MinHook的原理就在于重写目标函数。在这次分析的X86模式中,32位相对JMP覆盖了整个地址空间。因为在相对地址计算中溢出的位被忽略,所以在X86模式中,函数的地址是容易掌控的。
直接来进入正题。
使用时需要通过#pragma来导出模块定义文件 (.def)中的DLL函数:
LIBRARY
EXPORTS
SeInitialize
SeUninitialize
SeCreateHook
SeEnableHook
SeDisableHook
#if defined _M_X64
#pragma comment(lib, "libMinHook.x64.lib")
#elif defined _M_IX86
#pragma comment(lib, "..\\Debug\\MiniHook.x86.lib")
#endif
Hook的第一步是用HeapCreate创建了一个自动增长的堆,首先是提交了PAGE_SIZE大小,详细内容的话可以参考MSDN:
__HeapHandle = HeapCreate(0,
0, //提交 PAGE_SIZE
0); //If dwMaximumSize is 0, the heap can grow in size.自动增长
随后开始创建Hook了。需要注意的是这里的创建Hook只是写好了进行Hook所需要的信息,原始指令备份,Trampline等,添加到HOOK_INFORMATION的HookEntry成员中。
填充的hook信息结构体:
如果没有被自己Hook过的话,就先准备一下TRAMPOLINE结构体:
对于TRAMPOLINE的构建是一块相对复杂的内容。可以看到结构体的前两个成员分别是原函数地址和我们想要到达的自定义函数地址,第三个成员MemorySlot,记录的是原函数地址开头的五个字节,以及跳转回原函数的jmp指令,OldPos和NewPos则分别保存了在构建MemorySlot的过程中,已经读取的目标函数偏移字节数,和已经写入的Detour函数字节数。
构建MemorySlot是通过一个do_While循环来实现的,首先它需要保存好被覆盖的那些字节数,所以在原函数已经读取的字节数少于jmp+四字节offset,一共五字节之前,MemorySlot要先备份下原来的指令,一旦原函数已经读取的字节数超过或者等于覆盖所需要的五字节时,也就不必再备份原来函数基地址处的指令了,因为仅仅只是覆盖五字节的内容:
在这段do_while循环里,通过反汇编可以清晰地看到MemorySlot一步步的构建,在测试代码中我Hook的是MessageBox函数,所以在看MemorySlot的构造过程之前,先来看一看反汇编下原始的MessageBox的机器指令:
对应着MessageBox的机器指令,来看MemorySlot在do while循环中的构造过程:
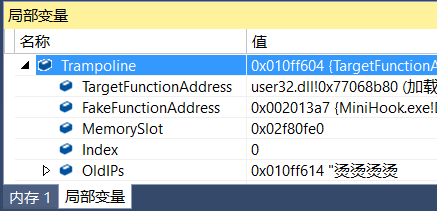
局部变量窗口找到MemorySlot的地址:
每记录一次指令字节长度的同时,也将即将被覆盖的原指令备份到MemorySlot中:
从图中也可以看出,卸载钩子回复指令的方法有两种:
1. 按照挂钩的反顺序卸载钩子,也即先Module1卸载钩子,然后Module2卸载钩子,Module1会将JMP Hook2-Temp的指令恢复到了CreatProcessW挂钩指令上,那么这时CreateProcessW处就变成了单个挂钩的情况,无论此时调用CreateProcessW,还是继续Module2的UnHook都不会有问题。
2. 直接卸载第一个挂钩,也即先让Module2卸载,那么CreateProcessW被Hook的地方指令被恢复为了原始的情况(Kernel32.dll初始映射的情况)。这时调用CreateProcessW不会出现问题。也就是说虽然Module1没有UnHook,但是它的钩子被覆盖掉了,也不会调用到Module1的Detours函数了。
但是~如果此时,Module1 继续执行卸载,那么很明显 JMP Hook2-Temp 指令被覆盖会了CreateProcessW Hook的五个字节指令上了,而很明显它要跳转到Module2的自定义Detours函数。而Trampoline函数所占用的内存空间可能已经被释放掉了,一旦释放掉了,将跳转到无效的内存空间,就要GG崩溃了~
LIBRARY
EXPORTS
SeInitialize
SeUninitialize
SeCreateHook
SeEnableHook
SeDisableHook
#if defined _M_X64
#pragma comment(lib, "libMinHook.x64.lib")
#elif defined _M_IX86
#pragma comment(lib, "..\\Debug\\MiniHook.x86.lib")
#endif
__HeapHandle = HeapCreate(0,
0, //提交 PAGE_SIZE
0); //If dwMaximumSize is 0, the heap can grow in size.自动增长
// Hook information.
