
IVAgent (Intelligent Vulnerability Analysis Agent) 是一个基于大语言模型(LLM)的智能漏洞挖掘系统,支持多种分析引擎和二进制/源码分析场景。
目录
核心特性
- 多引擎支持: IDA Pro (二进制)、JEB (Android)、ABC-Decompiler (HarmonyOS)、Source Code (源码)
- 递归深度分析: 基于调用链的深度漏洞挖掘,支持跨函数分析
- 约束传播: 支持污点源追踪和参数约束在调用链中的传播
- 智能调度: LLM 驱动的 Workflow 编排和任务调度
- 可视化: 完整的 Web 界面支持日志追踪、漏洞管理和 Agent 执行可视化
系统架构
IVAgent 采用分层设计,核心组件包括:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 用户界面层 │
│ (CLI / Web UI / API) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 编排调度层 │
│ (Orchestrator / Task Manager / Workflow Parser) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 智能分析层 │
│ (DeepVulnAgent / FunctionSummaryAgent / ...) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 引擎抽象层 │
│ (IDA Engine / JEB Engine / Source Engine / ...) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 数据存储层 │
│ (Vuln Storage / Log Storage / Cache) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
|
项目结构
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 | ivas/
├── ivagent/
│ ├── agents/
│ │ ├── deep_vuln_agent.py
│ │ ├── callsite_agent.py
│ │ ├── function_summary_agent.py
│ │ └── prompts.py
│ ├── backends/
│ │ ├── ida/
│ │ ├── jeb/
│ │ └── abc_decompiler/
│ ├── core/
│ │ ├── llm_logger.py
│ │ ├── agent_logger.py
│ │ ├── vuln_storage.py
│ │ └── tool_llm_client.py
│ ├── engines/
│ │ ├── base_static_analysis_engine.py
│ │ ├── ida_engine.py
│ │ ├── jeb_engine.py
│ │ ├── abc_engine.py
│ │ ├── source_code_engine.py
│ │ └── factory.py
│ ├── models/
│ │ ├── constraints.py
│ │ ├── vulnerability.py
│ │ └── workflow.py
│ ├── orchestrator/
│ │ ├── orchestrator_agent.py
│ │ ├── workflow_parser.py
│ │ └── tools.py
│ ├── scanner.py
│ └── web/
│ ├── server.py
│ ├── api.py
│ └── static/
├── preconditions/
│ ├── _template.md
│ ├── android.md
│ ├── binary.md
│ └── harmony.md
├── workflows/
│ ├── android_sql_injection.md
│ ├── arkts_ability_hijack.md
│ └── rpc_server_analysis.md
├── ivagent_scan.py
├── orchestrator_cli.py
├── launch_web.py
