128 size; // 数组元素个数
encoded_value values[]; // 数组元素,每个都是encoded_value
}
| 名称 |
格式 |
说明 |
| size |
uleb128 |
数组中的元素数量 |
| values |
encoded_value[size] |
采用本部分所指定格式的一系列 size<br/>encoded_value<br/> 字节序列;依序串联。 |
encoded_annotation {
uleb128 type_idx; // 注解类型的type_ids索引
uleb128 size; // 注解元素个数
annotation_element elements[]; // 注解元素数组
}
annotation_element {
uleb128 name_idx; // 元素名称的string_ids索引
encoded_value value; // 元素值
}
encoded_annotation {
uleb128 type_idx; // 注解类型的type_ids索引
uleb128 size; // 注解元素个数
annotation_element elements[]; // 注解元素数组
}
annotation_element {
uleb128 name_idx; // 元素名称的string_ids索引
encoded_value value; // 元素值
}
| 名称 |
格式 |
说明 |
| type_idx |
uleb128 |
注释的类型。这种类型必须是“类”(而非“数组”或“基元”)。 |
| size |
uleb128 |
此注解中 name-value 映射的数量 |
| elements |
annotation_element[size] |
注解的元素,直接以内嵌形式(不作为偏移量)表示。元素必须按 string_id<br/> 索引以升序进行排序。 |
@Override // 这是注解
public String toString() {
return "MyClass";
}
@MyAnnotation(value = "test", count = 42) // 带参数的注解
public class MyClass {
@Nullable // 标记可能为null
private String name;
@Inject // 依赖注入标记
private UserService userService;
}
@Override // 这是注解
public String toString() {
return "MyClass";
}
@MyAnnotation(value = "test", count = 42) // 带参数的注解
public class MyClass {
@Nullable // 标记可能为null
private String name;
@Inject // 依赖注入标记
private UserService userService;
}
struct dex_header {
// 文件标识部分
uint8_t magic[8]; // "dex\n035\0" 魔数标识
uint32_t checksum; // 文件完整性校验
uint8_t signature[20]; // SHA-1数字签名
// 文件基本信息
uint32_t file_size; // 整个dex文件大小
uint32_t header_size; // 头部大小(固定0x70)
uint32_t endian_tag; // 字节序标记
// 链接信息
uint32_t link_size; // 链接段大小
uint32_t link_off; // 链接段偏移
uint32_t map_off; // 映射表偏移
// 各索引区的大小和位置
uint32_t string_ids_size; // 字符串数量
uint32_t string_ids_off; // 字符串索引偏移
uint32_t type_ids_size; // 类型数量
uint32_t type_ids_off; // 类型索引偏移
uint32_t proto_ids_size; // 方法原型数量
uint32_t proto_ids_off; // 方法原型偏移
uint32_t field_ids_size; // 字段数量
uint32_t field_ids_off; // 字段索引偏移
uint32_t method_ids_size; // 方法数量
uint32_t method_ids_off; // 方法索引偏移
uint32_t class_defs_size; // 类定义数量
uint32_t class_defs_off; // 类定义偏移
// 数据区信息
uint32_t data_size; // 数据段大小
uint32_t data_off; // 数据段偏移
};
struct dex_header {
// 文件标识部分
uint8_t magic[8]; // "dex\n035\0" 魔数标识
uint32_t checksum; // 文件完整性校验
uint8_t signature[20]; // SHA-1数字签名
// 文件基本信息
uint32_t file_size; // 整个dex文件大小
uint32_t header_size; // 头部大小(固定0x70)
uint32_t endian_tag; // 字节序标记
// 链接信息
uint32_t link_size; // 链接段大小
uint32_t link_off; // 链接段偏移
uint32_t map_off; // 映射表偏移
// 各索引区的大小和位置
uint32_t string_ids_size; // 字符串数量
uint32_t string_ids_off; // 字符串索引偏移
uint32_t type_ids_size; // 类型数量
uint32_t type_ids_off; // 类型索引偏移
uint32_t proto_ids_size; // 方法原型数量
uint32_t proto_ids_off; // 方法原型偏移
uint32_t field_ids_size; // 字段数量
uint32_t field_ids_off; // 字段索引偏移
uint32_t method_ids_size; // 方法数量
uint32_t method_ids_off; // 方法索引偏移
uint32_t class_defs_size; // 类定义数量
uint32_t class_defs_off; // 类定义偏移
// 数据区信息
uint32_t data_size; // 数据段大小
uint32_t data_off; // 数据段偏移
};
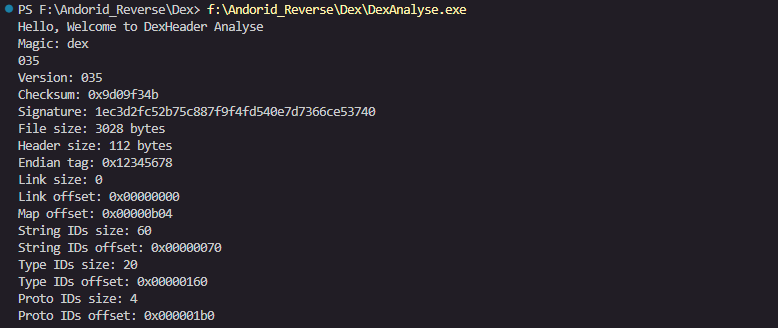
Hello, Welcome to DexHeader Analyse
Magic: dex
035
Version: 035
Checksum: 0x9d09f34b
Signature: 1ec3d2fc52b75c887f9f4fd540e7d7366ce53740
File size: 3028 bytes
Header size: 112 bytes
Endian tag: 0x12345678
Link size: 0
Link offset: 0x00000000
Map offset: 0x00000b04
String IDs size: 60
String IDs offset: 0x00000070
Type IDs size: 20
Type IDs offset: 0x00000160
Proto IDs size: 4
Proto IDs offset: 0x000001b0
Hello, Welcome to DexHeader Analyse
Magic: dex
035
Version: 035
Checksum: 0x9d09f34b
Signature: 1ec3d2fc52b75c887f9f4fd540e7d7366ce53740
File size: 3028 bytes
Header size: 112 bytes
Endian tag: 0x12345678
Link size: 0
Link offset: 0x00000000
Map offset: 0x00000b04
String IDs size: 60
String IDs offset: 0x00000070
Type IDs size: 20
Type IDs offset: 0x00000160
Proto IDs size: 4
Proto IDs offset: 0x000001b0
u1 magic[8]; // "dex\n035\0" 或 "dex\n038\0"
u1 magic[8]; // "dex\n035\0" 或 "dex\n038\0"
1. 前4字节:"dex\n" (0x64 0x65 0x78 0x0A) - 文件标识
2. 中3字节:版本号,如 "035" (Android 5.0-7.1) 或 "038" (Android 8.0+)
3. 最后1字节:\0 空字符
1. 前4字节:"dex\n" (0x64 0x65 0x78 0x0A) - 文件标识
2. 中3字节:版本号,如 "035" (Android 5.0-7.1) 或 "038" (Android 8.0+)
3. 最后1字节:\0 空字符
u4 checksum; // Adler-32校验和
u4 checksum; // Adler-32校验和
u1 signature[20]; // SHA-1哈希值
u1 signature[20]; // SHA-1哈希值
1. 唯一标识DEX文件
2. 更强的完整性验证
3. 用于签名验证和缓存机制
1. 唯一标识DEX文件
2. 更强的完整性验证
3. 用于签名验证和缓存机制
u4 file_size; // 整个DEX文件的大小(字节)
u4 file_size; // 整个DEX文件的大小(字节)
u4 header_size; // 固定为0x70 (112字节)
u4 header_size; // 固定为0x70 (112字节)
u4 endian_tag; // 0x12345678 (小端) 或 0x78563412 (大端)
u4 endian_tag; // 0x12345678 (小端) 或 0x78563412 (大端)
u4 link_size; // 链接段大小
u4 link_off; // 链接段偏移
u4 link_size; // 链接段大小
u4 link_off; // 链接段偏移
u4 map_off; // 映射表的文件偏移
struct map_list {
u4 size; // 映射条目数量
struct map_item list[]; // 映射条目数组
};
struct map_list {
u4 size; // 映射条目数量
struct map_item list[]; // 映射条目数组
};
// 映射表项
struct map_item {
u2 type; // 数据类型
u2 unused; // 未使用,对齐填充
u4 size; // 该类型的条目数量
u4 offset; // 该数据区在文件中的偏移
};
// 映射表项
struct map_item {
u2 type; // 数据类型
u2 unused; // 未使用,对齐填充
u4 size; // 该类型的条目数量
u4 offset; // 该数据区在文件中的偏移
};
HEADER_ITEM → DEX头部