typedef struct _HOOK_ENTRY
{
LPVOID TargetFunctionAddress;
LPVOID FakeFunctionAddress;
LPVOID MemorySlot;
UINT8 Backup[8]; //恢复Hook使用的存放原先数据
// UINT8 patchAbove : 1; // Uses the hot patch area. 位域:1位
UINT8 IsEnabled : 1; // Enabled.
// UINT8 queueEnable : 1; // Queued for enabling/disabling when != isEnabled.
UINT Index : 4; // Count of the instruction boundaries.???
UINT8 OldIPs[8]; // Instruction boundaries of the target function.???
UINT8 NewIPs[8]; // Instruction boundaries of the trampoline function ???
} HOOK_ENTRY, *PHOOK_ENTRY; //44字节
typedef struct _HOOK_INFORMATION_
{
PHOOK_ENTRY HookEntry;
UINT MaximumLength;
UINT Length;
}HOOK_INFORMATION,*PHOOK_INFORMATION;
UINT SeFindHookEntry(LPVOID FunctionAddress)
{
UINT i;
for (i = 0; i < __Hooks.Length; ++i)
{
if ((ULONG_PTR)FunctionAddress == (ULONG_PTR)__Hooks.HookEntry[i].TargetFunctionAddress)
return i;
}
return STATUS_NOT_FOUND;
}
如果没有被自己Hook过的话,就先准备一下TRAMPOLINE结构体:
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct _TRAMPOLINE
{
LPVOID TargetFunctionAddress;
LPVOID FakeFunctionAddress;
LPVOID MemorySlot; // MemorySlot 32字节
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
LPVOID pRelay; // [Out] Address of the relay function.
#endif
// BOOL patchAbove; // [Out] Should use the hot patch area? //Patch --->补丁 //0xA 0xB
UINT Index; // [Out] Number of the instruction boundaries.
UINT8 OldIPs[8]; // [Out] Instruction boundaries of the target function. //恢复
UINT8 NewIPs[8]; // [Out] Instruction boundaries of the trampoline function. //Hook
} TRAMPOLINE, *PTRAMPOLINE;
typedef struct _MEMORY_SLOT
{
union
{
struct _MEMORY_SLOT *Flink;
UINT8 BufferData[MEMORY_SLOT_SIZE];
};
} MEMORY_SLOT, *PMEMORY_SLOT; //32字节
对于TRAMPOLINE的构建是一块相对复杂的内容。可以看到结构体的前两个成员分别是原函数地址和我们想要到达的自定义函数地址,第三个成员MemorySlot,记录的是原函数地址开头的五个字节,以及跳转回原函数的jmp指令,OldPos和NewPos则分别保存了在构建MemorySlot的过程中,已经读取的目标函数偏移字节数,和已经写入的Detour函数字节数。
构建MemorySlot是通过一个do_While循环来实现的,首先它需要保存好被覆盖的那些字节数,所以在原函数已经读取的字节数少于jmp+四字节offset,一共五字节之前,MemorySlot要先备份下原来的指令,一旦原函数已经读取的字节数超过或者等于覆盖所需要的五字节时,也就不必再备份原来函数基地址处的指令了,因为仅仅只是覆盖五字节的内容:
do
{
HDE hde;
UINT CopyCodeLength;
LPVOID CopyCodeData;
//对于出现的相对偏移地址,在跳板中都要给出新的相对地址
/*
74CA8B80 8B FF mov edi,edi
74CA8B82 55 push ebp
74CA8B83 8B EC mov ebp,esp
74CA8B85 6A 00 push 0
74CA8B87 FF 75 14 push dword ptr [ebp+14h]
74CA8B8A FF 75 10 push dword ptr [ebp+10h]
74CA8B8D FF 75 0C push dword ptr [ebp+0Ch]
74CA8B90 FF 75 08 push dword ptr [ebp+8]
74CA8B93 E8 F8 FC FF FF call _MessageBoxExW@20 (74CA8890h)
*/
ULONG_PTROldInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos;
ULONG_PTRNewInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos;
//指令长度
CopyCodeLength = HDE_DISASM((LPVOID)OldInstance, &hde);
if(hde.flags & F_ERROR)
returnFALSE;
CopyCodeData = (LPVOID)OldInstance;//第一次时,CopyCodeData是MessageBox入口地址
if(OldPos >=sizeof(JMP_REL))
{
// The trampoline function is long enough.