└── start_ida_rpc.py
|
快速开始
安装依赖
1 | pip install -r requirements.txt
|
环境配置
1 2 3 | export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key"
export OPENAI_BASE_URL="ad2K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6S2M7r3W2Q4x3X3g2G2M7r3g2F1j5h3W2Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6$3x3b7`.`."
export OPENAI_MODEL="gpt-4"
|
启动 IDA RPC 服务器(如使用 IDA 引擎)
1 2 | python start_ida_rpc.py --idb /path/to/binary.i64 --port 9999
|
配置 ABC-Decompiler 引擎(HarmonyOS 应用分析)
ABC-Decompiler 用于分析 HarmonyOS 应用的 ABC 文件,基于 Jadx 的 MCP 插件实现。
架构流程:
1 | IVAgent → AbcDecompilerClient → MCP Server → Jadx AI MCP Plugin → ABC 文件
|
配置步骤:
安装 Jadx AI MCP 插件
启动 MCP 服务端
1 2 3 4 5 | cd ivagent/backends/abc_decompiler/server_scripts
python jadx_mcp_server.py --http --port 8651 --jadx-port 8650
|
参数说明:
--http: 启用 HTTP 传输模式--port: MCP Server 监听端口(默认 8651)--jadx-port: Jadx AI MCP Plugin 端口(默认 8650)
在 ABC-Decompiler 中加载 ABC 文件
- 打开 ABC-Decompiler
- 加载要分析的
.abc 文件
- 确保 AI MCP Plugin 已启用并连接到端口 8650
测试连接
配置 JEB 引擎(Android 应用分析)
JEB 引擎用于分析 Android APK 文件,通过 JSON-RPC 协议与 JEB 进程通信。
架构流程:
1 | IVAgent → JEBClient → HTTP JSON-RPC → JEB RPC Server (MCP.py) → JEB Decompiler → APK
|
配置步骤:
准备 JEB 环境
- 确保 JEB 已安装并可正常运行
- 需要 JEB 的脚本执行权限
启动 JEB RPC 服务
方式一:通过 JEB 控制台加载脚本
方式二:设置环境变量(守护模式)
1 2 3 4 5 6 | export JEB_MCP_DAEMON=1
export JEB_MCPC_HOST=127.0.0.1
export JEB_MCPC_PORT=16161
|
验证服务启动
- 脚本执行后会在控制台输出:
[MCP] Server started at 77aK9s2c8@1M7q4)9K6b7g2)9J5c8W2)9J5c8U0p5J5y4#2)9J5k6e0m8Q4x3X3f1H3i4K6u0W2x3g2)9K6b7e0p5$3x3e0j5I4
- 服务默认监听端口 16161
环境变量配置:
| 变量名 |
说明 |
默认值 |
JEB_MCPC_HOST |
RPC Server 监听地址 |
127.0.0.1 |
JEB_MCPC_PORT |
RPC Server 监听端口 |
16161 |
JEB_MCP_DAEMON |
是否启用守护模式 |
0 |
使用方式
IVAgent 提供两种主要使用方式:
- 直接扫描模式 (
ivagent_scan.py): 针对指定函数进行深度漏洞分析
- Workflow 编排模式 (
orchestrator_cli.py): LLM 驱动的自动化任务编排
方式一:直接扫描指定函数
使用 ivagent_scan.py 对单个或多个函数进行漏洞扫描。
基础用法
IDA 引擎(二进制分析):
1 2 3 4 5 6 | python ivagent_scan.py \
-e ida \
-t /path/to/binary.i64 \