STRING_ID_ITEM → 字符串索引表
STRING_DATA_ITEM → 字符串实际内容 ← Header没有!
TYPE_ID_ITEM → 类型索引表
TYPE_LIST → 参数类型列表 ← Header没有!
PROTO_ID_ITEM → 方法原型表
FIELD_ID_ITEM → 字段表
METHOD_ID_ITEM → 方法表
CLASS_DEF_ITEM → 类定义表
CLASS_DATA_ITEM → 类的具体数据 ← Header没有!
CODE_ITEM → 字节码 ← Header没有!
DEBUG_INFO_ITEM → 调试信息 ← Header没有!
ANNOTATION_ITEM → 注解 ← Header没有!
MAP_LIST → 映射表自己
HEADER_ITEM → DEX头部
STRING_ID_ITEM → 字符串索引表
STRING_DATA_ITEM → 字符串实际内容 ← Header没有!
TYPE_ID_ITEM → 类型索引表
TYPE_LIST → 参数类型列表 ← Header没有!
PROTO_ID_ITEM → 方法原型表
FIELD_ID_ITEM → 字段表
METHOD_ID_ITEM → 方法表
CLASS_DEF_ITEM → 类定义表
CLASS_DATA_ITEM → 类的具体数据 ← Header没有!
CODE_ITEM → 字节码 ← Header没有!
DEBUG_INFO_ITEM → 调试信息 ← Header没有!
ANNOTATION_ITEM → 注解 ← Header没有!
MAP_LIST → 映射表自己
1. 读Header → string_ids_off = 0x70
2. 去0x70位置 → 找到string_id_item[5] = 0x000001f8
3. 0x000001f8是什么?不知道!Header没说字符串数据在哪
1. 读Header → string_ids_off = 0x70
2. 去0x70位置 → 找到string_id_item[5] = 0x000001f8
3. 0x000001f8是什么?不知道!Header没说字符串数据在哪
1. 读Header → map_off = 0xb04
2. 去0xb04读映射表 → 找到TYPE_STRING_DATA_ITEM在0x1e0
3. 读Header → string_ids_off = 0x70
4. 去0x70位置 → 找到string_id_item[5] = 0x000001f8
5. 去0x1f8位置 → 读到 "Hello World"
1. 读Header → map_off = 0xb04
2. 去0xb04读映射表 → 找到TYPE_STRING_DATA_ITEM在0x1e0
3. 读Header → string_ids_off = 0x70
4. 去0x70位置 → 找到string_id_item[5] = 0x000001f8
5. 去0x1f8位置 → 读到 "Hello World"
void AnalyseMapList(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 map_off = header->map_off;
// 定位到map_list
struct map_list* map = (struct map_list*)(dex_data + map_off);
printf("\n========== Map List (Mapping table) ==========\n");
printf("Mapping table offset: 0x%08x\n", map_off);
printf("Number of mapping entries: %u\n\n", map->size);
printf("%-30s %-10s %-10s\n", "TYPE", "SIZE", "OFFSET");
printf("------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (u4 i = 0; i < map->size; i++) {
const char* type_name = get_map_type_name(map->list[i].type);
u4 size = map->list[i].size;
u4 offset = map->list[i].offset;
printf("%-30s %-10u 0x%08x\n", type_name, size, offset);
}
return;
}
void AnalyseMapList(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 map_off = header->map_off;
// 定位到map_list
struct map_list* map = (struct map_list*)(dex_data + map_off);
printf("\n========== Map List (Mapping table) ==========\n");
printf("Mapping table offset: 0x%08x\n", map_off);
printf("Number of mapping entries: %u\n\n", map->size);
printf("%-30s %-10s %-10s\n", "TYPE", "SIZE", "OFFSET");
printf("------------------------------------------------------\n");
for (u4 i = 0; i < map->size; i++) {
const char* type_name = get_map_type_name(map->list[i].type);
u4 size = map->list[i].size;
u4 offset = map->list[i].offset;
printf("%-30s %-10u 0x%08x\n", type_name, size, offset);
}
return;
}
const char* get_map_type_name(u2 type)
{
switch (type) {
case TYPE_HEADER_ITEM: return "HEADER_ITEM";
case TYPE_STRING_ID_ITEM: return "STRING_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_TYPE_ID_ITEM: return "TYPE_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_PROTO_ID_ITEM: return "PROTO_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_FIELD_ID_ITEM: return "FIELD_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_METHOD_ID_ITEM: return "METHOD_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_CLASS_DEF_ITEM: return "CLASS_DEF_ITEM";
case TYPE_CALL_SITE_ID_ITEM: return "CALL_SITE_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_METHOD_HANDLE_ITEM: return "METHOD_HANDLE_ITEM";
case TYPE_MAP_LIST: return "MAP_LIST";
case TYPE_TYPE_LIST: return "TYPE_LIST";
case TYPE_ANNOTATION_SET_REF_LIST: return "ANNOTATION_SET_REF_LIST";
case TYPE_ANNOTATION_SET_ITEM: return "ANNOTATION_SET_ITEM";
case TYPE_CLASS_DATA_ITEM: return "CLASS_DATA_ITEM";
case TYPE_CODE_ITEM: return "CODE_ITEM";
case TYPE_STRING_DATA_ITEM: return "STRING_DATA_ITEM";
case TYPE_DEBUG_INFO_ITEM: return "DEBUG_INFO_ITEM";
case TYPE_ANNOTATION_ITEM: return "ANNOTATION_ITEM";
case TYPE_ENCODED_ARRAY_ITEM: return "ENCODED_ARRAY_ITEM";
case TYPE_ANNOTATIONS_DIRECTORY_ITEM: return "ANNOTATIONS_DIRECTORY_ITEM";
default: return "UNKNOWN";
}
}
const char* get_map_type_name(u2 type)
{
switch (type) {
case TYPE_HEADER_ITEM: return "HEADER_ITEM";
case TYPE_STRING_ID_ITEM: return "STRING_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_TYPE_ID_ITEM: return "TYPE_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_PROTO_ID_ITEM: return "PROTO_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_FIELD_ID_ITEM: return "FIELD_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_METHOD_ID_ITEM: return "METHOD_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_CLASS_DEF_ITEM: return "CLASS_DEF_ITEM";
case TYPE_CALL_SITE_ID_ITEM: return "CALL_SITE_ID_ITEM";
case TYPE_METHOD_HANDLE_ITEM: return "METHOD_HANDLE_ITEM";
case TYPE_MAP_LIST: return "MAP_LIST";
case TYPE_TYPE_LIST: return "TYPE_LIST";
case TYPE_ANNOTATION_SET_REF_LIST: return "ANNOTATION_SET_REF_LIST";
case TYPE_ANNOTATION_SET_ITEM: return "ANNOTATION_SET_ITEM";
case TYPE_CLASS_DATA_ITEM: return "CLASS_DATA_ITEM";
case TYPE_CODE_ITEM: return "CODE_ITEM";
case TYPE_STRING_DATA_ITEM: return "STRING_DATA_ITEM";
case TYPE_DEBUG_INFO_ITEM: return "DEBUG_INFO_ITEM";
case TYPE_ANNOTATION_ITEM: return "ANNOTATION_ITEM";
case TYPE_ENCODED_ARRAY_ITEM: return "ENCODED_ARRAY_ITEM";
case TYPE_ANNOTATIONS_DIRECTORY_ITEM: return "ANNOTATIONS_DIRECTORY_ITEM";
default: return "UNKNOWN";
}
}
u4 string_ids_size; // 字符串数量
u4 string_ids_off; // 字符串索引表偏移
u4 string_ids_size; // 字符串数量
u4 string_ids_off; // 字符串索引表偏移
u4 type_ids_size; // 类型数量
u4 type_ids_off; // 类型索引表偏移
u4 type_ids_size; // 类型数量
u4 type_ids_off; // 类型索引表偏移
u4 proto_ids_size; // 方法原型数量
u4 proto_ids_off; // 方法原型索引表偏移
u4 proto_ids_size; // 方法原型数量
u4 proto_ids_off; // 方法原型索引表偏移
1. 方法签名去重
2. 快速匹配方法调用
u4 field_ids_size; // 字段数量
u4 field_ids_off; // 字段索引表偏移
u4 field_ids_size; // 字段数量
u4 field_ids_off; // 字段索引表偏移
u4 method_ids_size; // 方法数量
u4 method_ids_off; // 方法索引表偏移
u4 method_ids_size; // 方法数量
u4 method_ids_off; // 方法索引表偏移
u4 class_defs_size; // 类定义数量
u4 class_defs_off; // 类定义表偏移
u4 class_defs_size; // 类定义数量
u4 class_defs_off; // 类定义表偏移
u4 data_size; // 数据段大小
u4 data_off; // 数据段偏移
u4 data_size; // 数据段大小
u4 data_off; // 数据段偏移
void AnalyseDexHeader(struct dex_header* header)
{
printf("Hello, Welcome to DexHeader Analyse\n");
printf("Magic: %.8s\n", header->magic);
printf("Version: %.3s\n", &header->magic[4]); // 版本号在magic字段的第4-6字节
printf("Checksum: 0x%08x\n", header->checksum);
printf("Signature: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
printf("%02x", header->signature[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("File size: %u bytes\n", header->file_size);
printf("Header size: %u bytes\n", header->header_size);
printf("Endian tag: 0x%08x\n", header->endian_tag);
printf("Link size: %u\n", header->link_size);
printf("Link offset: 0x%08x\n", header->link_off);
printf("Map offset: 0x%08x\n", header->map_off);
printf("String IDs size: %u\n", header->string_ids_size);
printf("String IDs offset: 0x%08x\n", header->string_ids_off);
printf("Type IDs size: %u\n", header->type_ids_size);
printf("Type IDs offset: 0x%08x\n", header->type_ids_off);
printf("Proto IDs size: %u\n", header->proto_ids_size);
printf("Proto IDs offset: 0x%08x\n", header->proto_ids_off);
return;
}
void AnalyseDexHeader(struct dex_header* header)
{
printf("Hello, Welcome to DexHeader Analyse\n");
printf("Magic: %.8s\n", header->magic);
printf("Version: %.3s\n", &header->magic[4]); // 版本号在magic字段的第4-6字节
printf("Checksum: 0x%08x\n", header->checksum);
printf("Signature: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
printf("%02x", header->signature[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("File size: %u bytes\n", header->file_size);
printf("Header size: %u bytes\n", header->header_size);
printf("Endian tag: 0x%08x\n", header->endian_tag);
printf("Link size: %u\n", header->link_size);
printf("Link offset: 0x%08x\n", header->link_off);
printf("Map offset: 0x%08x\n", header->map_off);
printf("String IDs size: %u\n", header->string_ids_size);
printf("String IDs offset: 0x%08x\n", header->string_ids_off);
printf("Type IDs size: %u\n", header->type_ids_size);
printf("Type IDs offset: 0x%08x\n", header->type_ids_off);
printf("Proto IDs size: %u\n", header->proto_ids_size);
printf("Proto IDs offset: 0x%08x\n", header->proto_ids_off);
return;
}
struct string_id_item {
uint32_t string_data_off; // 指向data区中字符串数据的偏移
};
struct string_id_item {
uint32_t string_data_off; // 指向data区中字符串数据的偏移
};
struct string_data_item {
uleb128 utf16_size; // UTF-16长度
uint8_t data[]; // MUTF-8编码的字符串 + 0x00结尾
};
struct string_data_item {
uleb128 utf16_size; // UTF-16长度
uint8_t data[]; // MUTF-8编码的字符串 + 0x00结尾
};
DEX文件
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Header │
│ string_ids_size = 60 │
│ string_ids_off = 0x70 ──────────────┐ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────│───────────┤
│ 0x70: String IDs 表(索引表) │ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ string_id_item[0].string_data_off = 0x3a8 ───┐ │
│ string_id_item[1].string_data_off = 0x3b0 ───│─┐ │
│ string_id_item[2].string_data_off = 0x3b8 ───│─│─┐│
│ ... │ │ ││
├────────────────────────────────────────────────│─│─│┤
│ 0x3a8: String Data(实际字符串内容) │ │ ││
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ ││
│ ↓ │ ││
│ 0x3a8: [len=3] "dex" │ ││
│ 0x3b0: [len=3] "035" ←─────────────────────────┘ ││
│ 0x3b8: [len=1] "V" ←────────────────────────────┘│
│ ... │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
DEX文件
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Header │
│ string_ids_size = 60 │
│ string_ids_off = 0x70 ──────────────┐ │
├─────────────────────────────────────────│───────────┤
│ 0x70: String IDs 表(索引表) │ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ ↓ │
│ string_id_item[0].string_data_off = 0x3a8 ───┐ │
│ string_id_item[1].string_data_off = 0x3b0 ───│─┐ │
│ string_id_item[2].string_data_off = 0x3b8 ───│─│─┐│
│ ... │ │ ││
├────────────────────────────────────────────────│─│─│┤
│ 0x3a8: String Data(实际字符串内容) │ │ ││
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │ ││
│ ↓ │ ││
│ 0x3a8: [len=3] "dex" │ ││
│ 0x3b0: [len=3] "035" ←─────────────────────────┘ ││
│ 0x3b8: [len=1] "V" ←────────────────────────────┘│
│ ... │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
58 7E 7E 44 38 7B 22 63 6F 6D 70 69 6C 61 74 69
6F 6E 2D 6D 6F 64 65 22 3A 22 72 65 6C 65 61 73
65 22 2C 22 68 61 73 2D 63 68 65 63 6B 73 75 6D
73 22 3A 66 61 6C 73 65 2C 22 6D 69 6E 2D 61 70
69 22 3A 32 32 2C 22 76 65 72 73 69 6F 6E 22 3A
22 32 2E 30 2E 38 38 22 7D 00
58 7E 7E 44 38 7B 22 63 6F 6D 70 69 6C 61 74 69
6F 6E 2D 6D 6F 64 65 22 3A 22 72 65 6C 65 61 73
65 22 2C 22 68 61 73 2D 63 68 65 63 6B 73 75 6D
73 22 3A 66 61 6C 73 65 2C 22 6D 69 6E 2D 61 70
69 22 3A 32 32 2C 22 76 65 72 73 69 6F 6E 22 3A
22 32 2E 30 2E 38 38 22 7D 00
void AnalyseDexString(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 string_ids_size = header->string_ids_size;
printf("\n========== String IDs (String table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of strings: %u\n\n", string_ids_size);
// 遍历每个字符串,使用辅助函数
for (u4 i = 0; i < string_ids_size; i++) {
const char* str = get_string_by_idx(i);
printf("String[%u]: \"%s\"\n", i, str);
}
return;
}
void AnalyseDexString(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 string_ids_size = header->string_ids_size;
printf("\n========== String IDs (String table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of strings: %u\n\n", string_ids_size);
// 遍历每个字符串,使用辅助函数
for (u4 i = 0; i < string_ids_size; i++) {
const char* str = get_string_by_idx(i);
printf("String[%u]: \"%s\"\n", i, str);
}
return;
}
const char* get_string_by_idx(u4 string_idx)
{
if (string_idx >= header->string_ids_size) {
return "INVALID_STRING_INDEX";
}
struct string_id_item* string_ids = (struct string_id_item*)(dex_data + header->string_ids_off);
u4 string_data_off = string_ids[string_idx].string_data_off;
u1* ptr = dex_data + string_data_off;
// 跳过ULEB128长度
while (*ptr & 0x80) ptr++;
ptr++;
return (const char*)ptr;
}
const char* get_string_by_idx(u4 string_idx)
{
if (string_idx >= header->string_ids_size) {
return "INVALID_STRING_INDEX";
}
struct string_id_item* string_ids = (struct string_id_item*)(dex_data + header->string_ids_off);
u4 string_data_off = string_ids[string_idx].string_data_off;
u1* ptr = dex_data + string_data_off;
// 跳过ULEB128长度
while (*ptr & 0x80) ptr++;
ptr++;
return (const char*)ptr;
}
struct type_id_item {
uint32_t descriptor_idx; // 指向string_ids的索引
};
struct type_id_item {
uint32_t descriptor_idx; // 指向string_ids的索引
};
Type IDs表 (0x160) String IDs表 (0x70) String Data
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ type_ids[0] │ │ string_ids[0] │ │ │
│ descriptor_idx│──┐ │ string_data_off│ │ │
│ = 15 │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │
├─────────────────┤ │ │ string_ids[1] │ │ │
│ type_ids[1] │ │ │ ... │ │ │
│ descriptor_idx│ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │
│ = 23 │ │ │ ... │ │ │
├─────────────────┤ │ ├─────────────────┤ ├─────────────────┤
│ ... │ └─────>│ string_ids[15] │────────>│ "Ljava/lang/ │
└─────────────────┘ │ string_data_off│ │ Object;" │
│ = 0x2a0 │ ├─────────────────┤
├─────────────────┤ │ │
│ ... │ │ │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
Type IDs表 (0x160) String IDs表 (0x70) String Data
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ type_ids[0] │ │ string_ids[0] │ │ │
│ descriptor_idx│──┐ │ string_data_off│ │ │
│ = 15 │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │
├─────────────────┤ │ │ string_ids[1] │ │ │
│ type_ids[1] │ │ │ ... │ │ │
│ descriptor_idx│ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │
│ = 23 │ │ │ ... │ │ │
├─────────────────┤ │ ├─────────────────┤ ├─────────────────┤
│ ... │ └─────>│ string_ids[15] │────────>│ "Ljava/lang/ │
└─────────────────┘ │ string_data_off│ │ Object;" │
│ = 0x2a0 │ ├─────────────────┤
├─────────────────┤ │ │
│ ... │ │ │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
1. 读取 type_ids[i].descriptor_idx = 15
↓
2. 用15作为索引,读取 string_ids[15].string_data_off = 0x2a0
↓
3. 去0x2a0位置读取字符串 = "Ljava/lang/Object;"
1. 读取 type_ids[i].descriptor_idx = 15
↓
2. 用15作为索引,读取 string_ids[15].string_data_off = 0x2a0
↓
3. 去0x2a0位置读取字符串 = "Ljava/lang/Object;"
void AnalyseTypeId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 type_ids_size = header->type_ids_size;
printf("\n========== Type IDs (Type descriptor) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of types: %u\n\n", type_ids_size);
// 遍历每个类型,使用辅助函数
for (u4 i = 0; i < type_ids_size; i++) {
const char* type_desc = get_type_by_idx(i);
printf("Type[%u]: %s\n", i, type_desc);
}
return;
}
void AnalyseTypeId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 type_ids_size = header->type_ids_size;
printf("\n========== Type IDs (Type descriptor) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of types: %u\n\n", type_ids_size);
// 遍历每个类型,使用辅助函数
for (u4 i = 0; i < type_ids_size; i++) {
const char* type_desc = get_type_by_idx(i);
printf("Type[%u]: %s\n", i, type_desc);
}
return;
}
const char* get_type_by_idx(u4 type_idx)
{
//安全性检查
if (type_idx >= header->type_ids_size) {
return "INVALID_TYPE_INDEX";
}
struct type_id_item* type_ids = (struct type_id_item*)(dex_data + header->type_ids_off);
return get_string_by_idx(type_ids[type_idx].descriptor_idx);
}
const char* get_type_by_idx(u4 type_idx)
{
//安全性检查
if (type_idx >= header->type_ids_size) {
return "INVALID_TYPE_INDEX";
}
struct type_id_item* type_ids = (struct type_id_item*)(dex_data + header->type_ids_off);
return get_string_by_idx(type_ids[type_idx].descriptor_idx);
}
struct proto_id_item {
uint32_t shorty_idx; // 简短描述符的string_ids索引→ String IDs → "LLL"
uint32_t return_type_idx; // 返回类型的type_ids索引→ Type IDs → "Ljava/lang/String;"
uint32_t parameters_off; // 参数列表偏移(指向type_list)→ type_list → 参数类型列表
};
struct proto_id_item {
uint32_t shorty_idx; // 简短描述符的string_ids索引→ String IDs → "LLL"
uint32_t return_type_idx; // 返回类型的type_ids索引→ Type IDs → "Ljava/lang/String;"
uint32_t parameters_off; // 参数列表偏移(指向type_list)→ type_list → 参数类型列表
};
struct type_list {
uint32_t size; // 参数个数
struct type_item list[]; // 参数类型数组
};
struct type_item {
uint16_t type_idx; // type_ids索引
};
struct type_list {
uint32_t size; // 参数个数
struct type_item list[]; // 参数类型数组
};
struct type_item {
uint16_t type_idx; // type_ids索引
};
String concat(String str1, String str2)
String concat(String str1, String str2)
struct type_list {
size = 2, // 两个参数
list = [17, 17] // 都指向type_ids[17] = "Ljava/lang/String;"
}
struct type_list {
size = 2, // 两个参数
list = [17, 17] // 都指向type_ids[17] = "Ljava/lang/String;"
}
void AnalyseProtoId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 proto_ids_size = header->proto_ids_size;
u4 proto_ids_off = header->proto_ids_off;
// 定位到proto_ids表
struct proto_id_item* proto_ids = (struct proto_id_item*)(dex_data + proto_ids_off);
printf("\n========== Proto IDs (Method prototype) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of method prototypes: %u\n\n", proto_ids_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < proto_ids_size; i++) {
// 获取简短描述符 (shorty)
const char* shorty = get_string_by_idx(proto_ids[i].shorty_idx);
// 获取返回类型
const char* return_type = get_type_by_idx(proto_ids[i].return_type_idx);
// 获取参数列表偏移
u4 parameters_off = proto_ids[i].parameters_off;
printf("Proto[%u]:\n", i);
printf(" Shorty: %s\n", shorty);
printf(" Return: %s\n", return_type);
// 解析参数列表
if (parameters_off == 0) {
printf(" Params: (none)\n");
} else {
struct type_list* params = (struct type_list*)(dex_data + parameters_off);
printf(" Params: (");
for (u4 j = 0; j < params->size; j++) {
const char* param_type = get_type_by_idx(params->list[j]);
printf("%s", param_type);
if (j < params->size - 1) printf(", ");
}
printf(")\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
return;
}
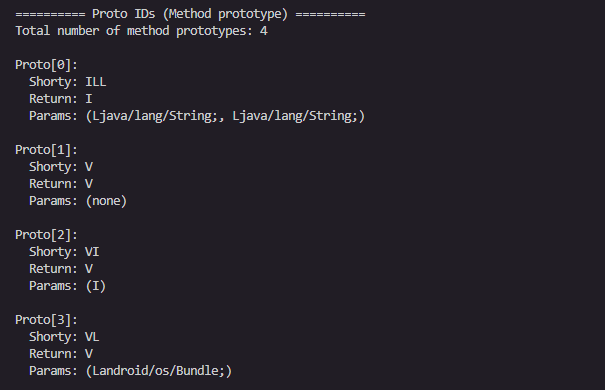
void AnalyseProtoId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 proto_ids_size = header->proto_ids_size;
u4 proto_ids_off = header->proto_ids_off;
// 定位到proto_ids表
struct proto_id_item* proto_ids = (struct proto_id_item*)(dex_data + proto_ids_off);
printf("\n========== Proto IDs (Method prototype) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of method prototypes: %u\n\n", proto_ids_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < proto_ids_size; i++) {
// 获取简短描述符 (shorty)
const char* shorty = get_string_by_idx(proto_ids[i].shorty_idx);
// 获取返回类型
const char* return_type = get_type_by_idx(proto_ids[i].return_type_idx);
// 获取参数列表偏移
u4 parameters_off = proto_ids[i].parameters_off;
printf("Proto[%u]:\n", i);
printf(" Shorty: %s\n", shorty);
printf(" Return: %s\n", return_type);
// 解析参数列表
if (parameters_off == 0) {
printf(" Params: (none)\n");
} else {
struct type_list* params = (struct type_list*)(dex_data + parameters_off);
printf(" Params: (");
for (u4 j = 0; j < params->size; j++) {
const char* param_type = get_type_by_idx(params->list[j]);
printf("%s", param_type);
if (j < params->size - 1) printf(", ");
}
printf(")\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
return;
}
struct field_id_item {
uint16_t class_idx; // 所属类的type_ids索引
uint16_t type_idx; // 字段类型的type_ids索引
uint32_t name_idx; // 字段名的string_ids索引
};
struct field_id_item {
uint16_t class_idx; // 所属类的type_ids索引
uint16_t type_idx; // 字段类型的type_ids索引
uint32_t name_idx; // 字段名的string_ids索引
};
public class MainActivity {
private String TAG = "test"; // Field: MainActivity -> String TAG
private int count = 0; // Field: MainActivity -> int count
}
public class MainActivity {
private String TAG = "test"; // Field: MainActivity -> String TAG
private int count = 0; // Field: MainActivity -> int count
}
void AnalyseFieldId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 field_ids_size = header->field_ids_size;
u4 field_ids_off = header->field_ids_off;
// 定位到field_ids表
struct field_id_item* field_ids = (struct field_id_item*)(dex_data + field_ids_off);
printf("\n========== Field IDs (Field table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of fields: %u\n\n", field_ids_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < field_ids_size; i++) {
// 获取所属类
const char* class_name = get_type_by_idx(field_ids[i].class_idx);
// 获取字段类型
const char* field_type = get_type_by_idx(field_ids[i].type_idx);
// 获取字段名
const char* field_name = get_string_by_idx(field_ids[i].name_idx);
printf("Field[%u]: %s -> %s %s\n", i, class_name, field_type, field_name);
}
return;
}
void AnalyseFieldId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 field_ids_size = header->field_ids_size;
u4 field_ids_off = header->field_ids_off;
// 定位到field_ids表
struct field_id_item* field_ids = (struct field_id_item*)(dex_data + field_ids_off);
printf("\n========== Field IDs (Field table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of fields: %u\n\n", field_ids_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < field_ids_size; i++) {
// 获取所属类
const char* class_name = get_type_by_idx(field_ids[i].class_idx);
// 获取字段类型
const char* field_type = get_type_by_idx(field_ids[i].type_idx);
// 获取字段名
const char* field_name = get_string_by_idx(field_ids[i].name_idx);
printf("Field[%u]: %s -> %s %s\n", i, class_name, field_type, field_name);
}
return;
}
struct method_id_item {
uint16_t class_idx; // 所属类的type_ids索引
uint16_t proto_idx; // 方法原型的proto_ids索引
uint32_t name_idx; // 方法名的string_ids索引
};
struct method_id_item {
uint16_t class_idx; // 所属类的type_ids索引
uint16_t proto_idx; // 方法原型的proto_ids索引
uint32_t name_idx; // 方法名的string_ids索引
};
Method IDs[i]
│
├── class_idx ──→ Type IDs ──→ "Lcom/kejian/test/MainActivity;"
│
├── proto_idx ──→ Proto IDs ──→ shorty="VL", return="V", params=(Bundle)
│
└── name_idx ──→ String IDs ──→ "onCreate"
Method IDs[i]
│
├── class_idx ──→ Type IDs ──→ "Lcom/kejian/test/MainActivity;"
│
├── proto_idx ──→ Proto IDs ──→ shorty="VL", return="V", params=(Bundle)
│
└── name_idx ──→ String IDs ──→ "onCreate"
void AnalyseMethodId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 method_ids_size = header->method_ids_size;
u4 method_ids_off = header->method_ids_off;
// 定位到method_ids表
struct method_id_item* method_ids = (struct method_id_item*)(dex_data + method_ids_off);
// 定位到proto_ids表(用于获取方法原型)
struct proto_id_item* proto_ids = (struct proto_id_item*)(dex_data + header->proto_ids_off);
printf("\n========== Method IDs (Method table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of methods: %u\n\n", method_ids_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < method_ids_size; i++) {
// 获取所属类
const char* class_name = get_type_by_idx(method_ids[i].class_idx);
// 获取方法名
const char* method_name = get_string_by_idx(method_ids[i].name_idx);
// 获取方法原型的简短描述符
u2 proto_idx = method_ids[i].proto_idx;
const char* shorty = get_string_by_idx(proto_ids[proto_idx].shorty_idx);
const char* return_type = get_type_by_idx(proto_ids[proto_idx].return_type_idx);
printf("Method[%u]: %s -> %s %s() [%s]\n",
i, class_name, return_type, method_name, shorty);
}
return;
}
void AnalyseMethodId(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 method_ids_size = header->method_ids_size;
u4 method_ids_off = header->method_ids_off;
// 定位到method_ids表
struct method_id_item* method_ids = (struct method_id_item*)(dex_data + method_ids_off);
// 定位到proto_ids表(用于获取方法原型)
struct proto_id_item* proto_ids = (struct proto_id_item*)(dex_data + header->proto_ids_off);
printf("\n========== Method IDs (Method table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of methods: %u\n\n", method_ids_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < method_ids_size; i++) {
// 获取所属类
const char* class_name = get_type_by_idx(method_ids[i].class_idx);
// 获取方法名
const char* method_name = get_string_by_idx(method_ids[i].name_idx);
// 获取方法原型的简短描述符
u2 proto_idx = method_ids[i].proto_idx;
const char* shorty = get_string_by_idx(proto_ids[proto_idx].shorty_idx);
const char* return_type = get_type_by_idx(proto_ids[proto_idx].return_type_idx);
printf("Method[%u]: %s -> %s %s() [%s]\n",
i, class_name, return_type, method_name, shorty);
}
return;
}
struct class_def_item {
u4 class_idx; // 类名索引
u4 access_flags; // 访问标志 (public/final/abstract等)
u4 superclass_idx; // 父类索引
u4 interfaces_off; // 接口列表偏移
u4 source_file_idx; // 源文件名索引
u4 annotations_off; // 注解信息
u4 class_data_off; // 类数据(字段和方法的具体定义)
u4 static_values_off; // 静态字段初始值
};
struct class_def_item {
u4 class_idx; // 类名索引
u4 access_flags; // 访问标志 (public/final/abstract等)
u4 superclass_idx; // 父类索引
u4 interfaces_off; // 接口列表偏移
u4 source_file_idx; // 源文件名索引
u4 annotations_off; // 注解信息
u4 class_data_off; // 类数据(字段和方法的具体定义)
u4 static_values_off; // 静态字段初始值
};
void AnalyseClassDef(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 class_defs_size = header->class_defs_size;
u4 class_defs_off = header->class_defs_off;
// 定位到class_defs表
struct class_def_item* class_defs = (struct class_def_item*)(dex_data + class_defs_off);
printf("\n========== Class Defs (Class Definition table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of class definitions: %u\n\n", class_defs_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < class_defs_size; i++) {
printf("==================== Class[%u] ====================\n", i);
// 获取类名
const char* class_name = get_type_by_idx(class_defs[i].class_idx);
// 获取父类名 (0xFFFFFFFF表示无父类,即java.lang.Object)
const char* superclass_name = "none";
if (class_defs[i].superclass_idx != DEX_NO_INDEX) {
superclass_name = get_type_by_idx(class_defs[i].superclass_idx);
}
// 获取源文件名 (可能为空)
const char* source_file = "unknown";
if (class_defs[i].source_file_idx != DEX_NO_INDEX) {
source_file = get_string_by_idx(class_defs[i].source_file_idx);
}
......
void AnalyseClassDef(struct dex_header* header)
{
u4 class_defs_size = header->class_defs_size;
u4 class_defs_off = header->class_defs_off;
// 定位到class_defs表
struct class_def_item* class_defs = (struct class_def_item*)(dex_data + class_defs_off);
printf("\n========== Class Defs (Class Definition table) ==========\n");
printf("Total number of class definitions: %u\n\n", class_defs_size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < class_defs_size; i++) {
printf("==================== Class[%u] ====================\n", i);
// 获取类名
const char* class_name = get_type_by_idx(class_defs[i].class_idx);
// 获取父类名 (0xFFFFFFFF表示无父类,即java.lang.Object)
const char* superclass_name = "none";
if (class_defs[i].superclass_idx != DEX_NO_INDEX) {
superclass_name = get_type_by_idx(class_defs[i].superclass_idx);
}
// 获取源文件名 (可能为空)
const char* source_file = "unknown";
if (class_defs[i].source_file_idx != DEX_NO_INDEX) {
source_file = get_string_by_idx(class_defs[i].source_file_idx);
}
......
#define ACC_PUBLIC 0x00000001 // public类
#define ACC_FINAL 0x00000010 // final类
#define ACC_SUPER 0x00000020 // 使用新的invokespecial语义
#define ACC_INTERFACE 0x00000200 // 接口
#define ACC_ABSTRACT 0x00000400 // 抽象类
#define ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x00001000 // 编译器生成
#define ACC_ANNOTATION 0x00002000 // 注解类型
#define ACC_ENUM 0x00004000 // 枚举类型
#define ACC_PUBLIC 0x00000001 // public类
#define ACC_FINAL 0x00000010 // final类
#define ACC_SUPER 0x00000020 // 使用新的invokespecial语义
#define ACC_INTERFACE 0x00000200 // 接口
#define ACC_ABSTRACT 0x00000400 // 抽象类
#define ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x00001000 // 编译器生成
#define ACC_ANNOTATION 0x00002000 // 注解类型
#define ACC_ENUM 0x00004000 // 枚举类型
#define ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001 // public
#define ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002 // private
#define ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004 // protected
#define ACC_STATIC 0x0008 // static
#define ACC_FINAL 0x0010 // final
#define ACC_VOLATILE 0x0040 // volatile
#define ACC_TRANSIENT 0x0080 // transient
#define ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x1000 // 编译器生成
#define ACC_ENUM 0x4000 // 枚举常量
#define ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001 // public
#define ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002 // private
#define ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004 // protected
#define ACC_STATIC 0x0008 // static
#define ACC_FINAL 0x0010 // final
#define ACC_VOLATILE 0x0040 // volatile
#define ACC_TRANSIENT 0x0080 // transient
#define ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x1000 // 编译器生成
#define ACC_ENUM 0x4000 // 枚举常量
#define ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001 // public
#define ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002 // private
#define ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004 // protected
#define ACC_STATIC 0x0008 // static
#define ACC_FINAL 0x0010 // final
#define ACC_SYNCHRONIZED 0x0020 // synchronized
#define ACC_BRIDGE 0x0040 // 桥接方法
#define ACC_VARARGS 0x0080 // 可变参数
#define ACC_NATIVE 0x0100 // native
#define ACC_ABSTRACT 0x0400 // abstract
#define ACC_STRICT 0x0800 // strictfp
#define ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x1000 // 编译器生成
#define ACC_CONSTRUCTOR 0x10000 // 构造函数
#define ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED 0x20000 // 声明同步
#define ACC_PUBLIC 0x0001 // public
#define ACC_PRIVATE 0x0002 // private
#define ACC_PROTECTED 0x0004 // protected
#define ACC_STATIC 0x0008 // static
#define ACC_FINAL 0x0010 // final
#define ACC_SYNCHRONIZED 0x0020 // synchronized
#define ACC_BRIDGE 0x0040 // 桥接方法
#define ACC_VARARGS 0x0080 // 可变参数
#define ACC_NATIVE 0x0100 // native
#define ACC_ABSTRACT 0x0400 // abstract
#define ACC_STRICT 0x0800 // strictfp
#define ACC_SYNTHETIC 0x1000 // 编译器生成
#define ACC_CONSTRUCTOR 0x10000 // 构造函数
#define ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED 0x20000 // 声明同步
u4 access_flags = class_defs[i].access_flags;
printf("Access Flags: 0x%04x (%s)\n", access_flags, get_access_flags_string(access_flags, 0)); //此处在分析类,所以第二个参数为0
u4 access_flags = class_defs[i].access_flags;
printf("Access Flags: 0x%04x (%s)\n", access_flags, get_access_flags_string(access_flags, 0)); //此处在分析类,所以第二个参数为0
// 获取访问标志字符串
const char* get_access_flags_string(u4 flags, int is_method)
{
static char flag_str[256];
flag_str[0] = '\0';
//如果是类的访问标志
if (flags & ACC_PUBLIC) strcat(flag_str, "public ");
if (flags & ACC_PRIVATE) strcat(flag_str, "private ");
if (flags & ACC_PROTECTED) strcat(flag_str, "protected ");
if (flags & ACC_STATIC) strcat(flag_str, "static ");
if (flags & ACC_FINAL) strcat(flag_str, "final ");
if (flags & ACC_SYNCHRONIZED) strcat(flag_str, "synchronized ");
if (flags & ACC_VOLATILE) strcat(flag_str, "volatile ");
if (flags & ACC_TRANSIENT) strcat(flag_str, "transient ");
if (flags & ACC_NATIVE) strcat(flag_str, "native ");
if (flags & ACC_INTERFACE) strcat(flag_str, "interface ");
if (flags & ACC_ABSTRACT) strcat(flag_str, "abstract ");