// Complete the function with the jump to the target function.
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
jmp.address = pOldInst;
#else
//OldInstance = 74CA8B85
//目标 = 源 + Offset + 5
//Offset = 目标 - (源 + 5)
jmp.Operand = (UINT32)(OldInstance - (NewInstance +sizeof(jmp))); //计算跳转到目标的偏移
#endif
CopyCodeData = &jmp;
CopyCodeLength =sizeof(jmp);
IsLoop = TRUE;
}
//......此处省略部分源码,突出重点
Trampoline->OldIPs[Trampoline->Index] = OldPos;
Trampoline->NewIPs[Trampoline->Index] = NewPos;
Trampoline->Index++;
// Avoid using memcpy to reduce the footprint.
#ifndef _MSC_VER
memcpy((LPBYTE)ct->pTrampoline + newPos, pCopySrc, copySize);
#else
__movsb((LPBYTE)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos, (constunsignedchar*)CopyCodeData, CopyCodeLength);
#endif
NewPos += CopyCodeLength;
OldPos += hde.len;
}while(!IsLoop);
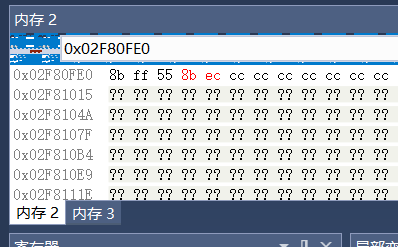
在这段do_while循环里,通过反汇编可以清晰地看到MemorySlot一步步的构建,在测试代码中我Hook的是MessageBox函数,所以在看MemorySlot的构造过程之前,先来看一看反汇编下原始的MessageBox的机器指令:
对应着MessageBox的机器指令,来看MemorySlot在do while循环中的构造过程:
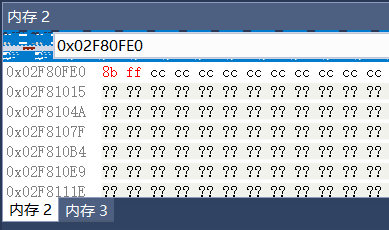
局部变量窗口找到MemorySlot的地址:
 先是申请了32字节的结构体大小:
先是申请了32字节的结构体大小:
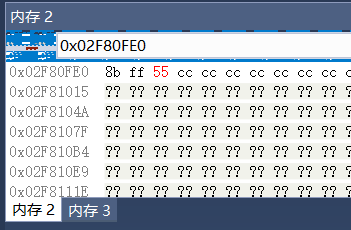
通过反汇编引擎HDE计算MessageBox函数基地址处开始,每几个字节是一条完整的机器指令,记录在Trampoline的OldIPs,NewIPs数组中:
//指令长度
CopyCodeLength = HDE_DISASM((LPVOID)OldInstance, &hde);
Trampoline->OldIPs[Trampoline->Index] = OldPos;
Trampoline->NewIPs[Trampoline->Index] = NewPos;
Trampoline->Index++;
每记录一次指令字节长度的同时,也将即将被覆盖的原指令备份到MemorySlot中:

;
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct _TRAMPOLINE
{
LPVOID TargetFunctionAddress;
LPVOID FakeFunctionAddress;
LPVOID MemorySlot; // MemorySlot 32字节
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
LPVOID pRelay; // [Out] Address of the relay function.
#endif
// BOOL patchAbove; // [Out] Should use the hot patch area? //Patch --->补丁 //0xA 0xB
UINT Index; // [Out] Number of the instruction boundaries.
UINT8 OldIPs[8]; // [Out] Instruction boundaries of the target function. //恢复
UINT8 NewIPs[8]; // [Out] Instruction boundaries of the trampoline function. //Hook
} TRAMPOLINE, *PTRAMPOLINE;
typedef struct _MEMORY_SLOT
{
union
{
struct _MEMORY_SLOT *Flink;
UINT8 BufferData[MEMORY_SLOT_SIZE];
};
} MEMORY_SLOT, *PMEMORY_SLOT; //32字节
对于TRAMPOLINE的构建是一块相对复杂的内容。可以看到结构体的前两个成员分别是原函数地址和我们想要到达的自定义函数地址,第三个成员MemorySlot,记录的是原函数地址开头的五个字节,以及跳转回原函数的jmp指令,OldPos和NewPos则分别保存了在构建MemorySlot的过程中,已经读取的目标函数偏移字节数,和已经写入的Detour函数字节数。
构建MemorySlot是通过一个do_While循环来实现的,首先它需要保存好被覆盖的那些字节数,所以在原函数已经读取的字节数少于jmp+四字节offset,一共五字节之前,MemorySlot要先备份下原来的指令,一旦原函数已经读取的字节数超过或者等于覆盖所需要的五字节时,也就不必再备份原来函数基地址处的指令了,因为仅仅只是覆盖五字节的内容:
do
{
HDE hde;
UINT CopyCodeLength;
LPVOID CopyCodeData;
//对于出现的相对偏移地址,在跳板中都要给出新的相对地址
/*
74CA8B80 8B FF mov edi,edi
74CA8B82 55 push ebp
74CA8B83 8B EC mov ebp,esp
74CA8B85 6A 00 push 0
74CA8B87 FF 75 14 push dword ptr [ebp+14h]
74CA8B8A FF 75 10 push dword ptr [ebp+10h]
74CA8B8D FF 75 0C push dword ptr [ebp+0Ch]
74CA8B90 FF 75 08 push dword ptr [ebp+8]
74CA8B93 E8 F8 FC FF FF call _MessageBoxExW@20 (74CA8890h)
*/
ULONG_PTROldInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos;
ULONG_PTRNewInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos;
//指令长度
CopyCodeLength = HDE_DISASM((LPVOID)OldInstance, &hde);
if(hde.flags & F_ERROR)
returnFALSE;
CopyCodeData = (LPVOID)OldInstance;//第一次时,CopyCodeData是MessageBox入口地址
if(OldPos >=sizeof(JMP_REL))
{
// The trampoline function is long enough.
// Complete the function with the jump to the target function.
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
jmp.address = pOldInst;
#else
//OldInstance = 74CA8B85
//目标 = 源 + Offset + 5
//Offset = 目标 - (源 + 5)
jmp.Operand = (UINT32)(OldInstance - (NewInstance +sizeof(jmp))); //计算跳转到目标的偏移
#endif
CopyCodeData = &jmp;
CopyCodeLength =sizeof(jmp);
IsLoop = TRUE;
}
//......此处省略部分源码,突出重点
Trampoline->OldIPs[Trampoline->Index] = OldPos;
Trampoline->NewIPs[Trampoline->Index] = NewPos;
Trampoline->Index++;
// Avoid using memcpy to reduce the footprint.
#ifndef _MSC_VER
memcpy((LPBYTE)ct->pTrampoline + newPos, pCopySrc, copySize);
#else
__movsb((LPBYTE)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos, (constunsignedchar*)CopyCodeData, CopyCodeLength);
#endif
NewPos += CopyCodeLength;
OldPos += hde.len;
}while(!IsLoop);
在这段do_while循环里,通过反汇编可以清晰地看到MemorySlot一步步的构建,在测试代码中我Hook的是MessageBox函数,所以在看MemorySlot的构造过程之前,先来看一看反汇编下原始的MessageBox的机器指令:
对应着MessageBox的机器指令,来看MemorySlot在do while循环中的构造过程:
局部变量窗口找到MemorySlot的地址:
 先是申请了32字节的结构体大小:
先是申请了32字节的结构体大小:
do
{
HDE hde;
UINT CopyCodeLength;
LPVOID CopyCodeData;
//对于出现的相对偏移地址,在跳板中都要给出新的相对地址
/*
74CA8B80 8B FF mov edi,edi
74CA8B82 55 push ebp
74CA8B83 8B EC mov ebp,esp
74CA8B85 6A 00 push 0
74CA8B87 FF 75 14 push dword ptr [ebp+14h]
74CA8B8A FF 75 10 push dword ptr [ebp+10h]
74CA8B8D FF 75 0C push dword ptr [ebp+0Ch]
74CA8B90 FF 75 08 push dword ptr [ebp+8]
74CA8B93 E8 F8 FC FF FF call _MessageBoxExW@20 (74CA8890h)
*/
ULONG_PTROldInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos;
ULONG_PTRNewInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos;
//指令长度
CopyCodeLength = HDE_DISASM((LPVOID)OldInstance, &hde);
if(hde.flags & F_ERROR)
returnFALSE;
CopyCodeData = (LPVOID)OldInstance;//第一次时,CopyCodeData是MessageBox入口地址
if(OldPos >=sizeof(JMP_REL))
{
// The trampoline function is long enough.
// Complete the function with the jump to the target function.
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
jmp.address = pOldInst;
#else
//OldInstance = 74CA8B85
//目标 = 源 + Offset + 5
//Offset = 目标 - (源 + 5)
jmp.Operand = (UINT32)(OldInstance - (NewInstance +sizeof(jmp))); //计算跳转到目标的偏移
#endif
CopyCodeData = &jmp;
CopyCodeLength =sizeof(jmp);
IsLoop = TRUE;
}
//......此处省略部分源码,突出重点
Trampoline->OldIPs[Trampoline->Index] = OldPos;
Trampoline->NewIPs[Trampoline->Index] = NewPos;
Trampoline->Index++;
// Avoid using memcpy to reduce the footprint.
#ifndef _MSC_VER
memcpy((LPBYTE)ct->pTrampoline + newPos, pCopySrc, copySize);
#else
__movsb((LPBYTE)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos, (constunsignedchar*)CopyCodeData, CopyCodeLength);
#endif
NewPos += CopyCodeLength;
OldPos += hde.len;
}while(!IsLoop);
do
{
HDE hde;
UINT CopyCodeLength;
LPVOID CopyCodeData;
//对于出现的相对偏移地址,在跳板中都要给出新的相对地址
/*
74CA8B80 8B FF mov edi,edi
74CA8B82 55 push ebp
74CA8B83 8B EC mov ebp,esp
74CA8B85 6A 00 push 0
74CA8B87 FF 75 14 push dword ptr [ebp+14h]
74CA8B8A FF 75 10 push dword ptr [ebp+10h]
74CA8B8D FF 75 0C push dword ptr [ebp+0Ch]
74CA8B90 FF 75 08 push dword ptr [ebp+8]
74CA8B93 E8 F8 FC FF FF call _MessageBoxExW@20 (74CA8890h)
*/
ULONG_PTROldInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->TargetFunctionAddress + OldPos;
ULONG_PTRNewInstance = (ULONG_PTR)Trampoline->MemorySlot + NewPos;
//指令长度
CopyCodeLength = HDE_DISASM((LPVOID)OldInstance, &hde);
if(hde.flags & F_ERROR)
returnFALSE;
CopyCodeData = (LPVOID)OldInstance;//第一次时,CopyCodeData是MessageBox入口地址
if(OldPos >=sizeof(JMP_REL))
{
// The trampoline function is long enough.
// Complete the function with the jump to the target function.
#if defined(_M_X64) || defined(__x86_64__)
jmp.address = pOldInst;
#else
//OldInstance = 74CA8B85
[招生]科锐逆向工程师培训(2024年11月15日实地,远程教学同时开班, 第51期)