-f "sub_140001000" \
--preset binary
|
JEB 引擎(Android APK 分析):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | python ivagent_scan.py \
-e jeb \
-t /path/to/app.apk \
-f "Lcom/example/MainActivity;->onCreate" \
--preset android
python ivagent_scan.py \
-e jeb \
-t /path/to/app.apk \
--host 127.0.0.1 \
--port 16161 \
-f "Lcom/example/LoginActivity;->checkLogin" \
--preset android
|
ABC-Decompiler 引擎(HarmonyOS 应用分析):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | python ivagent_scan.py \
-e abc \
-t /path/to/app.abc \
-f "com.example.EntryAbility.onCreate" \
--preset harmony
python ivagent_scan.py \
-e abc \
--host "216K9s2c8@1M7q4)9K6b7g2)9J5c8W2)9J5c8U0p5J5y4#2)9J5k6e0m8Q4x3X3f1H3i4K6u0W2x3g2)9K6b7e0R3$3y4e0q4Q4x3V1k6E0j5%4l9`." \
-f "com.example.MyAbility.parseData" \
--preset harmony
|
参数说明
| 参数 |
说明 |
示例 |
-e, --engine |
分析引擎类型 (ida/jeb/abc/source) |
-e ida |
-t, --target |
目标文件路径 |
-t app.apk |
-f, --function |
要扫描的函数签名或地址 |
-f "sub_140001000" |
--host |
引擎 RPC 主机地址 |
--host 127.0.0.1 |
--port |
引擎 RPC 端口 |
--port 9999 |
--preset |
使用预置 Precondition |
--preset binary |
--config |
自定义 Precondition 配置文件 |
--config my_config.md |
-c, --concurrency |
最大并发数 |
-c 5 |
-o, --output |
输出结果文件 (JSON) |
-o results.json |
--source-root |
源码根目录(用于源码分析) |
--source-root /path/to/src |
使用 Precondition 配置
Precondition 用于描述目标函数的已知约束,帮助 Agent 更精准地分析:
1 2 3 4 5 | python ivagent_scan.py -e ida -t driver.i64 -f "parse_input" --preset binary
python ivagent_scan.py -e ida -t driver.i64 -f "parse_input" --config ./my_precondition.md
|
内置 preset 包括:
binary: 二进制解析函数分析android: Android 入口点分析harmony: HarmonyOS 应用分析
Precondition 配置示例
---
name: Binary Parser Function
description: 二进制解析函数的安全分析配置
target: binary_parser
taint_sources:
- "param1"
---
## 参数说明
### 第一个参数
- 指向攻击者控制的数据缓冲区
### 第二个参数
- 数据长度(可能由攻击者指定)
## 常见风险点
- 长度验证缺失或不当
- 整数溢出(长度计算)
- 缓冲区溢出
方式二:Workflow 编排分析
使用 orchestrator_cli.py 通过 Workflow 文档描述分析意图,由 LLM 自主规划执行。
基础用法
源码分析模式:
1 2 3 4 5 | python orchestrator_cli.py \
--workflow workflows/android_sql_injection.md \
--engine source \
--target /path/to/source \
--source-root /path/to/source
|
IDA 引擎 + Workflow:
1 2 3 4 | python orchestrator_cli.py \
--workflow workflows/rpc_server_analysis.md \
--engine ida \
--target /path/to/binary.i64
|
JEB 引擎 + Workflow(Android 分析):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | python orchestrator_cli.py \
--workflow workflows/android_sql_injection.md \
--engine jeb \
--target /path/to/app.apk \
--source-root /path/to/source
|
ABC-Decompiler 引擎 + Workflow(HarmonyOS 分析):
1 2 3 4 5 6 | python orchestrator_cli.py \
--workflow workflows/arkts_ability_hijack.md \
--engine abc \
--target /path/to/app.abc
|
参数说明
| 参数 |
说明 |
示例 |
-w, --workflow |
Workflow 文档路径(必需) |
--workflow workflows/test.md |
-e, --engine |
分析引擎类型 (ida/jeb/source) |
-e source |
-t, --target |
目标程序路径 |
-t /path/to/source |
-s, --source-root |
源代码根目录 |
-s /path/to/src |
-v, --verbose |
详细日志输出 |
-v |
-q, --quiet |
静默模式 |
-q |
Workflow 文档格式
Workflow 使用 Markdown 描述分析意图:
---
name: "Android SQL 注入漏洞挖掘"
description: 针对 Android 应用的 SQL 注入分析
version: "1.0"
---
## 分析范围
重点关注 ContentProvider 和数据库操作代码
## 工作流
1. 搜索可能的 ContentProvider
2. 分析对外暴露的回调函数
3. 对暴露接口开展漏洞挖掘
## 漏洞关注点
- rawQuery 的参数拼接
- execSQL 的动态 SQL 构造
启动 Web 可视化界面
Web 界面功能:
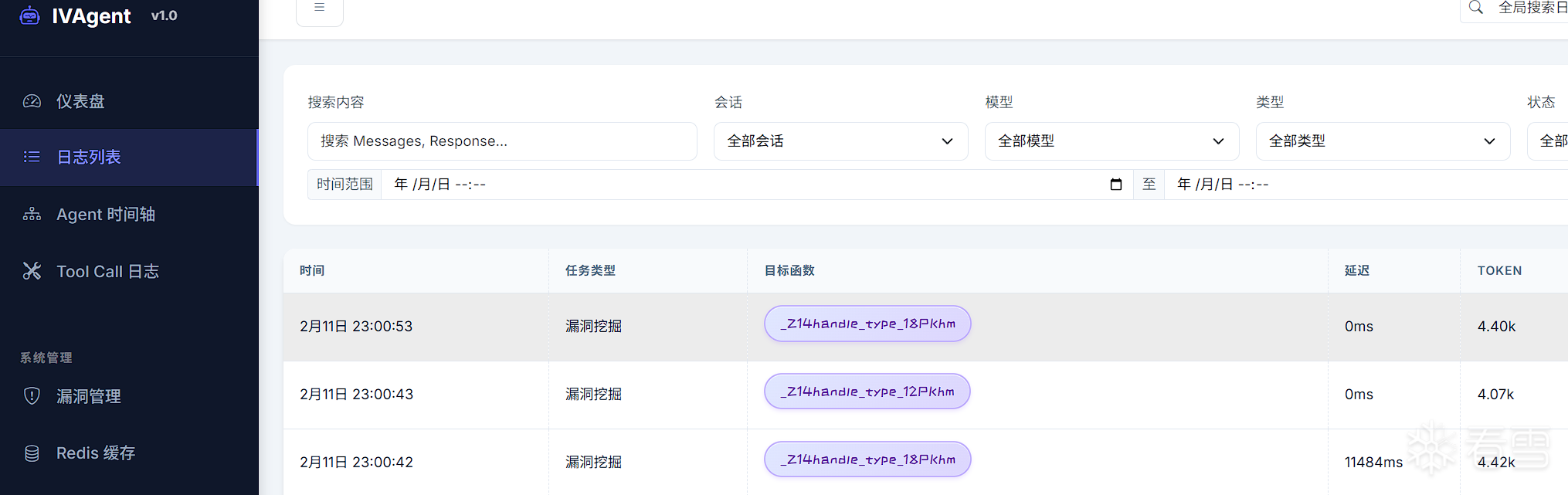
- 日志查询: 查看 LLM 调用日志、支持筛选和搜索
- Agent 追踪: 可视化 Agent 执行树和调用链
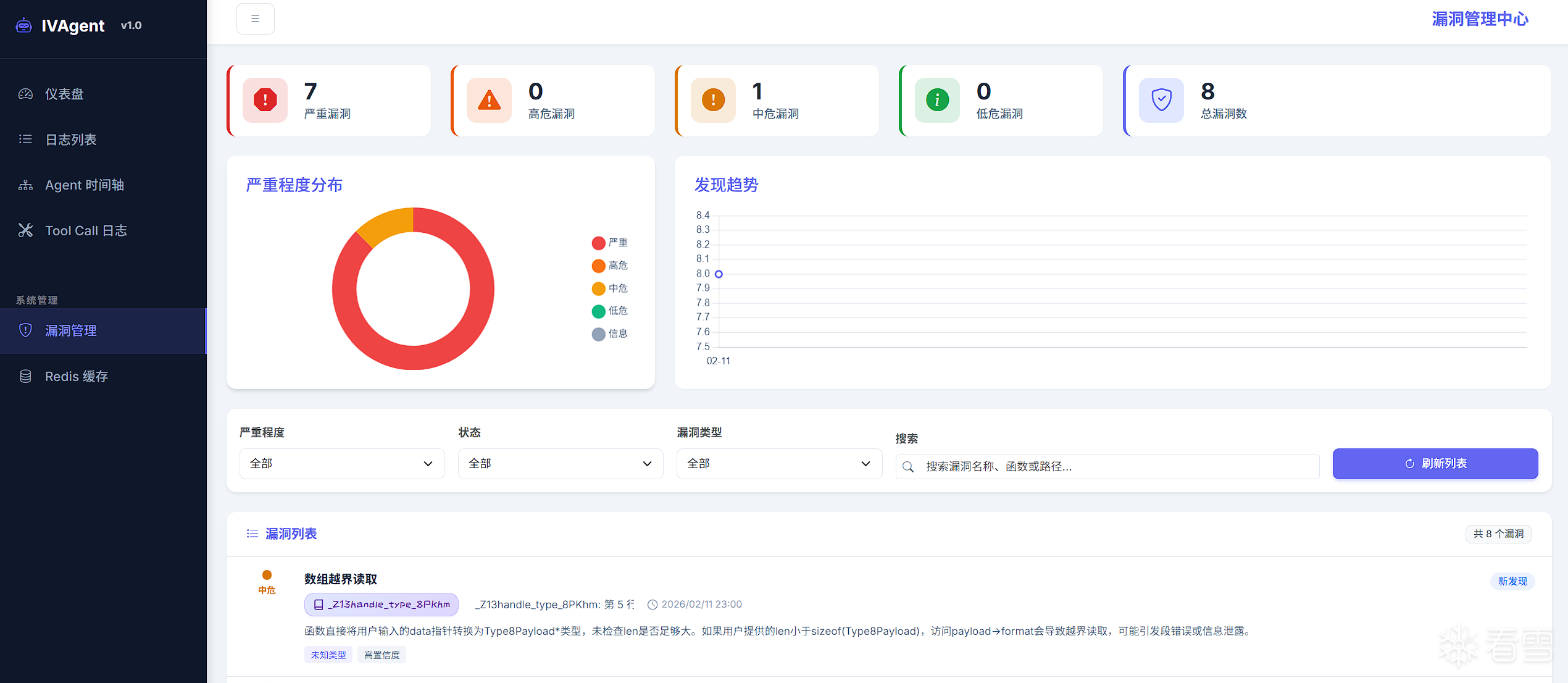
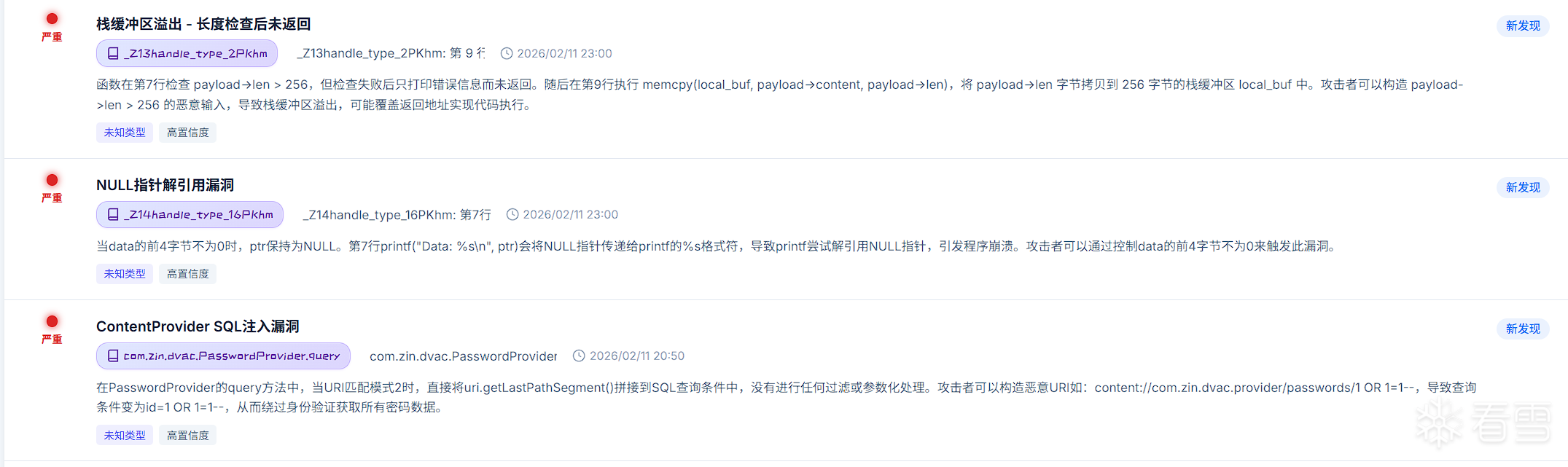
- 漏洞管理: 漏洞列表、详情、统计和状态管理
- Tool Call 分析: 查看工具调用详情和统计
- 实时推送: WebSocket 实时更新
llm 日志交互
漏洞信息
核心概念
1. DeepVulnAgent - 深度漏洞挖掘
系统的核心 Agent,采用多轮对话和 Tool Call 机制:
Tool Call 机制: LLM 通过调用工具主动获取信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | 第 1 轮: 提供完整上下文(函数代码、调用点、约束条件)
↓
LLM 分析 → Tool Call 请求(获取子函数摘要 / 创建子 Agent)
↓
第 2 轮: 返回 Tool 执行结果
↓
LLM 继续分析 → 可能发现漏洞或继续深入
↓
...
第 N 轮: finalize_analysis_tool 结束分析
|
主要工具:
get_function_summary_tool: 获取子函数摘要create_sub_agent_tool: 创建子 Agent 深入分析report_vulnerability_tool: 报告发现的漏洞finalize_analysis_tool: 完成分析
2. 分析引擎 (Engine)
统一的引擎接口支持多种后端:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | from ivagent.engines.factory import create_engine
engine = create_engine(
"ida",
target_path="/path/to/binary.i64",
host="127.0.0.1",
port=9999
)
func_def = await engine.get_function_def(function_identifier="sub_140001000")
sites = await engine.get_callee(function_identifier)
|
3. 约束传播机制
在跨函数分析中,约束传播是关键:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | 父函数: process_input(buf, size)
↓ 调用
子函数: memcpy(dst, src, len)
argument_constraints = [
"src 指向用户可控数据(污点)",
"len 最大为 1024 字节",
"dst 是局部缓冲区,大小 256 字节"
]
|
约束以纯文本格式传播,降低了对 LLM 的结构化输出要求。
配置说明
环境变量
LLM 配置
| 变量名 |
说明 |
默认值 |
OPENAI_API_KEY |
LLM API Key |
- |
OPENAI_BASE_URL |
API 基础 URL |
- |
OPENAI_MODEL |
模型名称 |
gpt-4 |
LLM_LOG_STORAGE |
日志存储类型 (sqlite/memory) |
sqlite |
JEB 引擎配置
| 变量名 |
说明 |
默认值 |
JEB_MCPC_HOST |
RPC Server 监听地址 |
127.0.0.1 |
JEB_MCPC_PORT |
RPC Server 监听端口 |
16161 |
JEB_MCP_DAEMON |
是否启用守护模式 (1/0) |
0 |
引擎连接参数
| 引擎 |
参数 |
说明 |
默认值 |
| IDA |
host |
RPC Server 地址 |
127.0.0.1 |
| IDA |
port |
RPC Server 端口 |
9999 |
| JEB |
host |
RPC Server 地址 |
127.0.0.1 |
| JEB |
port |
RPC Server 端口 |
16161 |
| JEB |
timeout |
连接超时(秒) |
120 |
| ABC |
host |
MCP Server 完整 URL |
ea2K9s2c8@1M7q4)9K6b7g2)9J5c8W2)9J5c8U0p5J5y4#2)9J5k6e0m8Q4x3X3f1H3i4K6u0W2x3g2)9K6b7e0R3$3y4e0q4Q4x3V1k6E0j5%4l9`. |
| Source |
source_root |
源代码根目录 |
- |
API 参考
扫描器 API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | from ivagent.scanner import IVAgentScanner, ScanConfig
config = ScanConfig(
engine_type="ida",
target_path="/path/to/binary.i64",
llm_api_key="your-key",
llm_model="gpt-4",
max_concurrency=10
)
scanner = IVAgentScanner(config)
results = await scanner.scan_functions(["func1", "func2"], precondition)
|
编排器 API
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | from ivagent.orchestrator import TaskOrchestratorAgent
orchestrator = TaskOrchestratorAgent(
llm_client=llm,
engine_type="ida",
target_path="/path/to/binary"
)
result = await orchestrator.execute_workflow("workflows/analysis.md")
|
漏洞输出格式
{
"vulnerabilities": [
{
"type": "BUFFER_OVERFLOW",
"name": "缓冲区溢出",
"description": "函数使用 memcpy 时未检查长度",
"location": "sub_140001000: 第 15 行",
"severity": 0.9,
"confidence": 0.8,
"data_flow": {
"source": "用户输入",
"sink": "局部缓冲区",
"path_description": "污点传播路径"
},
"remediation": "添加长度检查",
"metadata": {
"call_stack": ["main", "process_input", "sub_140001000"],
"evidence": ["代码证据行"]
}
}
]
}
扩展开发
添加新的分析引擎
继承 BaseStaticAnalysisEngine:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | from ivagent.engines.base_static_analysis_engine import BaseStaticAnalysisEngine
class MyEngine(BaseStaticAnalysisEngine):
async def get_function_def(self, function_identifier, **kwargs):
pass
async def get_callee(self, function_identifier):
pass
async def _resolve_static_callsite(self, callsite, caller_identifier):
pass
|
添加新的 Agent
继承 BaseAgent:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | from ivagent.agents.base import BaseAgent
class MyAgent(BaseAgent):
async def run(self, **kwargs) -> Dict[str, Any]:
pass
|
性能优化
并发控制
1 2 3 4 5 6 | semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(max_concurrency)
async def _scan_single(idx, sig):
async with semaphore:
return await agent.run(sig)
|
请求去重
1 2 3 4 | if func_name in requested_summaries:
continue
requested_summaries.add(func_name)
|
缓存机制
局限性与改进方向
当前局限
- LLM 成本: 大规模分析时 API 调用成本较高
- 响应延迟: LLM 调用有几百毫秒到数秒的延迟
- 上下文限制: 长函数代码可能超出 LLM 上下文窗口
- 幻觉问题: LLM 可能产生不准确的分析结果
改进方向
- 本地模型支持: 集成开源 LLM 降低使用成本
- 增量分析: 只分析修改的函数,利用历史结果
- RAG 增强: 结合向量数据库存储和检索安全知识
- 多模型集成: 使用多个模型投票减少幻觉
参考
贡献指南
欢迎贡献代码、报告问题或提出改进建议!
项目地址: bb4K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6E0j5h3N6A6j5$3I4X3i4K6u0V1j5h3W2Q4x3V1k6u0g2V1q4Y4k6h3&6@1
抛砖引玉,在这个 AI 时代,希望找些同路人一起探索 !
传播安全知识、拓宽行业人脉——看雪讲师团队等你加入!
最后于 2026-2-12 00:43
被xxxxxxx_798269编辑
,原因: