-
-
[原创]从ANGR-CTF项目入手ANGR和符号执行技术
-
发表于: 2025-11-27 14:18 7260
-
安装angr,部署angr-ctf项目。
先安装angr:
angr用project调用来加载二进制文件
其他的操作可以通过题目来学习
相关接口可参考下面的文章,本文的学习还是从angr-ctf这个项目中去学习。7a4K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6^5P5W2)9J5k6h3q4D9K9i4W2#2L8W2)9J5k6h3y4G2L8g2)9J5c8X3&6W2N6%4y4Q4x3V1j5$3y4K6p5K6i4K6t1K6N6r3!0U0i4K6u0V1x3e0b7`.
本文前面的几个会介绍的比较详细,后面的因为会技术有重复,所以简略的贴了一下脚本,所以只是angr的入门技术的讲解,深入学习需要在更多的实际程序中去跑。
项目的可执行文件再dist文件夹中,每个程序的目的都是让程序输出good job
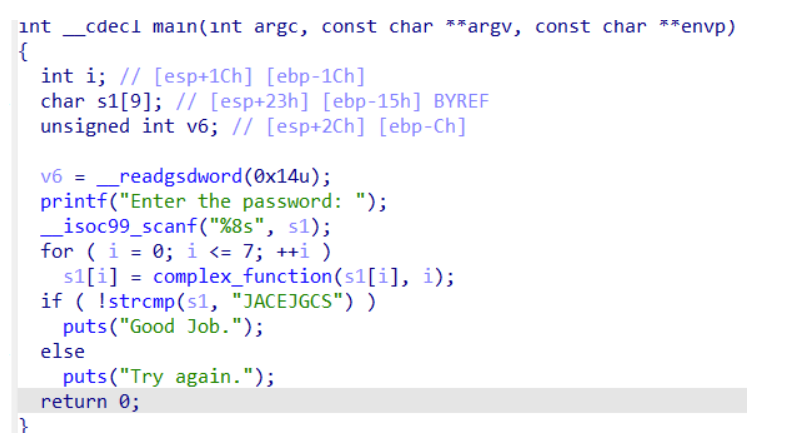
可以看到逻辑就是一个输入,然后之后验证的过程。
现在需要用angr来进行分析。
load_options = {'auto_load_libs': False}: 是要求他不要载入其他的依赖文件,可以降低复杂性跟时间。main_opts = {'base_addr': 0x804850}: 设置 entrypoint,也可以不加
然后设置:
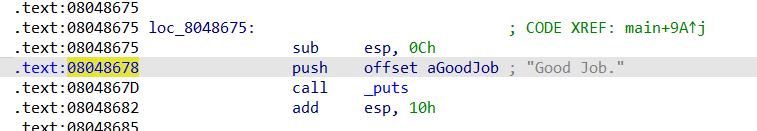
下面需要让angt开始搜索路径
完整脚本:
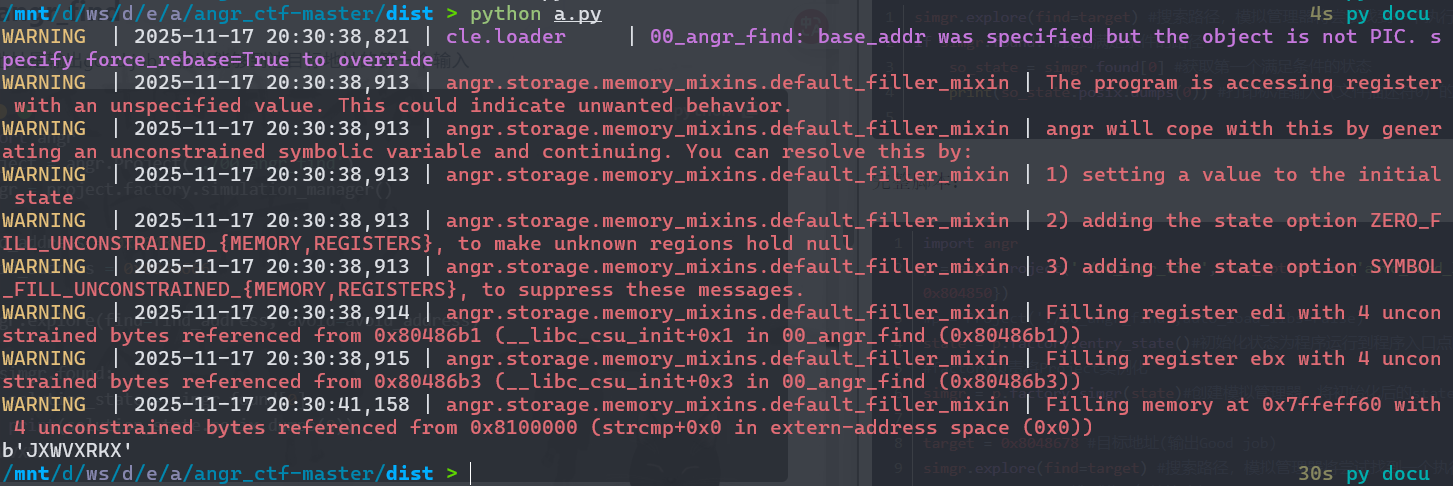
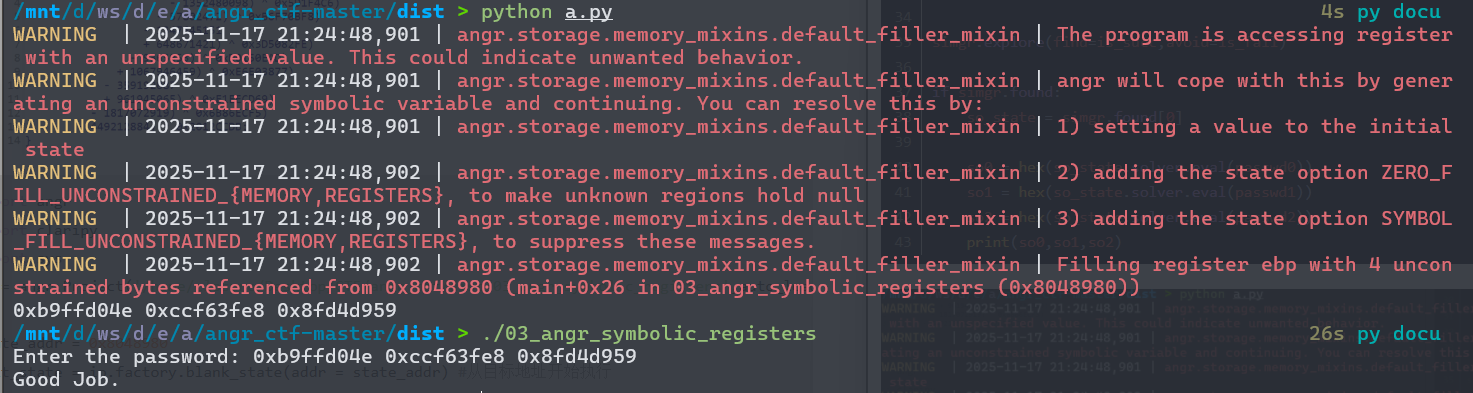
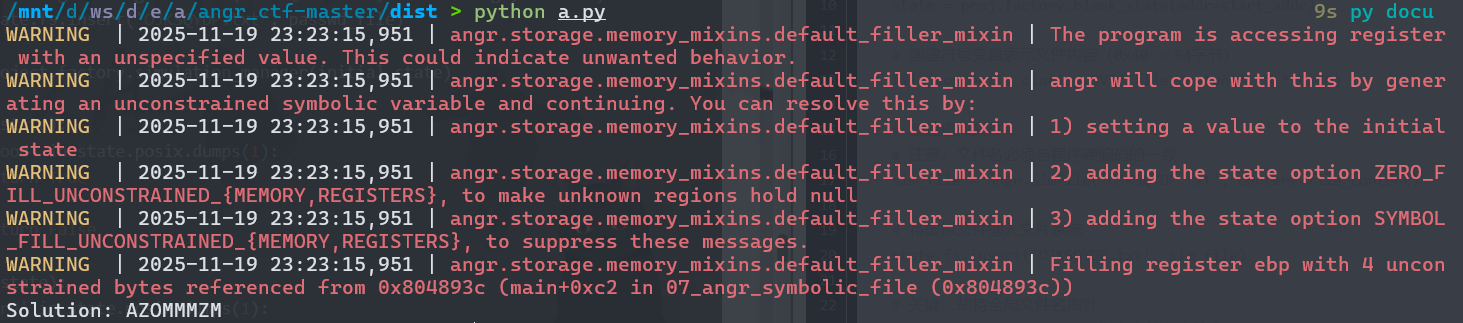
找到了“JXWVXRKX”
输出的日志中angr.storage.memory*_mixins.default_*filler*_mixin* 这是在说遇到了一个没有初始值的寄存器或地址,angr会在稍后自动创建一个未约束的符号变量来填充,警告提到了三个提示:
暂时这些可以无视,这个00程序的目的就是让我们了解angr的基本调用,以及find参数去寻找指定的地址。
程序用Ida静态分析的时候会发现:
太长了,不能直接查看流程图。这也意味着如果我们直接按照00程序那样去find,会有超级多的路径,另外分析发现有个函数avoid_me被调用了过多次,并注意到这个函数只有一个作用,就是让should_succeed为0,所以这里要使用另一个参数avoid来避开设计这个函数的路径分支。
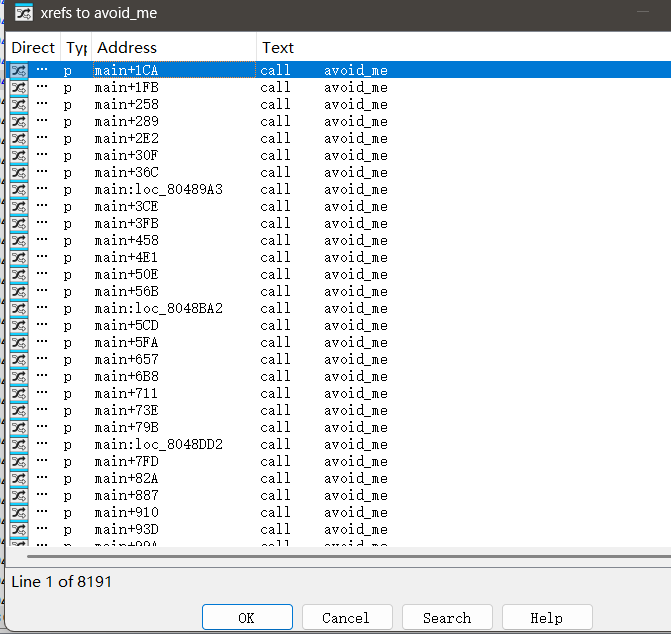
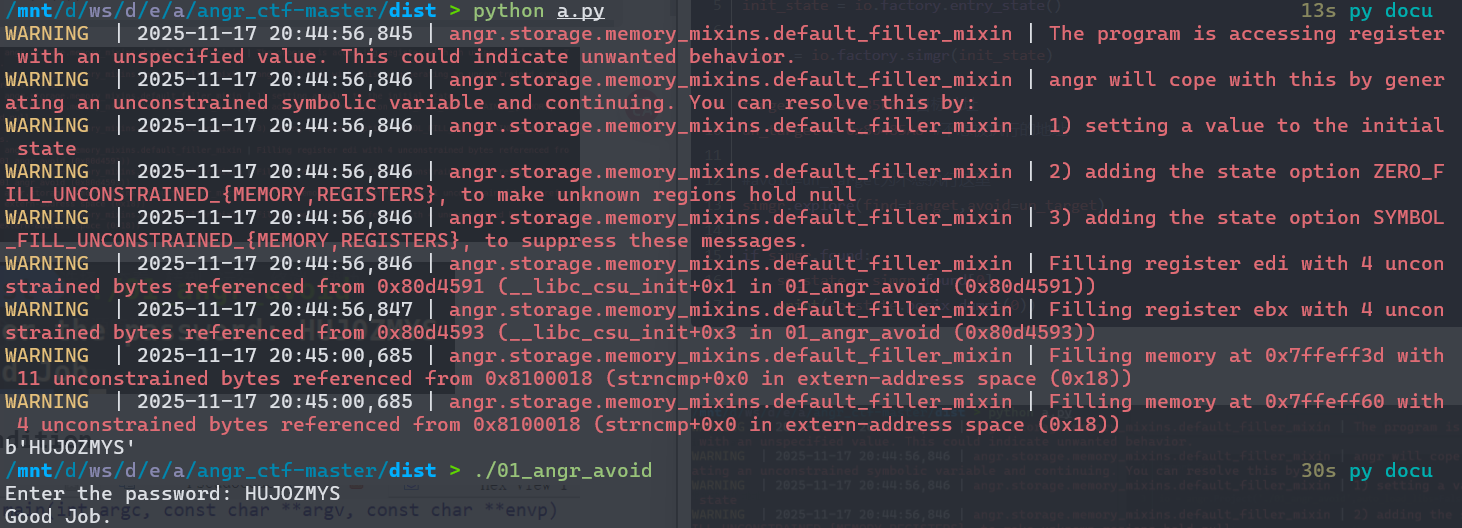
这样就跑出来了。
02程序跟前两个逻辑基本一致,这里是让我们去动态选择需要的state,也就是用strings参数去找正确和错误的字符串,不再直接输入地址。
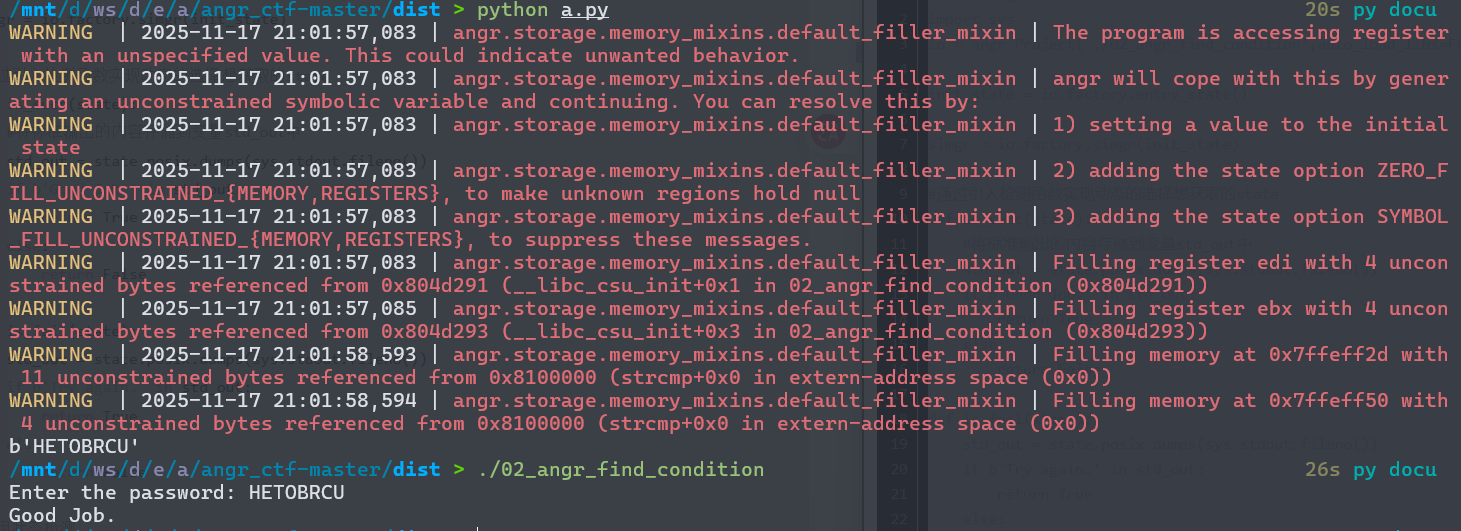
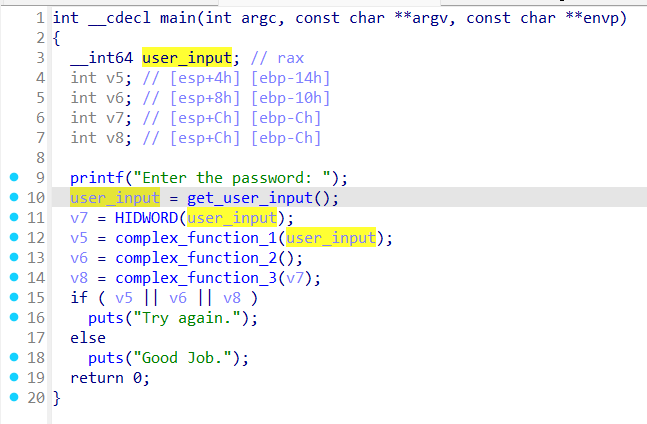
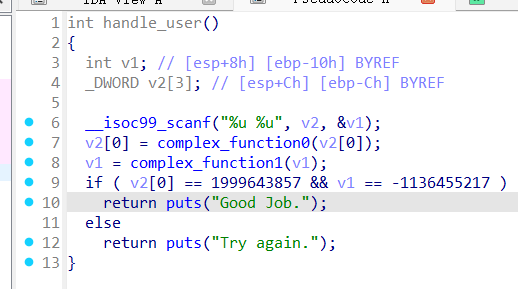
程序读取一个输入,然后分别做了三个复杂的变换,之后判定满足条件就能输出。angr 对 scanf 的复杂输入处理的不是很好,但是发现输入之后的三个参数被放在了三个寄存器里面。程序从这三个寄存器中再取值到三个变量里,然后进行三次复杂变换。我们可以直接控制寄存器的值,跳过用户的输入,这样更方便angr去分析。
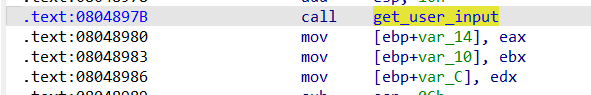
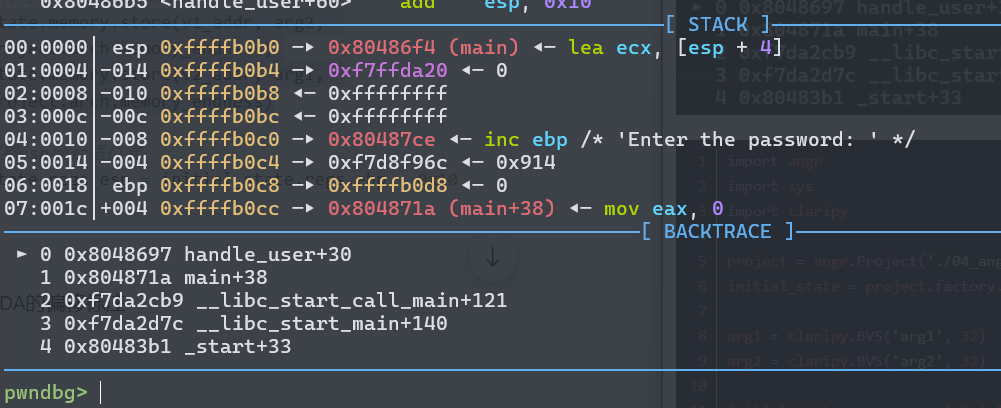
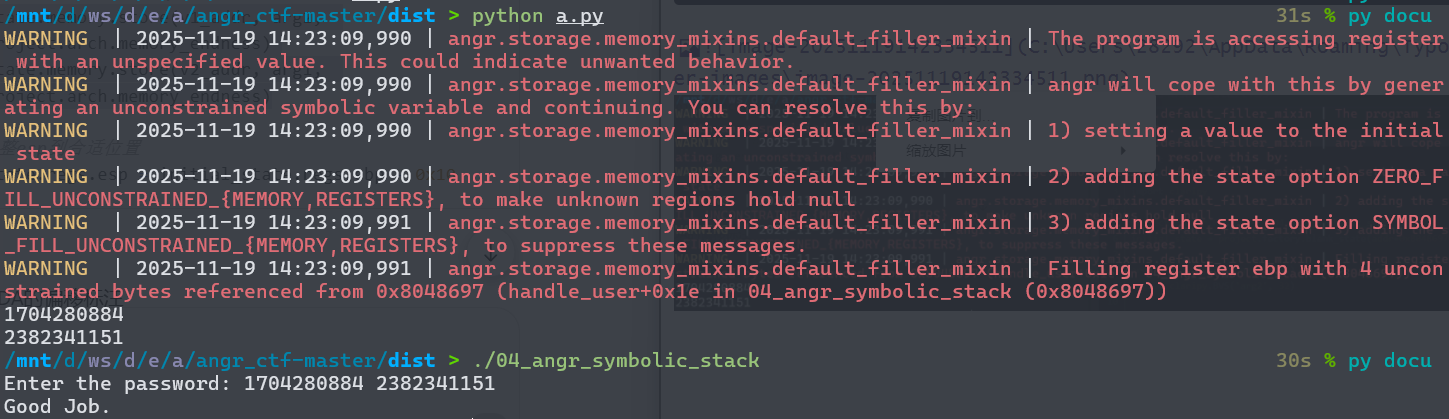
输入值先被写入栈,然后被变换,最后与常量比较。要找到正确输入,必须让angr追踪这两个栈位置上的符号值。注意之类与03的区别,这里是scnaf把数据读取到栈里面,03是把数据读取到寄存器里,上一道题我们直接跳过了输入函数,因此eax,ebx,edx依次压入栈,所以我们直接修改寄存器的值就行,但是04需要我们去手动布置栈。从ida里面看,一个是[ebp-Ch],一个是[ebp-10h]。我们将符号执行的位置放在0x8048697开始,gdb看一下scanf之后的时候的栈,此时栈中以及被压入了2个4字节的数据,所以想要符号化栈中的这两个数据,我们先要将栈抬高,也就是esp-8,让esp指向目标变量区域的"顶部",然后再将两个符号化的栈值压入栈.
这个与4类似,但是这里是要用指定地址去设置参数,刚刚的04的脚本里面注释掉的那几行就是指定地址传参的形式。
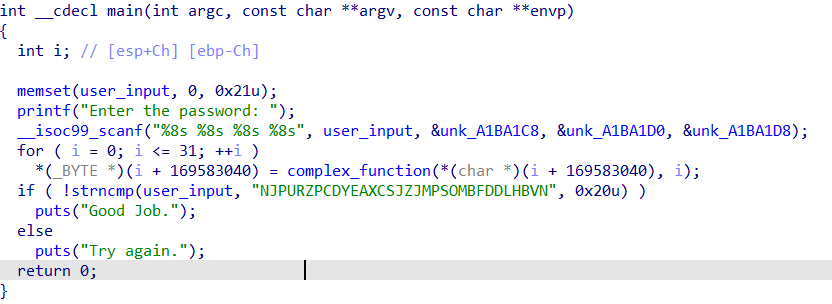
注意这里scanf的是%8s,8字符,一个字符8字节,所以长度是64
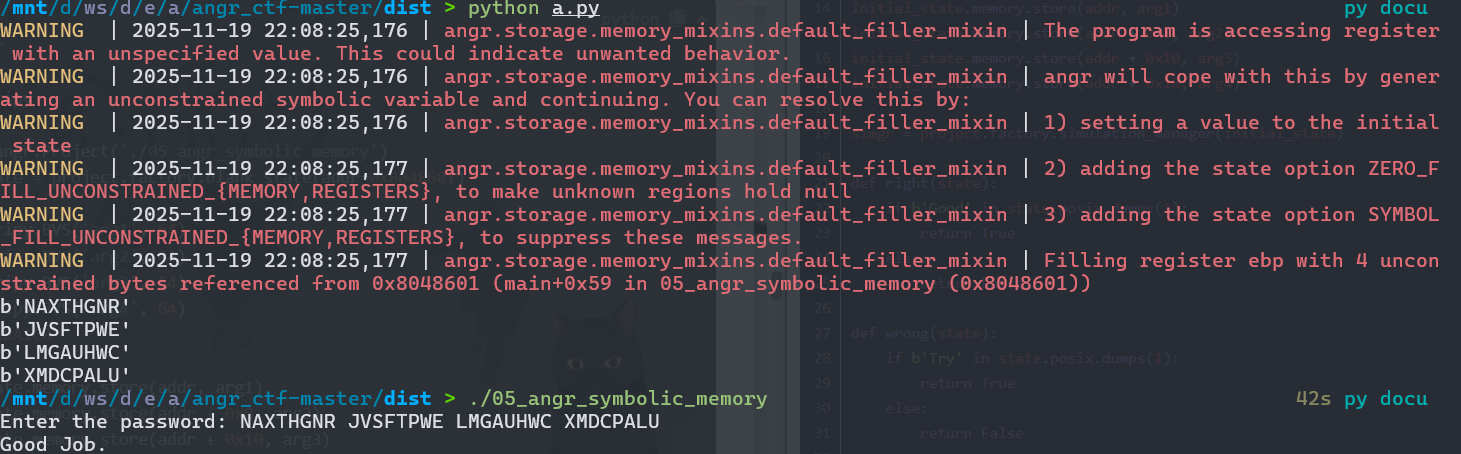
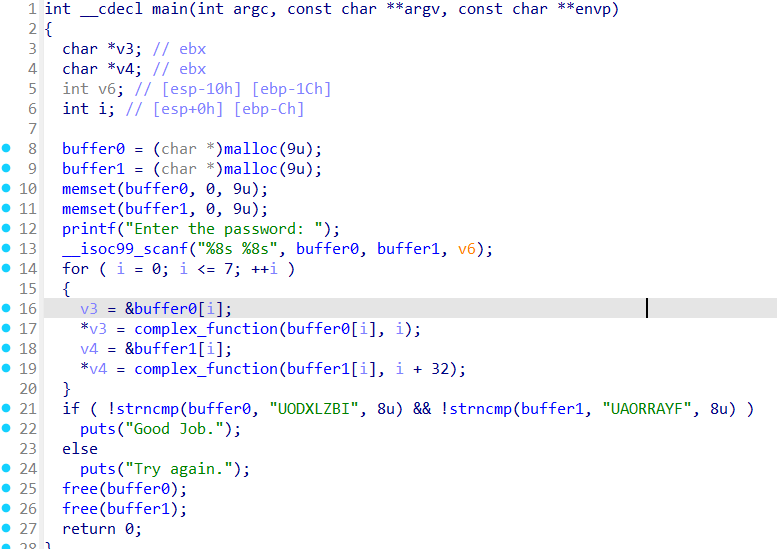
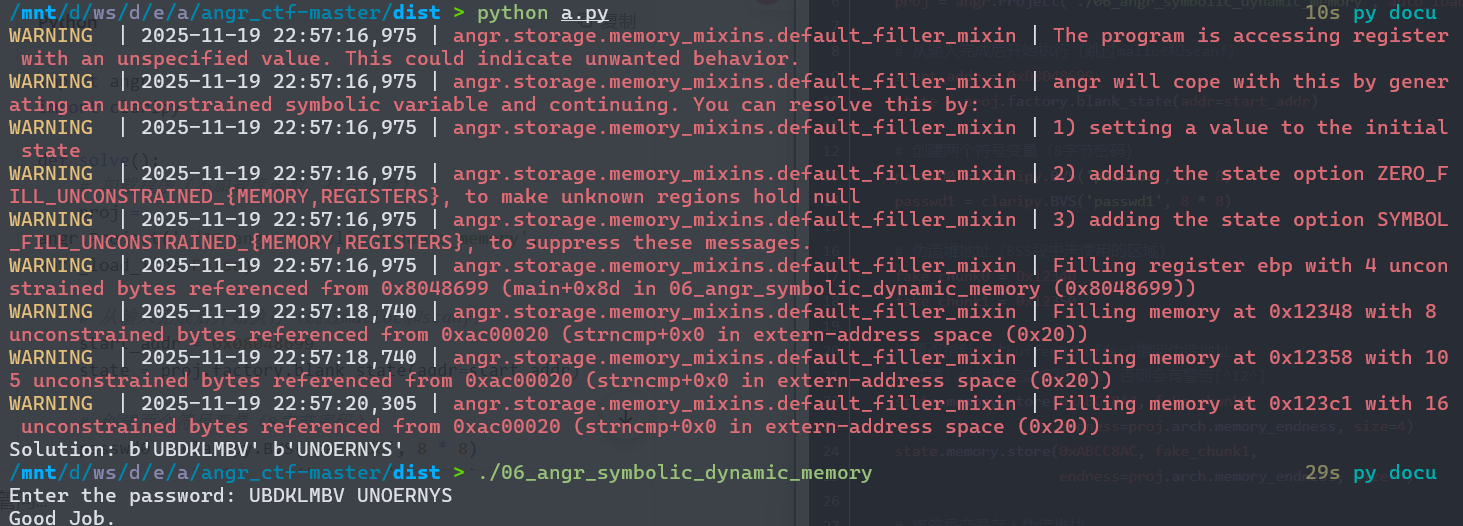
前面是栈的符号化,现在是内存的符号化,scanf的两个参数是动态分配地址的,所以之前的方法并不能直接利用了,但是我们可以指定一个地址作为堆地址,堆地址存储在 bss 段的一个地址中,所以给 bss 段的变量一个自定义地址,往自定义地址里写输入位向量。
也就是说选择两个未使用的内存地址作为"伪造"的堆地址,将 buffer0 和 buffer1 中的指针值改为我们的伪造地址,将符号化输入直接存储到伪造地址中,让程序认为输入数据已经在 malloc 分配的内存中。
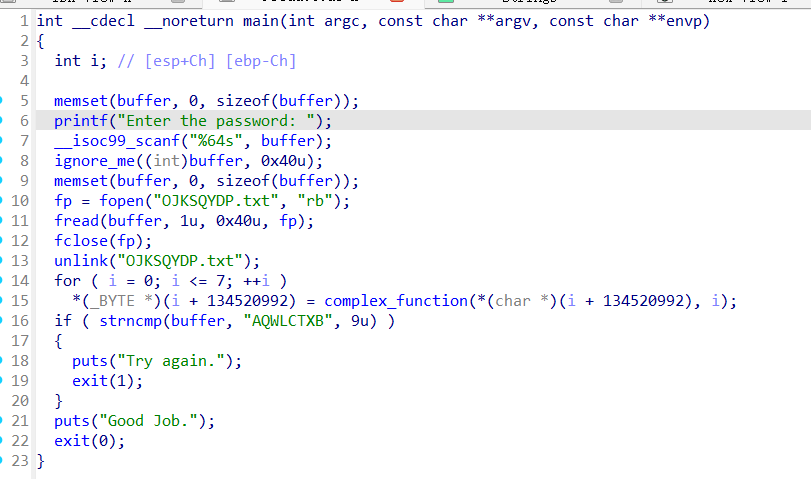
这个程序是考察文件系统符号化能力。程序从硬编码的文件名中读取密码,而非从标准输入获取。angr 默认不模拟真实文件系统,程序无法打开实际文件。需要将整个文件内容转换为符号变量。程序通过指针访问文件名,需确保地址解析正确。
构造虚拟文件对象,内容用符号变量填充。通过 state.fs.insert() 将虚拟文件挂载到指定路径。将 BSS 段的 file_str 指针指向我们控制的字符串地址。
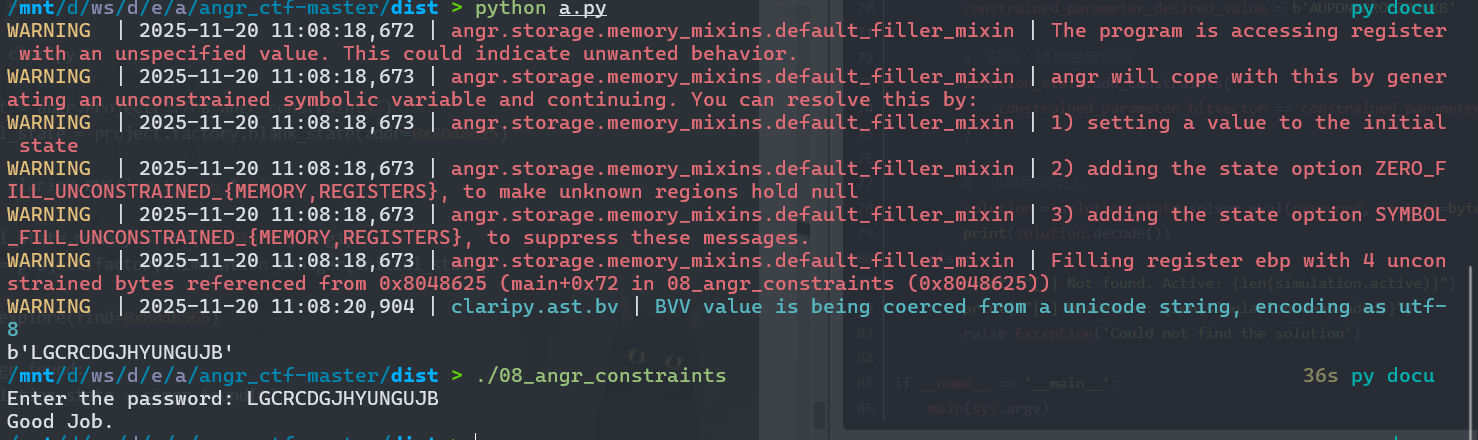
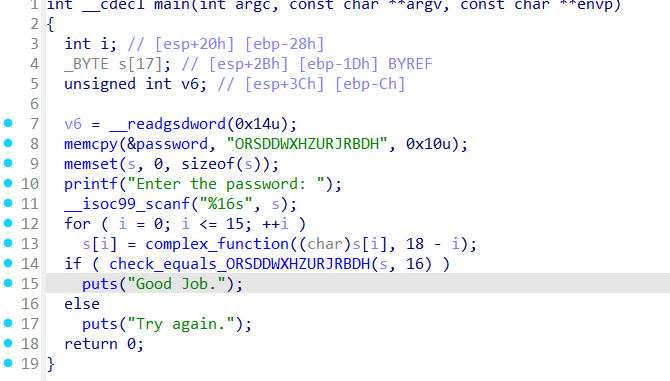
08程序是约束条件的控制,必须要绕过 check_equals 的 2^16 路径爆炸。直接执行的话会路径爆炸,所以需要进行剪枝、聚焦到有效的解空间。
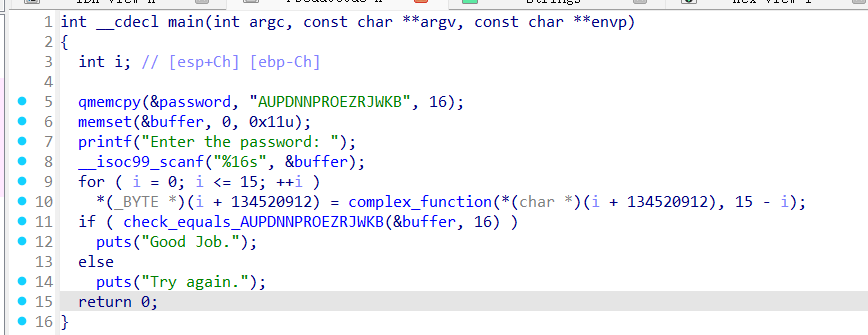
在创建符号变量的时候,主动添加约束条件,减少路径。(使用 state.solver.add() 主动限制变量范围)
09程序是让我们区写一个hook的函数。通过拦截并替换复杂函数,彻底避免路径爆炸。第一次比较在check函数中按位比较,路径爆炸发生在check函数中,在函数调用点直接替换整个函数逻辑,用一行代码完成判断和返回值设置,不产生任何分支。
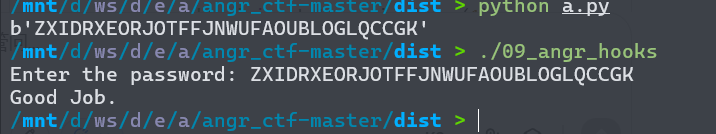
第一步:让 scanf 真实执行(不 Hook)
关键洞察:无需手动 memory.store(),scanf 自己会完成输入符号化。
第二步:Hook check_equals 函数(消除循环)
为什么用 hook_symbol 而非 @hook(addr)?
第三步:在 Hook 内部读取 Buffer 并判断
此时 res 的值是什么?
res** 是 16 字节的符号表达式链**,基于 stdin 的符号变量。
第四步:探索到 Good Job 路径
执行流:
第五步:求解 stdin 内容
求解器内部逻辑:
完整的代码
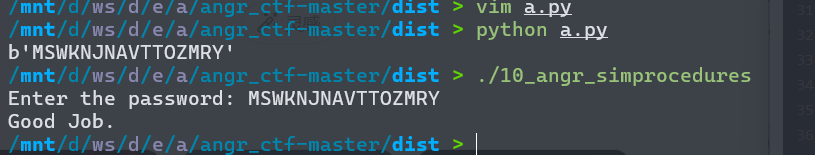
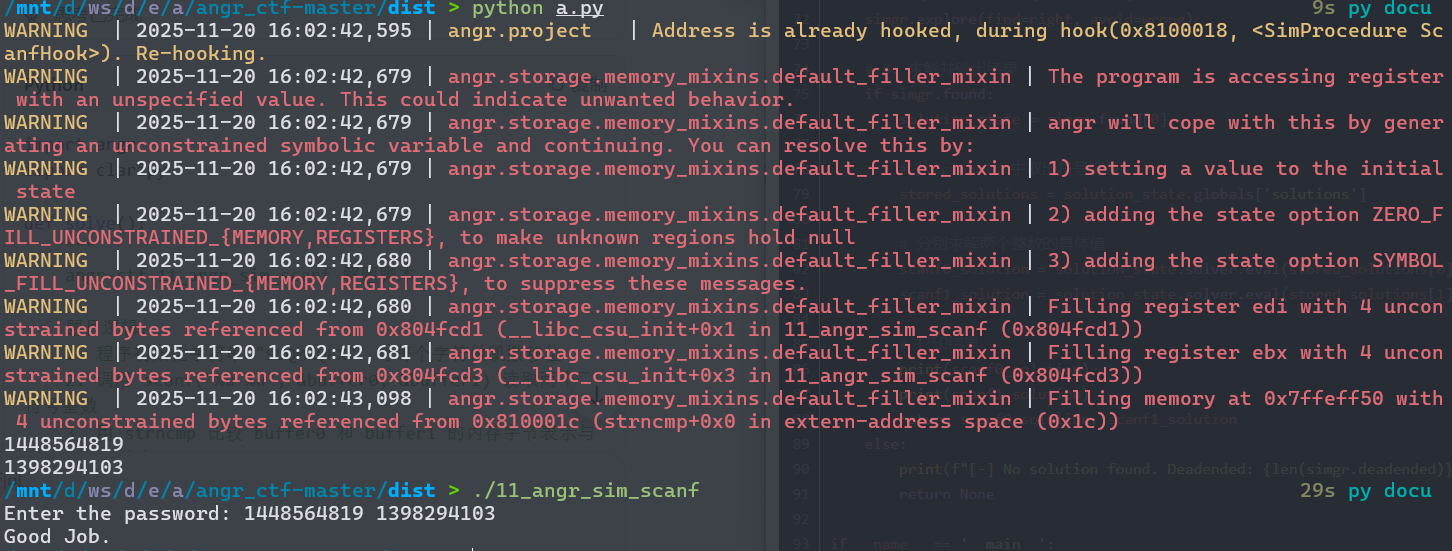
这个题目要求找出两个无符号整数,使得它们经过scanf读入后,在内存中的字节表示能够匹配一个经过变换的8字节字符串。程序首先在栈上初始化一个字符串"SUQMKQFX",然后对每个字符应用complex_function进行位置相关的凯撒移位变换。接着程序调用scanf尝试从标准输入读取两个无符号整数到buffer0和buffer1指向的内存位置。这里的关键点在于,scanf被调用时传入的是两个指向无符号整数的指针,而随后的strncmp实际上比较的是这些整数在内存中的字节表示,而非整数值本身。
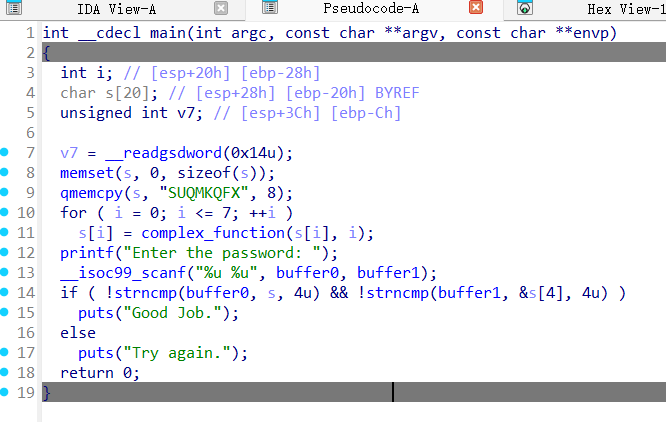
为了破解这个题目,我们需要hook scanf函数,因为真实执行scanf会从标准输入读取具体值,这会导致符号执行无法探索所有可能。脚本中定义了一个SimProcedure类来替换scanf的行为。在run方法中,我们创建两个32位的符号变量arg1和arg2,它们代表我们要寻找的两个整数。然后我们将这两个符号变量存储到scanf的参数指针所指向的内存位置,并使用小端序存储,这符合scanf对无符号整数的处理惯例。同时,我们将这两个符号变量的引用保存在state.globals字典中,以便后续求解时能够访问它们。
通过这种方式,我们让程序继续执行时,strncmp会比较符号变量在内存中的字节表示与变换后的目标字符串。当符号变量的值不符合要求时,程序会走向输出"Try again."的分支,这条路径会被标记为avoid。只有当符号变量的字节表示完全匹配目标字符串时,程序才会输出"Good Job.",这条路径会被保留下来。探索完成后,我们从全局状态中取出保存的符号变量,使用求解器计算它们的具体值。求解器会找到满足所有约束条件的整数解,即第一个整数的内存表示等于变换后字符串的前4个字节,第二个整数的内存表示等于后4个字节。
程序包含大量条件分支导致路径爆炸。利用 angr 的 Veritesting 技术自动合并相似路径,无需手动 hook。
静态链接的二进制文件,所有库函数都在二进制内部。需要 hook 系统调用(如 strlen)以避免复杂实现。
程序加载共享库(.so),验证函数在库中。需要加载库并直接对库函数执行符号执行。
用格式化字符串漏洞任意读取内存。需要找到正确的偏移读取 secret 字符串。
利用栈溢出漏洞任意写入内存。需要覆盖返回地址跳转到 secret 函数。
利用任意跳转漏洞控制程序计数器。需要找到输入使程序跳转到 secret 函数。
$sudo pip install angr$sudo pip install angrimport angrp = angr.Project('file_path')import angrp = angr.Project('file_path')git clone https://github.com/jakespringer/angr_ctfgit clone https://github.com/jakespringer/angr_ctfimport angrp = Project('./00_angr_find',load_options = {'auto_load_libs': False},main_opts = {'base_addr': 0x804850})#p = Project('./00_angr_find',auto_load_libs=False) import angrp = Project('./00_angr_find',load_options = {'auto_load_libs': False},main_opts = {'base_addr': 0x804850})#p = Project('./00_angr_find',auto_load_libs=False) state = p.factory.entry_state()#初始化状态为程序运行到程序入口点的状态#factory负责将Project实例化simgr = p.factory.simgr(state)#创建模拟管理器,将初始化后的state添加到SM中target = 0x8048678 #目标地址(输出Good job)state = p.factory.entry_state()#初始化状态为程序运行到程序入口点的状态#factory负责将Project实例化simgr = p.factory.simgr(state)#创建模拟管理器,将初始化后的state添加到SM中target = 0x8048678 #目标地址(输出Good job)simgr.explore(find=target) #搜索路径,模拟管理器将尝试找到一个执行路径,使程序到达目标地址if simgr.found: #找到满足条件的路径 so_state = simgr.found[0] #获取第一个满足条件的状态 print(so_state.posix.dumps(0)) #打印标准输入(文件描述符0)的内容==》程序运行过程中的输入内容simgr.explore(find=target) #搜索路径,模拟管理器将尝试找到一个执行路径,使程序到达目标地址if simgr.found: #找到满足条件的路径 so_state = simgr.found[0] #获取第一个满足条件的状态 print(so_state.posix.dumps(0)) #打印标准输入(文件描述符0)的内容==》程序运行过程中的输入内容import angrp = angr.Project('./00_angr_find',load_options = {'auto_load_libs': False},main_opts = {'base_addr': 0x804850})#p = Project('./00_angr_find',auto_load_libs=False) state = p.factory.entry_state()#初始化状态为程序运行到程序入口点的状态#factory负责将Project实例化simgr = p.factory.simgr(state)#创建模拟管理器,将初始化后的state添加到SM中target = 0x8048678 #目标地址(输出Good job)simgr.explore(find=target) #搜索路径,模拟管理器将尝试找到一个执行路径,使程序到达目标地址if simgr.found: #找到满足条件的路径 so_state = simgr.found[0] #获取第一个满足条件的状态 print(so_state.posix.dumps(0)) #打印标准输入(文件描述符0)的内容==》程序运行过程中的输入内容import angrp = angr.Project('./00_angr_find',load_options = {'auto_load_libs': False},main_opts = {'base_addr': 0x804850})#p = Project('./00_angr_find',auto_load_libs=False) state = p.factory.entry_state()#初始化状态为程序运行到程序入口点的状态#factory负责将Project实例化simgr = p.factory.simgr(state)#创建模拟管理器,将初始化后的state添加到SM中target = 0x8048678 #目标地址(输出Good job)simgr.explore(find=target) #搜索路径,模拟管理器将尝试找到一个执行路径,使程序到达目标地址if simgr.found: #找到满足条件的路径 so_state = simgr.found[0] #获取第一个满足条件的状态 print(so_state.posix.dumps(0)) #打印标准输入(文件描述符0)的内容==》程序运行过程中的输入内容import angrio = angr.Project('./01_angr_avoid',auto_load_libs=False)init_state = io.factory.entry_state()simgr = io.factory.simgr(init_state)target = 0x80485E0 #目标地址un_target = 0x80485A8 #不想被执行的地址#avoid=un_target为不想执行这里simgr.explore(find=target,avoid=un_target)if simgr.found: so_state = simgr.found[0] print(so_state.posix.dumps(0))import angrio = angr.Project('./01_angr_avoid',auto_load_libs=False)init_state = io.factory.entry_state()simgr = io.factory.simgr(init_state)target = 0x80485E0 #目标地址un_target = 0x80485A8 #不想被执行的地址#avoid=un_target为不想执行这里simgr.explore(find=target,avoid=un_target)if simgr.found: so_state = simgr.found[0] print(so_state.posix.dumps(0))import angrimport sysio = angr.Project('./02_angr_find_condition',auto_load_libs=False)init_state = io.factory.entry_state()simgr = io.factory.simgr(init_state)#通过引入检测函数实现动态的选择想获取的statedef is_succ(state): #将标准输出的内容存储到变量std_out中 std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Good Job.' in std_out: return True else: return Falsedef is_fail(state): std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Try again.' in std_out: return True else: return False#采用状态检测simgr.explore(find=is_succ,avoid=is_fail)if simgr.found: so_state = simgr.found[0] print(so_state.posix.dumps(0))import angrimport sysio = angr.Project('./02_angr_find_condition',auto_load_libs=False)init_state = io.factory.entry_state()simgr = io.factory.simgr(init_state)#通过引入检测函数实现动态的选择想获取的statedef is_succ(state): #将标准输出的内容存储到变量std_out中 std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Good Job.' in std_out: return True else: return Falsedef is_fail(state): std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Try again.' in std_out: return True else: return False#采用状态检测simgr.explore(find=is_succ,avoid=is_fail)if simgr.found: so_state = simgr.found[0] print(so_state.posix.dumps(0))import angrimport claripyimport sysio = angr.Project('./03_angr_symbolic_registers',auto_load_libs=False)state_addr = 0x8048980init_state = io.factory.blank_state(addr = state_addr) #跳过输入函数,从目标地址开始执行passwd_size = 32 #符号向量大小#通过claripy创建符号向量passwd0 = claripy.BVS('passwd0',passwd_size)passwd1 = claripy.BVS('passwd1',passwd_size)passwd2 = claripy.BVS('passwd2',passwd_size)#对寄存器进行赋值init_state.regs.eax = passwd0init_state.regs.ebx = passwd1init_state.regs.edx = passwd2simgr = io.factory.simgr(init_state)def is_succ(state): std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Good Job.' in std_out: return True else: return Falsedef is_fail(state): std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Try again.' in std_out: return True else: return Falsesimgr.explore(find=is_succ,avoid=is_fail)if simgr.found: so_state = simgr.found[0] so0 = hex(so_state.solver.eval(passwd0)) so1 = hex(so_state.solver.eval(passwd1)) so2 = hex(so_state.solver.eval(passwd2)) print(so0,so1,so2)import angrimport claripyimport sysio = angr.Project('./03_angr_symbolic_registers',auto_load_libs=False)state_addr = 0x8048980init_state = io.factory.blank_state(addr = state_addr) #跳过输入函数,从目标地址开始执行passwd_size = 32 #符号向量大小#通过claripy创建符号向量passwd0 = claripy.BVS('passwd0',passwd_size)passwd1 = claripy.BVS('passwd1',passwd_size)passwd2 = claripy.BVS('passwd2',passwd_size)#对寄存器进行赋值init_state.regs.eax = passwd0init_state.regs.ebx = passwd1init_state.regs.edx = passwd2simgr = io.factory.simgr(init_state)def is_succ(state): std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Good Job.' in std_out: return True else: return Falsedef is_fail(state): std_out = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Try again.' in std_out: return True else: return Falsesimgr.explore(find=is_succ,avoid=is_fail)if simgr.found: so_state = simgr.found[0] so0 = hex(so_state.solver.eval(passwd0)) so1 = hex(so_state.solver.eval(passwd1)) so2 = hex(so_state.solver.eval(passwd2)) print(so0,so1,so2)import angrimport sysimport claripyproject = angr.Project('./04_angr_symbolic_stack')initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=0x8048697)arg1 = claripy.BVS('arg1', 32)arg2 = claripy.BVS('arg2', 32)initial_state.regs.esp = initial_state.regs.ebpinitial_state.regs.esp -= 8 #esp-8initial_state.stack_push(arg1)initial_state.stack_push(arg2)#v1_addr = initial_state.regs.ebp - 0x10 # 第二个输入直接指定地址#v2_addr = initial_state.regs.ebp - 0x0C # 第一个输入指定地址#initial_state.memory.store(v1_addr, arg2, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)#initial_state.memory.store(v2_addr, arg1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state)def right(state): if b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsedef wrong(state): if b'Try' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsesimgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong)if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg1)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg2))import angrimport sysimport claripyproject = angr.Project('./04_angr_symbolic_stack')initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=0x8048697)arg1 = claripy.BVS('arg1', 32)arg2 = claripy.BVS('arg2', 32)initial_state.regs.esp = initial_state.regs.ebpinitial_state.regs.esp -= 8 #esp-8initial_state.stack_push(arg1)initial_state.stack_push(arg2)#v1_addr = initial_state.regs.ebp - 0x10 # 第二个输入直接指定地址#v2_addr = initial_state.regs.ebp - 0x0C # 第一个输入指定地址#initial_state.memory.store(v1_addr, arg2, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)#initial_state.memory.store(v2_addr, arg1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness)simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state)def right(state): if b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsedef wrong(state): if b'Try' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsesimgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong)if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg1)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg2))import angrimport sysimport claripyproject = angr.Project('./05_angr_symbolic_memory')initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=0x8048601)arg1 = claripy.BVS('arg1', 64)arg2 = claripy.BVS('arg2', 64)arg3 = claripy.BVS('arg3', 64)arg4 = claripy.BVS('arg4', 64)addr = 0xA1BA1C0initial_state.memory.store(addr, arg1)initial_state.memory.store(addr + 0x8, arg2)initial_state.memory.store(addr + 0x10, arg3)initial_state.memory.store(addr + 0x18, arg4)simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state)def right(state): if b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsedef wrong(state): if b'Try' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsesimgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong)if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg1, cast_to=bytes)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg2, cast_to=bytes)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg3, cast_to=bytes)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg4, cast_to=bytes))import angrimport sysimport claripyproject = angr.Project('./05_angr_symbolic_memory')initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=0x8048601)arg1 = claripy.BVS('arg1', 64)arg2 = claripy.BVS('arg2', 64)arg3 = claripy.BVS('arg3', 64)arg4 = claripy.BVS('arg4', 64)addr = 0xA1BA1C0initial_state.memory.store(addr, arg1)initial_state.memory.store(addr + 0x8, arg2)initial_state.memory.store(addr + 0x10, arg3)initial_state.memory.store(addr + 0x18, arg4)simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state)def right(state): if b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsedef wrong(state): if b'Try' in state.posix.dumps(1): return True else: return Falsesimgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong)if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg1, cast_to=bytes)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg2, cast_to=bytes)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg3, cast_to=bytes)) print(solution_state.solver.eval(arg4, cast_to=bytes))import angrimport claripydef solve(): # 加载程序(不加载库函数,提升速度) proj = angr.Project('./06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory', auto_load_libs=False) # 从输入完成后开始执行(跳过malloc和scanf) start_addr = 0x08048699 state = proj.factory.blank_state(addr=start_addr) # 创建两个符号变量(8字节密码) passwd0 = claripy.BVS('passwd0', 8 * 8) passwd1 = claripy.BVS('passwd1', 8 * 8) # 伪造堆地址(BSS段中未使用的区域) fake_chunk0 = 0x12340 fake_chunk1 = 0x12350 # 篡改指针:让buffer0/buffer1指向伪造地址 # 注意:必须指定端序和size,否则会有警告[^12^] state.memory.store(0xABCC8A4, fake_chunk0, endness=proj.arch.memory_endness, size=4) state.memory.store(0xABCC8AC, fake_chunk1, endness=proj.arch.memory_endness, size=4) # 将符号变量存入伪造堆块 state.memory.store(fake_chunk0, passwd0) state.memory.store(fake_chunk1, passwd1) # 创建模拟管理器 simgr = proj.factory.simulation_manager(state) # 定义成功/失败条件 def is_success(s): return b'Good Job.' in s.posix.dumps(1) def is_fail(s): return b'Try again.' in s.posix.dumps(1) # 探索路径 simgr.explore(find=is_success, avoid=is_fail) if simgr.found: sol_state = simgr.found[0] # 求解并转换为字节 sol0 = sol_state.solver.eval(passwd0, cast_to=bytes) sol1 = sol_state.solver.eval(passwd1, cast_to=bytes) print(f"Solution: {sol0} {sol1}") return sol0, sol1 else: print("No solution found") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): # 加载程序(不加载库函数,提升速度) proj = angr.Project('./06_angr_symbolic_dynamic_memory', auto_load_libs=False) # 从输入完成后开始执行(跳过malloc和scanf) start_addr = 0x08048699 state = proj.factory.blank_state(addr=start_addr) # 创建两个符号变量(8字节密码) passwd0 = claripy.BVS('passwd0', 8 * 8) passwd1 = claripy.BVS('passwd1', 8 * 8) # 伪造堆地址(BSS段中未使用的区域) fake_chunk0 = 0x12340 fake_chunk1 = 0x12350 # 篡改指针:让buffer0/buffer1指向伪造地址 # 注意:必须指定端序和size,否则会有警告[^12^] state.memory.store(0xABCC8A4, fake_chunk0, endness=proj.arch.memory_endness, size=4) state.memory.store(0xABCC8AC, fake_chunk1, endness=proj.arch.memory_endness, size=4) # 将符号变量存入伪造堆块 state.memory.store(fake_chunk0, passwd0) state.memory.store(fake_chunk1, passwd1) # 创建模拟管理器 simgr = proj.factory.simulation_manager(state) # 定义成功/失败条件 def is_success(s): return b'Good Job.' in s.posix.dumps(1) def is_fail(s): return b'Try again.' in s.posix.dumps(1) # 探索路径 simgr.explore(find=is_success, avoid=is_fail) if simgr.found: sol_state = simgr.found[0] # 求解并转换为字节 sol0 = sol_state.solver.eval(passwd0, cast_to=bytes) sol1 = sol_state.solver.eval(passwd1, cast_to=bytes) print(f"Solution: {sol0} {sol1}") return sol0, sol1 else: print("No solution found") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): # 加载程序 proj = angr.Project('./07_angr_symbolic_file', auto_load_libs=False) # 从文件读取完成后开始执行(跳过fopen/fscanf) start_addr = 0x080488D3 state = proj.factory.blank_state(addr=start_addr) # 创建符号变量表示文件内容(0x40 = 64字节) file_content = claripy.BVS('file_content', 8 * 0x40) # 创建虚拟文件 # 注意:文件名必须与程序硬编码的一致 sim_file = angr.SimFile('OJKSQYDP.txt', content=file_content) # 将虚拟文件插入文件系统 state.fs.insert('OJKSQYDP.txt', sim_file) # 关键:劫持全局文件名指针 # file_str = 0xA1BA1C0,指向文件名字符串 fake_path_addr = 0x12345 state.memory.store(0xA1BA1C0, fake_path_addr, endness=proj.arch.memory_endness, size=4) # 写入实际路径字符串 state.memory.store(fake_path_addr, b'OJKSQYDP.txt\x00') # 创建模拟管理器 simgr = proj.factory.simulation_manager(state) # 定义成功/失败条件 def is_success(s): return b'Good Job.' in s.posix.dumps(1) def is_fail(s): return b'Try again.' in s.posix.dumps(1) # 探索路径 simgr.explore(find=is_success, avoid=is_fail) if simgr.found: sol_state = simgr.found[0] # 求解文件内容并转换为字符串 solution = sol_state.solver.eval(file_content, cast_to=bytes) # 提取有效部分(到\0为止) solution_str = solution[:solution.index(b'\x00')] print(f"Solution: {solution_str.decode()}") return solution_str else: print("No solution found") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): # 加载程序 proj = angr.Project('./07_angr_symbolic_file', auto_load_libs=False) # 从文件读取完成后开始执行(跳过fopen/fscanf) start_addr = 0x080488D3 state = proj.factory.blank_state(addr=start_addr) # 创建符号变量表示文件内容(0x40 = 64字节) file_content = claripy.BVS('file_content', 8 * 0x40) # 创建虚拟文件 # 注意:文件名必须与程序硬编码的一致 sim_file = angr.SimFile('OJKSQYDP.txt', content=file_content) # 将虚拟文件插入文件系统 state.fs.insert('OJKSQYDP.txt', sim_file) # 关键:劫持全局文件名指针 # file_str = 0xA1BA1C0,指向文件名字符串 fake_path_addr = 0x12345 state.memory.store(0xA1BA1C0, fake_path_addr, endness=proj.arch.memory_endness, size=4) # 写入实际路径字符串 state.memory.store(fake_path_addr, b'OJKSQYDP.txt\x00') # 创建模拟管理器 simgr = proj.factory.simulation_manager(state) # 定义成功/失败条件 def is_success(s): return b'Good Job.' in s.posix.dumps(1) def is_fail(s): return b'Try again.' in s.posix.dumps(1) # 探索路径 simgr.explore(find=is_success, avoid=is_fail) if simgr.found: sol_state = simgr.found[0] # 求解文件内容并转换为字符串 solution = sol_state.solver.eval(file_content, cast_to=bytes) # 提取有效部分(到\0为止) solution_str = solution[:solution.index(b'\x00')] print(f"Solution: {solution_str.decode()}") return solution_str else: print("No solution found") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): project = angr.Project('./08_angr_constraints', auto_load_libs=False) # 从 scanf 返回后开始 initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=0x08048625) sym_password = claripy.BVS('password', 8 * 16) buffer_addr = 0x0804A050 initial_state.memory.store(buffer_addr, sym_password) simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state) # 探索到 Good Job. 之前的状态 simgr.explore(find=0x08048696) if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] # 变换后的 buffer transformed_buffer = solution_state.memory.load(buffer_addr, 16) # 延迟约束 solution_state.add_constraints(transformed_buffer == b'AUPDNNPROEZRJWKB') # 求解 solution = solution_state.solver.eval(sym_password, cast_to=bytes) print(solution) return solution else: print(f"Not found. Active: {len(simgr.active)}") print(f"Deadended: {len(simgr.deadended)}") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): project = angr.Project('./08_angr_constraints', auto_load_libs=False) # 从 scanf 返回后开始 initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=0x08048625) sym_password = claripy.BVS('password', 8 * 16) buffer_addr = 0x0804A050 initial_state.memory.store(buffer_addr, sym_password) simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state) # 探索到 Good Job. 之前的状态 simgr.explore(find=0x08048696) if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] # 变换后的 buffer transformed_buffer = solution_state.memory.load(buffer_addr, 16) # 延迟约束 solution_state.add_constraints(transformed_buffer == b'AUPDNNPROEZRJWKB') # 求解 solution = solution_state.solver.eval(sym_password, cast_to=bytes) print(solution) return solution else: print(f"Not found. Active: {len(simgr.active)}") print(f"Deadended: {len(simgr.deadended)}") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): project = angr.Project('./09_angr_hooks', auto_load_libs=False) # 1. entry_state:自动初始化栈、寄存器 initial_state = project.factory.entry_state( add_options={angr.options.ZERO_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) # 2. Hook check_equals(在函数内部做判断) check_equals_call = 0x80486B3 # buffer_addr = 0x804A054 # target_str = b'XYMKBKUHNIQYNQXE' # 从函数名提取 @project.hook(check_equals_call, length=5) def hook_check_equals(state): # 读取 buffer 内容 res = state.memory.load(buffer_addr, 16) # 直接判断并设置返回值(eax) # 只有 res == target 时,eax=1 → Good Job 路径 state.regs.eax = claripy.If(res == target_str, claripy.BVV(1, 32), claripy.BVV(0, 32)) # 3. 创建模拟管理器 simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state) # 4. 探索与规避 def right(state): return b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1) def wrong(state): return b'Try' in state.posix.dumps(1) simgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong) # 5. 输出解 if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.posix.dumps(0)) # 打印输入 return solution_state.posix.dumps(0) else: print("[-] No solution") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()import angrimport claripydef solve(): project = angr.Project('./09_angr_hooks', auto_load_libs=False) # 1. entry_state:自动初始化栈、寄存器 initial_state = project.factory.entry_state( add_options={angr.options.ZERO_FILL_UNCONSTRAINED_REGISTERS} ) # 2. Hook check_equals(在函数内部做判断) check_equals_call = 0x80486B3 # buffer_addr = 0x804A054 # target_str = b'XYMKBKUHNIQYNQXE' # 从函数名提取 @project.hook(check_equals_call, length=5) def hook_check_equals(state): # 读取 buffer 内容 res = state.memory.load(buffer_addr, 16) # 直接判断并设置返回值(eax) # 只有 res == target 时,eax=1 → Good Job 路径 state.regs.eax = claripy.If(res == target_str, claripy.BVV(1, 32), claripy.BVV(0, 32)) # 3. 创建模拟管理器 simgr = project.factory.simulation_manager(initial_state) # 4. 探索与规避 def right(state): return b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1) def wrong(state): return b'Try' in state.posix.dumps(1) simgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong) # 5. 输出解 if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.posix.dumps(0)) # 打印输入 return solution_state.posix.dumps(0) else: print("[-] No solution") return Noneif __name__ == '__main__': solve()initial_state = project.factory.entry_state()initial_state = project.factory.entry_state()@project.hook_symbol('check_equals_ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH', func())@project.hook_symbol('check_equals_ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH', func())def run(self, a1, a2): res = self.state.memory.load(a1, a2) # 读取 s 的内容(已变换) return claripy.If(res == target, BVV(1, 32), BVV(0, 32))def run(self, a1, a2): res = self.state.memory.load(a1, a2) # 读取 s 的内容(已变换) return claripy.If(res == target, BVV(1, 32), BVV(0, 32))// 程序执行到 check_equals 时:s[i] = complex_function(original_input[i], 18-i);// s 里已是变换后的值(符号表达式)// 例如:// res[0] = (stdin[0] + 18) % 26 + 'A'// res[1] = (stdin[1] + 17) % 26 + 'A'// ...// 程序执行到 check_equals 时:s[i] = complex_function(original_input[i], 18-i);// s 里已是变换后的值(符号表达式)// 例如:// res[0] = (stdin[0] + 18) % 26 + 'A'// res[1] = (stdin[1] + 17) % 26 + 'A'// ...simgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong)def right(state): return b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1)simgr.explore(find=right, avoid=wrong)def right(state): return b'Good' in state.posix.dumps(1)if simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.posix.dumps(0)) # 求解符号化的 stdinif simgr.found: solution_state = simgr.found[0] print(solution_state.posix.dumps(0)) # 求解符号化的 stdin# 约束方程组:(stdin[0] + 18) % 26 + 'A' == 'O'(stdin[1] + 17) % 26 + 'A' == 'R'...(stdin[15] + 3) % 26 + 'A' == 'H'# 求解器逆向求解:stdin[0] = ('O' - 'A' - 18) % 26 = 'M'stdin[1] = ('R' - 'A' - 17) % 26 = 'S'...stdin[15] = ('H' - 'A' - 3) % 26 = 'K'# 结果:b'MSWKNJNAVTTOZMRY'# 约束方程组:(stdin[0] + 18) % 26 + 'A' == 'O'(stdin[1] + 17) % 26 + 'A' == 'R'...(stdin[15] + 3) % 26 + 'A' == 'H'# 求解器逆向求解:stdin[0] = ('O' - 'A' - 18) % 26 = 'M'stdin[1] = ('R' - 'A' - 17) % 26 = 'S'