-
-
[原创]从Java到Native,so中的函数是如何一步步被加载的?
-
发表于: 2025-3-10 21:17 36049
-
so?what can i do?

首先在java层肯定是要去调用so层文件,本篇重点讲解native层的加载流程,此处不再赘述。
“Dynamic Link” 动态装载库,我们会想到windows系统中,存在加载dll文件的动态加载类型,在linux中,类似的文件就是.so文件了,而加载文件的重要函数就是dlopen。
dlopen:该函数将打开一个新库,并把它装入内存。该函数主要用来加载库中的符号,这些符号在编译的时候是不知道的。这种机制使得在系统中添加或者删除一个模块时,都不需要重新进行编译。
函数原型
第一个参数是头文件所在的文件名,也就是so文件,第二个标志参数有很多,例如有RTLD_NOW和RTLD_LAZY立即计算和需要时计算,以及RTLD_GLOBAL使得那些在以后才加载的库可以获得其中的符号。方式就是dlopen返回的句柄作为dlsym()的第一个参数,获取符号在库中的地址。
此函数作为安卓平台上特有的函数 是dlopen函数的拓展版本,进一步增强了dlopen函数的功能
函数原型
可以看到在原函数基础上增加了ext_data参数
参照源码可以大致了解增强的功能,其中大部分功能与第二个参数flag中的一些功能标志位相关联

此版本为安卓4源码分析,最新版本的安卓号的加载流程在代码量上有进一步的提升,但是基础原理类似。
上面的dlopen函数只是一个引子,真正的核心功能代码实现在do_dlopen函数中
此函数的类型为soinfo指针,soinfo代表的含义是“进程加载的so链”,其中包含了已经被加载的so 的信息。这里所返回的值也是si——进程加载的so链。
其中涉及的主要两步函数为find_library和CallConstructor下面会继续介绍。
find_library函数传入参数后也会进行进一步的函数调用,流程见注释
涉及知识点:elf文件格式,文件分区的加载
此函数根据上面的soinfo链接映像函数分析的section动态节区中的信息,获取共享库依赖的所有的so文件名,所有的依赖库初始化完成后,执行init_func、init_array方法初始化该动态库。
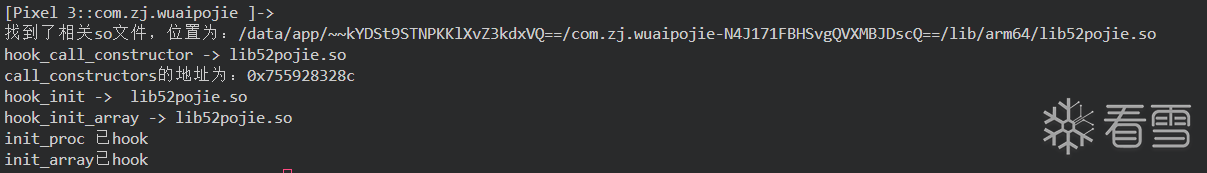
这两个函数是so文件在被加载或者卸载时自动执行的函数,用于初始化的操作,其中init函数优先于init_array函数。作为so层加载很早的函数,可以通过实现hook他来绕过一些关键的检测点。
也正是因为加载过早且初始化后只加载一次,我们如果直接去hook是无法get到的,通过上面的流程我们知道了这两个函数是在call_constructors中进行加载,我们就可以通过逆向hook相关的native函数进行加载hook。通过在android_dlopen_ext加载过程中进行hook操作。
这里有一步很关键的操作,关于call_constructors 函数,call_constructors 是在共享库加载时被调用的函数。意思就是他是存储在安卓本机中的本地链接库函数,而他的位置文件具体就在/system/bin/linker64中,我们将他从手机上pull下来进行反编译并查找相关函数可以看到。
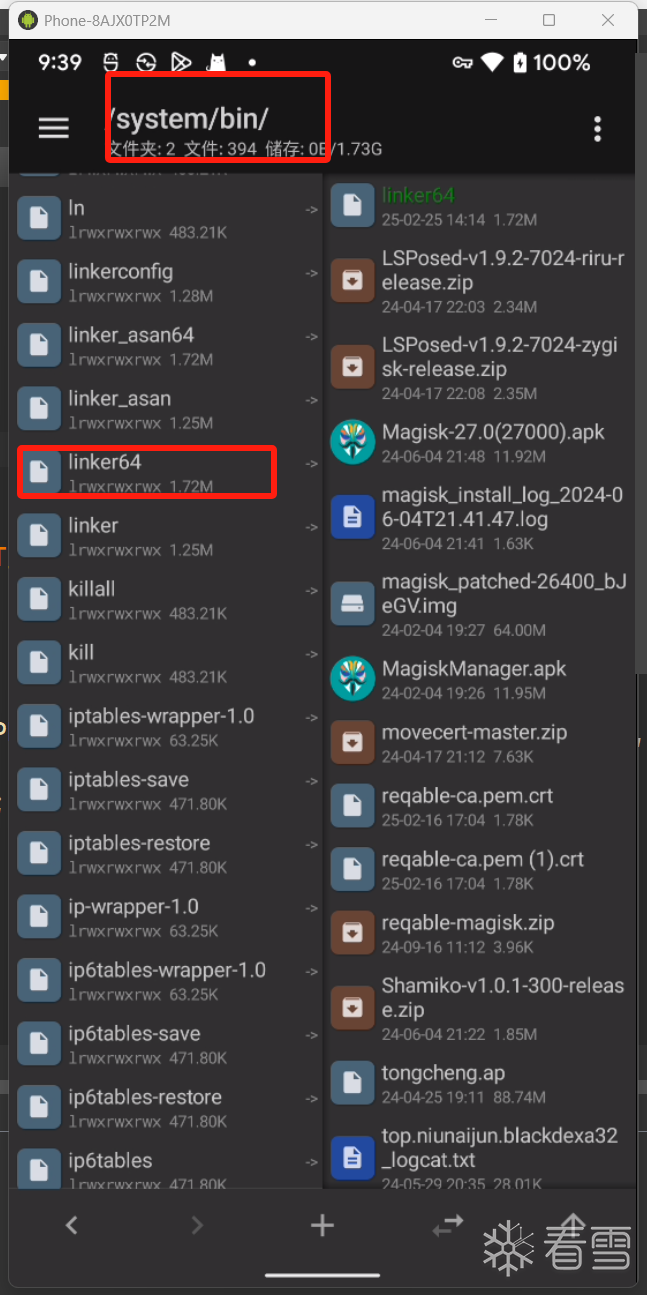
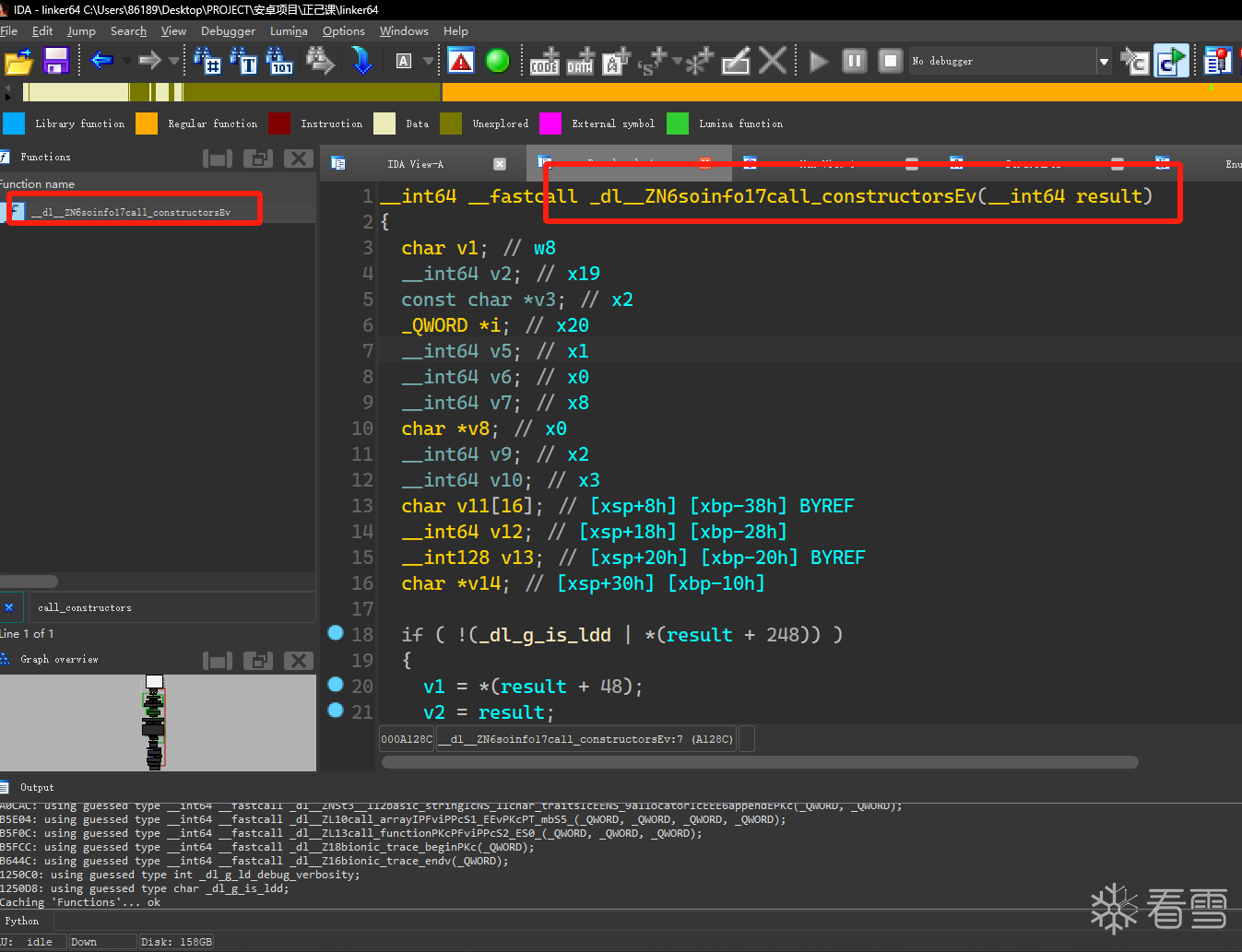
反编译的结果与我们上文看到的函数功能接近。
通过hookandroid_dlopen_ext定位我们要hook的so文件,通过hook linker64中的 call_constructors函数可以修改init和init_array的流程。
这里需要注意的是关于偏移地址的查找,可以通过pie,ida等工具 或者在linux环境中执行命令
通过 JNIEXPORT 和 JNICALL 两个宏定义声明,在虚拟机加载 so 时发现上面两个宏定义的函数时就会链接到对应的 native 方法。
通过 RegisterNatives 方法手动完成 native 方法和 so 中的方法的绑定,这样虚拟机就可以通过这个函数映射表直接找到相应的方法了。
流程如下。
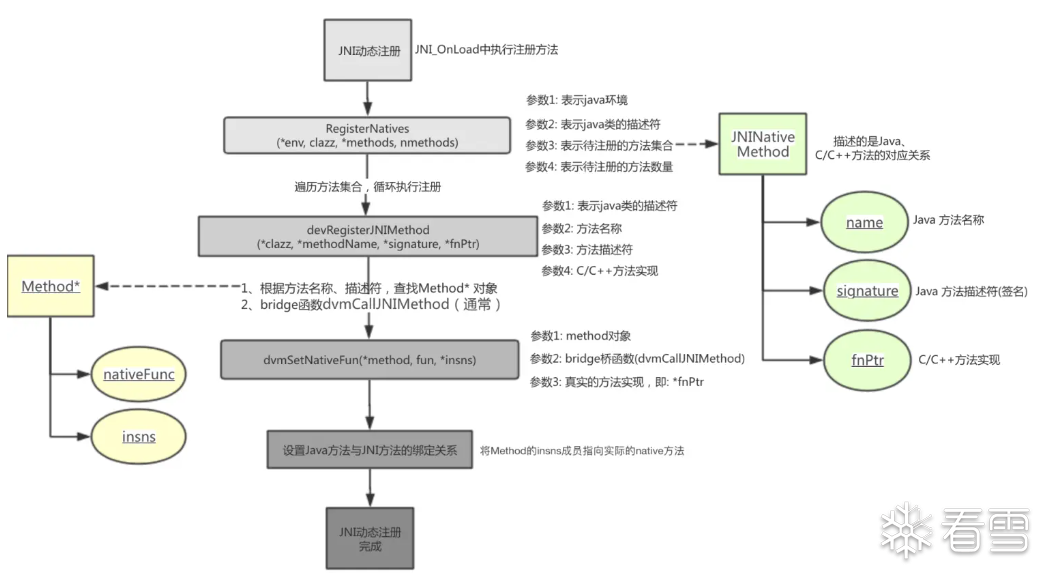
通过RegisterNatives(JNI *env ,jclass clazz ,const JNINativeMethord *methord ,jint nmethods)函数,参数分别代表:java环境,java类的描述符,待注册的方法集合,待注册方法数量。
其中“待注册方法集合”是名为JNINativeMethord的结构体,内容如下
这里的第二个参数为方法签名需要注意,类型为字符串,由一对小括号和若干签名符号组成,其中括号内写传入参数的签名符号,没有参数则不写,括号外写返回参数的签名符号。
实例:Java层函数String getText(int a,byte[] b)就是(I[B)Ljava/lang/String;
可以看出,在动态加载的过程中,很关键的方法就是流程图中的RegisterNatives在这其中的参数有很多设置方法名的敏感信息。
《安卓逆向这档事》十七、你的RPCvs佬的RPC - 吾爱破解 - 52pojie.cn
[原创] 细说So动态库的加载流程-Android安全-看雪-安全社区|安全招聘|kanxue.com
android so加载 - vendanner - 博客园
so逆向筑基-hook init init_array 和JNI_OnLoad
void *dlopen(const char *filename, int flag);void *dlopen(const char *filename, int flag);void* android_dlopen_ext(const char* path, int flag, const void* ext_data);void* android_dlopen_ext(const char* path, int flag, const void* ext_data);typedef struct { /** A bitmask of `ANDROID_DLEXT_` enum values. */ uint64_t flags; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS` and `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_HINT`. */ void* _Nullable reserved_addr; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS` and `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_HINT`. */ size_t reserved_size; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_WRITE_RELRO` and `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_RELRO`. */ int relro_fd; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD`. */ int library_fd; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET` */ off64_t library_fd_offset; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_NAMESPACE`. */ struct android_namespace_t* _Nullable library_namespace;} android_dlextinfo;typedef struct { /** A bitmask of `ANDROID_DLEXT_` enum values. */ uint64_t flags; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS` and `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_HINT`. */ void* _Nullable reserved_addr; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS` and `ANDROID_DLEXT_RESERVED_ADDRESS_HINT`. */ size_t reserved_size; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_WRITE_RELRO` and `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_RELRO`. */ int relro_fd; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD`. */ int library_fd; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_LIBRARY_FD_OFFSET` */ off64_t library_fd_offset; /** Used by `ANDROID_DLEXT_USE_NAMESPACE`. */ struct android_namespace_t* _Nullable library_namespace;} android_dlextinfo;void* dlopen(const char* filename, int flags) { ScopedPthreadMutexLocker locker(&gDlMutex); soinfo* result = do_dlopen(filename, flags); if (result == NULL) { __bionic_format_dlerror("dlopen failed", linker_get_error_buffer()); return NULL; } return result;}soinfo* do_dlopen(const char* name, int flags) { //判断传入标志的类型 if ((flags & ~(RTLD_NOW|RTLD_LAZY|RTLD_LOCAL|RTLD_GLOBAL)) != 0) { DL_ERR("invalid flags to dlopen: %x", flags); return NULL; } //内存保护权限设置 此处为可读可写,目的是在加载find_library函数后可以对soinfo结构体的内容进行修改 set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE); soinfo* si = find_library(name); //这里返回了so信息链 if (si != NULL) { si->CallConstructors(); //这里执行了此构造方法 } //在这里就没有可写权限了 set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ); return si;}void* dlopen(const char* filename, int flags) { ScopedPthreadMutexLocker locker(&gDlMutex); soinfo* result = do_dlopen(filename, flags); if (result == NULL) { __bionic_format_dlerror("dlopen failed", linker_get_error_buffer()); return NULL; } return result;}soinfo* do_dlopen(const char* name, int flags) { //判断传入标志的类型 if ((flags & ~(RTLD_NOW|RTLD_LAZY|RTLD_LOCAL|RTLD_GLOBAL)) != 0) { DL_ERR("invalid flags to dlopen: %x", flags); return NULL; } //内存保护权限设置 此处为可读可写,目的是在加载find_library函数后可以对soinfo结构体的内容进行修改 set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE); soinfo* si = find_library(name); //这里返回了so信息链 if (si != NULL) { si->CallConstructors(); //这里执行了此构造方法 } //在这里就没有可写权限了 set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ); return si;}static soinfo *find_loaded_library(const char *name){ soinfo *si; const char *bname; // TODO: don't use basename only for determining libraries // 42bK9s2c8@1M7q4)9K6b7g2)9J5c8W2)9J5c8X3y4G2k6r3g2Q4x3X3g2Y4L8$3!0Y4L8r3g2Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6H3i4K6u0r3j5h3&6V1M7X3!0A6k6q4)9J5c8X3W2K6M7%4g2W2M7#2)9J5c8X3c8W2N6r3q4A6L8q4)9K6c8X3W2V1i4K6y4p5y4U0j5%4x3l9`.`. bname = strrchr(name, '/'); //分割so文件的名称 bname = bname ? bname + 1 : name; for (si = solist; si != NULL; si = si->next) {//递归查找是否存在so文件名称 if (!strcmp(bname, si->name)) { return si; } } return NULL;}static soinfo* find_library_internal(const char* name) { if (name == NULL) { return somain; //返回共享库 } soinfo* si = find_loaded_library(name); if (si != NULL) { if (si->flags & FLAG_LINKED) {// 前者检查是否有flag标志字段,后者检查是否被链接 return si; //如果被链接就直接加载 } DL_ERR("OOPS: recursive link to \"%s\"", si->name); //报错递归链接错误。 //【递归链接:在动态库的加载过程中,如果同一个库被多次请求加载,可能会发生递归链接。通常这是不希望发生的情况,因为这会导致循环依赖或重复加载的错误。】 return NULL; } TRACE("[ '%s' has not been loaded yet. Locating...]", name); //发现未被加载后会通过load_library重新加载 si = load_library(name); //load_library的函数在下面介绍 if (si == NULL) { //如果再次加载仍为null 则返回null return NULL; } // At this point we know that whatever is loaded @ base is a valid ELF // shared library whose segments are properly mapped in. //返回了基址,大小和名称 TRACE("[ init_library base=0x%08x sz=0x%08x name='%s' ]", si->base, si->size, si->name); //通过此函数 if (!soinfo_link_image(si)) {//此函数实现了动态链接库中section信息解析。 munmap(reinterpret_cast<void*>(si->base), si->size); soinfo_free(si); return NULL; } return si;}static soinfo* find_library(const char* name) { soinfo* si = find_library_internal(name); if (si != NULL) { si->ref_count++; } return si;}static soinfo *find_loaded_library(const char *name){ soinfo *si; const char *bname; // TODO: don't use basename only for determining libraries // 46fK9s2c8@1M7q4)9K6b7g2)9J5c8W2)9J5c8X3y4G2k6r3g2Q4x3X3g2Y4L8$3!0Y4L8r3g2Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6H3i4K6u0r3j5h3&6V1M7X3!0A6k6q4)9J5c8X3W2K6M7%4g2W2M7#2)9J5c8X3c8W2N6r3q4A6L8q4)9K6c8X3W2V1i4K6y4p5y4U0j5%4x3l9`.`. bname = strrchr(name, '/'); //分割so文件的名称 bname = bname ? bname + 1 : name; for (si = solist; si != NULL; si = si->next) {//递归查找是否存在so文件名称 if (!strcmp(bname, si->name)) { return si; } } return NULL;}static soinfo* find_library_internal(const char* name) { if (name == NULL) { return somain; //返回共享库 } soinfo* si = find_loaded_library(name); if (si != NULL) { if (si->flags & FLAG_LINKED) {// 前者检查是否有flag标志字段,后者检查是否被链接 return si; //如果被链接就直接加载 } DL_ERR("OOPS: recursive link to \"%s\"", si->name); //报错递归链接错误。 //【递归链接:在动态库的加载过程中,如果同一个库被多次请求加载,可能会发生递归链接。通常这是不希望发生的情况,因为这会导致循环依赖或重复加载的错误。】 return NULL; } TRACE("[ '%s' has not been loaded yet. Locating...]", name); //发现未被加载后会通过load_library重新加载 si = load_library(name); //load_library的函数在下面介绍 if (si == NULL) { //如果再次加载仍为null 则返回null return NULL; } // At this point we know that whatever is loaded @ base is a valid ELF // shared library whose segments are properly mapped in. //返回了基址,大小和名称 TRACE("[ init_library base=0x%08x sz=0x%08x name='%s' ]", si->base, si->size, si->name); //通过此函数 if (!soinfo_link_image(si)) {//此函数实现了动态链接库中section信息解析。 munmap(reinterpret_cast<void*>(si->base), si->size); soinfo_free(si); return NULL; } return si;}static soinfo* find_library(const char* name) { soinfo* si = find_library_internal(name); if (si != NULL) { si->ref_count++; } return si;}void soinfo::CallConstructors() {if (constructors_called) { return;}// We set constructors_called before actually calling the constructors, otherwise it doesn't// protect against recursive constructor calls. One simple example of constructor recursion// is the libc debug malloc, which is implemented in libc_malloc_debug_leak.so:// 1. The program depends on libc, so libc's constructor is called here.// 2. The libc constructor calls dlopen() to load libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.// 3. dlopen() calls the constructors on the newly created// soinfo for libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.// 4. The debug .so depends on libc, so CallConstructors is// called again with the libc soinfo. If it doesn't trigger the early-// out above, the libc constructor will be called again (recursively!).constructors_called = true;if ((flags & FLAG_EXE) == 0 && preinit_array != NULL) { // The GNU dynamic linker silently ignores these, but we warn the developer. PRINT("\"%s\": ignoring %d-entry DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!", name, preinit_array_count);} //确保库已被初始化加载if (dynamic != NULL) { for (Elf32_Dyn* d = dynamic; d->d_tag != DT_NULL; ++d) { if (d->d_tag == DT_NEEDED) { const char* library_name = strtab + d->d_un.d_val; TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors in DT_NEEDED \"%s\"", name, library_name); find_loaded_library(library_name)->CallConstructors(); } }}TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors", name); //最后进行初始化函数的执行// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.CallFunction("DT_INIT", init_func);CallArray("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array, init_array_count, false);}void soinfo::CallConstructors() {if (constructors_called) { return;}// We set constructors_called before actually calling the constructors, otherwise it doesn't// protect against recursive constructor calls. One simple example of constructor recursion// is the libc debug malloc, which is implemented in libc_malloc_debug_leak.so:// 1. The program depends on libc, so libc's constructor is called here.// 2. The libc constructor calls dlopen() to load libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.// 3. dlopen() calls the constructors on the newly created// soinfo for libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.// 4. The debug .so depends on libc, so CallConstructors is// called again with the libc soinfo. If it doesn't trigger the early-// out above, the libc constructor will be called again (recursively!).constructors_called = true;if ((flags & FLAG_EXE) == 0 && preinit_array != NULL) { // The GNU dynamic linker silently ignores these, but we warn the developer. PRINT("\"%s\": ignoring %d-entry DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!", name, preinit_array_count);} //确保库已被初始化加载if (dynamic != NULL) { for (Elf32_Dyn* d = dynamic; d->d_tag != DT_NULL; ++d) { if (d->d_tag == DT_NEEDED) { const char* library_name = strtab + d->d_un.d_val; TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors in DT_NEEDED \"%s\"", name, library_name); find_loaded_library(library_name)->CallConstructors(); } }}TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors", name); //最后进行初始化函数的执行// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.CallFunction("DT_INIT", init_func);CallArray("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array, init_array_count, false);}__int64 __fastcall _dl__ZN6soinfo17call_constructorsEv(__int64 result){ char v1; // w8 __int64 v2; // x19 const char *v3; // x2 _QWORD *i; // x20 __int64 v5; // x1 __int64 v6; // x0 __int64 v7; // x8 char *v8; // x0 __int64 v9; // x2 __int64 v10; // x3 char v11[16]; // [xsp+8h] [xbp-38h] BYREF __int64 v12; // [xsp+18h] [xbp-28h] __int128 v13; // [xsp+20h] [xbp-20h] BYREF char *v14; // [xsp+30h] [xbp-10h] if ( !(_dl_g_is_ldd | *(result + 248)) ) { v1 = *(result + 48); v2 = result; *(result + 248) = 1; if ( (v1 & 4) == 0 && *(result + 136) && (_dl_g_ld_debug_verbosity & 0x80000000) == 0 ) { if ( (*(result + 432) & 1) != 0 ) v3 = *(result + 448); else v3 = (result + 433); _dl__Z10linker_logiPKcz(0xFFFFFFFFLL, "\"%s\": ignoring DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!", v3); } for ( i = *(v2 + 288); i; i = *i ) _dl__ZN6soinfo17call_constructorsEv(i[1]); if ( (*(v2 + 48) & 0x10) == 0 ) { _dl__ZNSt3__112basic_stringIcNS_11char_traitsIcEENS_9allocatorIcEEEC2IDnEEPKc(v11, "calling constructors: "); if ( (*(v2 + 432) & 1) != 0 ) v5 = *(v2 + 448); else v5 = v2 + 433; v6 = _dl__ZNSt3__112basic_stringIcNS_11char_traitsIcEENS_9allocatorIcEEE6appendEPKc(v11, v5); v7 = *(v6 + 16); v13 = *v6; v14 = v7; *(v6 + 8) = 0LL; *(v6 + 16) = 0LL; *v6 = 0LL; if ( (v13 & 1) != 0 ) v8 = v14; else v8 = &v13 + 1; _dl__Z18bionic_trace_beginPKc(v8); if ( (v13 & 1) != 0 ) _dl__ZdlPv(v14); if ( (v11[0] & 1) != 0 ) _dl__ZdlPv(v12); } if ( (*(v2 + 432) & 1) != 0 ) v9 = *(v2 + 448); else v9 = v2 + 433; _dl__ZL13call_functionPKcPFviPPcS2_ES0_("DT_INIT", *(v2 + 184), v9); if ( (*(v2 + 432) & 1) != 0 ) v10 = *(v2 + 448); else v10 = v2 + 433; result = _dl__ZL10call_arrayIPFviPPcS1_EEvPKcPT_mbS5_("DT_INIT_ARRAY", *(v2 + 152), *(v2 + 160), v10); if ( (*(v2 + 48) & 0x10) == 0 ) return _dl__Z16bionic_trace_endv(result); } return result;}__int64 __fastcall _dl__ZN6soinfo17call_constructorsEv(__int64 result){ char v1; // w8 __int64 v2; // x19 const char *v3; // x2 _QWORD *i; // x20 __int64 v5; // x1 __int64 v6; // x0 __int64 v7; // x8 char *v8; // x0 __int64 v9; // x2 __int64 v10; // x3 char v11[16]; // [xsp+8h] [xbp-38h] BYREF __int64 v12; // [xsp+18h] [xbp-28h] __int128 v13; // [xsp+20h] [xbp-20h] BYREF char *v14; // [xsp+30h] [xbp-10h] if ( !(_dl_g_is_ldd | *(result + 248)) ) { v1 = *(result + 48); v2 = result; *(result + 248) = 1; if ( (v1 & 4) == 0 && *(result + 136) && (_dl_g_ld_debug_verbosity & 0x80000000) == 0 ) { if ( (*(result + 432) & 1) != 0 ) v3 = *(result + 448); else v3 = (result + 433); _dl__Z10linker_logiPKcz(0xFFFFFFFFLL, "\"%s\": ignoring DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!", v3); } for ( i = *(v2 + 288); i; i = *i ) _dl__ZN6soinfo17call_constructorsEv(i[1]); if ( (*(v2 + 48) & 0x10) == 0 ) { _dl__ZNSt3__112basic_stringIcNS_11char_traitsIcEENS_9allocatorIcEEEC2IDnEEPKc(v11, "calling constructors: "); if ( (*(v2 + 432) & 1) != 0 ) v5 = *(v2 + 448); else v5 = v2 + 433; v6 = _dl__ZNSt3__112basic_stringIcNS_11char_traitsIcEENS_9allocatorIcEEE6appendEPKc(v11, v5); v7 = *(v6 + 16); v13 = *v6; v14 = v7;[培训]Windows内核深度攻防:从Hook技术到Rootkit实战!
赞赏
- [原创]安卓中so的加载 54777
- [原创]从Java到Native,so中的函数是如何一步步被加载的? 36050
- [原创]安卓启动流程初探 41350