if (flags & ACC_STRICT) strcat(flag_str, "strictfp ");
if (flags & ACC_SYNTHETIC) strcat(flag_str, "synthetic ");
if (flags & ACC_ANNOTATION) strcat(flag_str, "annotation ");
if (flags & ACC_ENUM) strcat(flag_str, "enum ");
//如果是方法的访问标志
if (is_method) {
if (flags & ACC_BRIDGE) strcat(flag_str, "bridge ");
if (flags & ACC_VARARGS) strcat(flag_str, "varargs ");
if (flags & ACC_CONSTRUCTOR) strcat(flag_str, "constructor ");
if (flags & ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED) strcat(flag_str, "declared_synchronized ");
}
return flag_str;
}
// 获取访问标志字符串
const char* get_access_flags_string(u4 flags, int is_method)
{
static char flag_str[256];
flag_str[0] = '\0';
//如果是类的访问标志
if (flags & ACC_PUBLIC) strcat(flag_str, "public ");
if (flags & ACC_PRIVATE) strcat(flag_str, "private ");
if (flags & ACC_PROTECTED) strcat(flag_str, "protected ");
if (flags & ACC_STATIC) strcat(flag_str, "static ");
if (flags & ACC_FINAL) strcat(flag_str, "final ");
if (flags & ACC_SYNCHRONIZED) strcat(flag_str, "synchronized ");
if (flags & ACC_VOLATILE) strcat(flag_str, "volatile ");
if (flags & ACC_TRANSIENT) strcat(flag_str, "transient ");
if (flags & ACC_NATIVE) strcat(flag_str, "native ");
if (flags & ACC_INTERFACE) strcat(flag_str, "interface ");
if (flags & ACC_ABSTRACT) strcat(flag_str, "abstract ");
if (flags & ACC_STRICT) strcat(flag_str, "strictfp ");
if (flags & ACC_SYNTHETIC) strcat(flag_str, "synthetic ");
if (flags & ACC_ANNOTATION) strcat(flag_str, "annotation ");
if (flags & ACC_ENUM) strcat(flag_str, "enum ");
//如果是方法的访问标志
if (is_method) {
if (flags & ACC_BRIDGE) strcat(flag_str, "bridge ");
if (flags & ACC_VARARGS) strcat(flag_str, "varargs ");
if (flags & ACC_CONSTRUCTOR) strcat(flag_str, "constructor ");
if (flags & ACC_DECLARED_SYNCHRONIZED) strcat(flag_str, "declared_synchronized ");
}
return flag_str;
}
struct type_list {
uint32_t size; // 接口数量
uint16_t list[size]; // 接口类型索引数组
};
struct type_list {
uint32_t size; // 接口数量
uint16_t list[size]; // 接口类型索引数组
};
class_def_item
┌─────────────────────┐
│ class_idx │
│ access_flags │
│ superclass_idx │
│ interfaces_off ─────┼──────┐
│ ... │ │
└─────────────────────┘ │
▼
type_list (接口列表)
┌─────────────────────┐
│ size = 3 │ // 实现了3个接口
├─────────────────────┤
│ list[0] = 5 │ → Type[5]: Ljava/io/Serializable;
│ list[1] = 8 │ → Type[8]: Ljava/lang/Comparable;
│ list[2] = 12 │ → Type[12]: Ljava/lang/Cloneable;
└─────────────────────┘
class_def_item
┌─────────────────────┐
│ class_idx │
│ access_flags │
│ superclass_idx │
│ interfaces_off ─────┼──────┐
│ ... │ │
└─────────────────────┘ │
▼
type_list (接口列表)
┌─────────────────────┐
│ size = 3 │ // 实现了3个接口
├─────────────────────┤
│ list[0] = 5 │ → Type[5]: Ljava/io/Serializable;
│ list[1] = 8 │ → Type[8]: Ljava/lang/Comparable;
│ list[2] = 12 │ → Type[12]: Ljava/lang/Cloneable;
└─────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ DEX 文件结构 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ string_ids → 存储所有字符串 │
│ ↑ │
│ type_ids → 存储类型描述符 (引用 string_ids) │
│ ↑ │
│ type_list → 接口列表 (引用 type_ids) │
│ ↑ │
│ class_def → 类定义 (interfaces_off 指向 type_list) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ DEX 文件结构 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ string_ids → 存储所有字符串 │
│ ↑ │
│ type_ids → 存储类型描述符 (引用 string_ids) │
│ ↑ │
│ type_list → 接口列表 (引用 type_ids) │
│ ↑ │
│ class_def → 类定义 (interfaces_off 指向 type_list) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
if (class_defs[i].interfaces_off != 0) {
printf("\n--- Interfaces ---\n");
parse_interfaces(class_defs[i].interfaces_off);
} else {
printf("Interfaces: none\n");
}
if (class_defs[i].interfaces_off != 0) {
printf("\n--- Interfaces ---\n");
parse_interfaces(class_defs[i].interfaces_off);
} else {
printf("Interfaces: none\n");
}
// 解析接口列表
void parse_interfaces(u4 interfaces_off)
{
struct type_list* interfaces = (struct type_list*)(dex_data + interfaces_off);
printf("Interface count: %u\n", interfaces->size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < interfaces->size; i++) {
const char* interface_name = get_type_by_idx(interfaces->list[i]);
printf(" [%u] %s\n", i, interface_name);
}
}
// 解析接口列表
void parse_interfaces(u4 interfaces_off)
{
struct type_list* interfaces = (struct type_list*)(dex_data + interfaces_off);
printf("Interface count: %u\n", interfaces->size);
for (u4 i = 0; i < interfaces->size; i++) {
const char* interface_name = get_type_by_idx(interfaces->list[i]);
printf(" [%u] %s\n", i, interface_name);
}
}
// 注意:这个结构使用 ULEB128 编码,不是固定大小!
struct class_data_item {
uleb128 static_fields_size; // 静态字段数量
uleb128 instance_fields_size; // 实例字段数量
uleb128 direct_methods_size; // 直接方法数量
uleb128 virtual_methods_size; // 虚方法数量
encoded_field static_fields[static_fields_size]; // 静态字段数组
encoded_field instance_fields[instance_fields_size]; // 实例字段数组
encoded_method direct_methods[direct_methods_size]; // 直接方法数组
encoded_method virtual_methods[virtual_methods_size]; // 虚方法数组
};
// 注意:这个结构使用 ULEB128 编码,不是固定大小!
struct class_data_item {
uleb128 static_fields_size; // 静态字段数量
传播安全知识、拓宽行业人脉——看雪讲师团队等你加入!
最后于 2025-12-20 20:39
被A0tem编辑
,原因: