函数抽取壳这个词不知道从哪起源的,但我理解的函数抽取壳是那种将dex文件中的函数代码给nop,然后在运行时再把字节码给填回dex的这么一种壳。
函数抽取前:
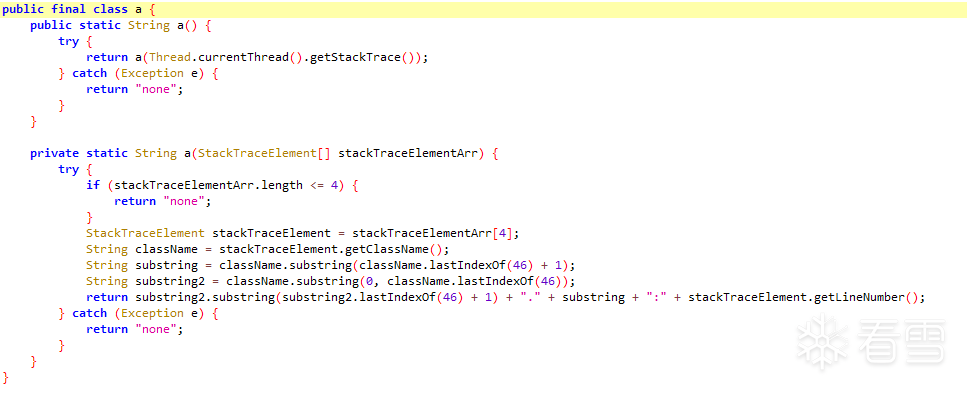
函数抽取后:
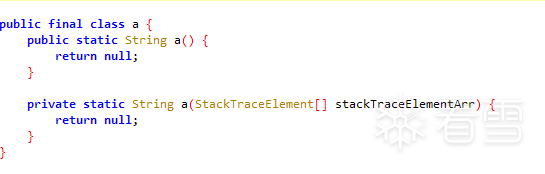
很早之前就想写这类的壳,最近终于把它做出来了,取名为dpt。现在将代码分享出来,欢迎把玩。项目地址:027K9s2c8@1M7s2y4Q4x3@1q4Q4x3V1k6Q4x3V1k6Y4K9i4c8Z5N6h3u0Q4x3X3g2U0L8$3#2Q4x3V1k6D9N6h3!0&6k6i4y4A6M7h3W2#2i4K6u0r3k6s2m8@1i4K6u0V1M7$3S2W2L8r3H3`.
dpt代码分为两个部分,一个是proccessor,另一个是shell。
proccessor是可以将普通apk处理成加壳apk的模块。它的主要功能有:
解压apk
提取apk中的dex的codeitem保存起来
修改Androidmanifest.xml中的Application类名
生成新的apk
它的流程如下:

shell模块最终生成的dex文件和so文件将被集成到需要加壳的apk中。它的要功能有:
处理App的启动
替换dexElements
hook相关函数
调用目标Application
codeitem文件读取
codeitem填回
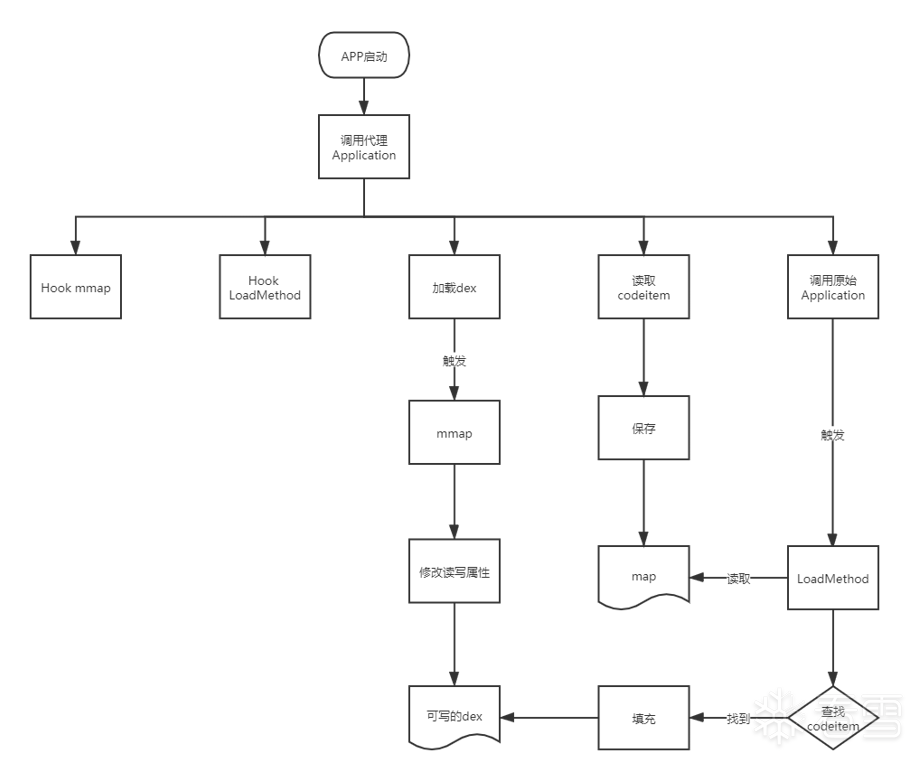
shell模块的流程如下:
proccessor比较重要的逻辑两点,AndroidManiest.xml的处理和Codeitem的提取
我们处理AndroidManifest.xml的操作主要是备份原Application的类名和写入壳的代理Application的类名。备份原Application类名目的是在壳的流程执行完成后,调用我们原APK的Application。写入壳的代理Application类名的目的是在app启动时尽早的启动我们的代理Application,这样我们就可以做一些准备工作,比如自定义加载dex,Hook一些函数等。我们知道,AndroidManifest.xml在生成apk后它不是以普通xml文件的格式来存放的,而是以axml格式来存放的。不过幸运的是,已经有许多大佬写了对axml解析和编辑的库,我们直接拿来用就行。这里用到的axml处理的库是ManifestEditor。
提取原Androidmanifest.xml Application完整类名代码如下,直接调用getApplicationName函数即可
写入Application类名的代码如下:
CodeItem是什么东西,CodeItem就是dex文件中存放函数字节码相关数据的结构。下图显示的就是CodeItem大概的样子。

说是提取CodeItem,其实我们提取的是CodeItem中的insns,它里面存放的是函数真正的字节码。提取insns,我们使用的是Android源码中的dx工具,使用dx工具可以很方便的读取dex文件的各个部分。
下面的代码遍历所有ClassDef,并遍历其中的所有函数,再调用extractMethod对单个函数进行处理。
处理函数的过程中发现没有代码(通常为native函数)或者insns的容量不足以填充return语句则跳过处理。这里就是对应函数抽取壳的抽取操作
shell模块是函数抽取壳的主要逻辑,它的功能我们上面已经讲过。
Hook函数时机最好要早点,dpt在_init函数中开始进行一系列HOOK
Hook框架使用的Dobby,主要Hook两个函数:MapFileAtAddress和LoadMethod。
Hook MapFileAtAddress函数的目的是在我们加载dex能够修改dex的属性,让加载的dex可写,这样我们才能把字节码填回dex,有大佬详细的分析过,具体参考这篇文章。
Hook到了之后,给prot参数追加PROT_WRITE属性
在Hook LoadMethod函数之前,我们需要了解LoadMethod函数流程。为什么是这个LoadMethod函数,其他函数是否可行?
当一个类被加载的时候,它的调用链是这样的(部分流程已省略):
也就是说,当一个类被加载,它是会去调用LoadMethod函数的,我们看一下它的函数原型:
这个函数太爆炸了,它有两个爆炸性的参数,DexFile和ClassDataItemIterator,我们可以从这个函数得到当前加载函数所在的DexFile结构和当前函数的一些信息,可以看一下ClassDataItemIterator结构:
其中最重要的字段就是code_off_它的值是当前加载的函数的CodeItem相对于DexFile的偏移,当相应的函数被加载,我们就可以直接访问到它的CodeItem。其他函数是否也可以?在上面的流程中没有比LoadMethod更适合我们Hook的函数,所以它是最佳的Hook点。
Hook LoadMethod稍微复杂一些,倒不是Hook代码复杂,而是Hook触发后处理的代码比较复杂,我们要适配多个Android版本,每个版本LoadMethod函数的参数都可能有改变,幸运的是,LoadMethod改动也不是很大。那么,我们如何读取ClassDataItemIterator类中的code_off_呢?比较直接的做法是计算偏移,然后在代码中维护一份偏移。不过这样的做法不易阅读很容易出错。dpt的做法是把ClassDataItemIterator类拷过来,然后将ClassDataItemIterator引用直接转换为我们自定义的ClassDataItemIterator引用,这样就可以方便的读取字段的值。
下面是LoadMethod被调用后做的操作,逻辑是读取存在map中的insns,然后将它们填回指定位置。
其实dex在App启动的时候已经被加载过一次了,但是,我们为什么还要再加载一次?因为系统加载的dex是以只读方式加载的,我们没办法去修改那一部分的内存。而且App的dex加载早于我们Application的启动,这样,我们在代码根本没法感知到,所以我们要重新加载dex。
自定义的ClassLoader
这一步也非常重要,这一步的目的是使ClassLoader从我们新加载的dex文件中加载类。代码如下:
做这个壳确实花了不少的时间,其中走过的弯路只有自己知道,不过还好做出来了。dpt未经过大量测试,后续发现问题再慢慢解决。
public static String getValue(String file,String tag,String ns,String attrName){
byte[] axmlData = IoUtils.readFile(file);
AxmlParser axmlParser = new AxmlParser(axmlData);
try {
while (axmlParser.next() != AxmlParser.END_FILE) {
if (axmlParser.getAttrCount() != 0 && !axmlParser.getName().equals(tag)) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < axmlParser.getAttrCount(); i++) {
if (axmlParser.getNamespacePrefix().equals(ns) && axmlParser.getAttrName(i).equals(attrName)) {
return (String) axmlParser.getAttrValue(i);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String getApplicationName(String file) {
return getValue(file,"application","android","name");
}
public static String getValue(String file,String tag,String ns,String attrName){
byte[] axmlData = IoUtils.readFile(file);
AxmlParser axmlParser = new AxmlParser(axmlData);
try {
while (axmlParser.next() != AxmlParser.END_FILE) {
if (axmlParser.getAttrCount() != 0 && !axmlParser.getName().equals(tag)) {
continue;
}
for (int i = 0; i < axmlParser.getAttrCount(); i++) {
if (axmlParser.getNamespacePrefix().equals(ns) && axmlParser.getAttrName(i).equals(attrName)) {
return (String) axmlParser.getAttrValue(i);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
public static String getApplicationName(String file) {
return getValue(file,"application","android","name");
}
public static void writeApplicationName(String inManifestFile, String outManifestFile, String newApplicationName){
ModificationProperty property = new ModificationProperty();
property.addApplicationAttribute(new AttributeItem(NodeValue.Application.NAME,newApplicationName));
FileProcesser.processManifestFile(inManifestFile, outManifestFile, property);
}
public static void writeApplicationName(String inManifestFile, String outManifestFile, String newApplicationName){
ModificationProperty property = new ModificationProperty();
property.addApplicationAttribute(new AttributeItem(NodeValue.Application.NAME,newApplicationName));
FileProcesser.processManifestFile(inManifestFile, outManifestFile, property);
}
public static List<Instruction> extractAllMethods(File dexFile, File outDexFile) {
List<Instruction> instructionList = new ArrayList<>();
Dex dex = null;
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
byte[] dexData = IoUtils.readFile(dexFile.getAbsolutePath());
IoUtils.writeFile(outDexFile.getAbsolutePath(),dexData);
try {
dex = new Dex(dexFile);
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(outDexFile, "rw");
Iterable<ClassDef> classDefs = dex.classDefs();
for (ClassDef classDef : classDefs) {
......
if(classDef.getClassDataOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("class '%s' data offset is zero",classDef.toString());
logger.warn(log);
continue;
}
ClassData classData = dex.readClassData(classDef);
ClassData.Method[] directMethods = classData.getDirectMethods();
ClassData.Method[] virtualMethods = classData.getVirtualMethods();
for (ClassData.Method method : directMethods) {
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex,randomAccessFile,classDef,method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
for (ClassData.Method method : virtualMethods) {
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex, randomAccessFile,classDef, method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
IoUtils.close(randomAccessFile);
}
return instructionList;
}
public static List<Instruction> extractAllMethods(File dexFile, File outDexFile) {
List<Instruction> instructionList = new ArrayList<>();
Dex dex = null;
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null;
byte[] dexData = IoUtils.readFile(dexFile.getAbsolutePath());
IoUtils.writeFile(outDexFile.getAbsolutePath(),dexData);
try {
dex = new Dex(dexFile);
randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(outDexFile, "rw");
Iterable<ClassDef> classDefs = dex.classDefs();
for (ClassDef classDef : classDefs) {
......
if(classDef.getClassDataOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("class '%s' data offset is zero",classDef.toString());
logger.warn(log);
continue;
}
ClassData classData = dex.readClassData(classDef);
ClassData.Method[] directMethods = classData.getDirectMethods();
ClassData.Method[] virtualMethods = classData.getVirtualMethods();
for (ClassData.Method method : directMethods) {
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex,randomAccessFile,classDef,method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
for (ClassData.Method method : virtualMethods) {
Instruction instruction = extractMethod(dex, randomAccessFile,classDef, method);
if(instruction != null) {
instructionList.add(instruction);
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
IoUtils.close(randomAccessFile);
}
return instructionList;
}
private static Instruction extractMethod(Dex dex ,RandomAccessFile outRandomAccessFile,ClassDef classDef,ClassData.Method method)
throws Exception{
String returnTypeName = dex.typeNames().get(dex.protoIds().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getProtoIndex()).getReturnTypeIndex());
String methodName = dex.strings().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getNameIndex());
String className = dex.typeNames().get(classDef.getTypeIndex());
//native函数
if(method.getCodeOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("method code offset is zero,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
Instruction instruction = new Instruction();
//16 = registers_size + ins_size + outs_size + tries_size + debug_info_off + insns_size
int insnsOffset = method.getCodeOffset() + 16;
Code code = dex.readCode(method);
//容错处理
if(code.getInstructions().length == 0){
String log = String.format("method has no code,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
int insnsCapacity = code.getInstructions().length;
//insns容量不足以存放return语句,跳过
byte[] returnByteCodes = getReturnByteCodes(returnTypeName);
if(insnsCapacity * 2 < returnByteCodes.length){
logger.warn("The capacity of insns is not enough to store the return statement. {}.{}() -> {} insnsCapacity = {}byte(s),returnByteCodes = {}byte(s)",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName),
insnsCapacity * 2,
returnByteCodes.length);
return null;
}
instruction.setOffsetOfDex(insnsOffset);
//这里的MethodIndex对应method_ids区的索引
instruction.setMethodIndex(method.getMethodIndex());
//注意:这里是数组的大小
instruction.setInstructionDataSize(insnsCapacity * 2);
byte[] byteCode = new byte[insnsCapacity * 2];
//写入nop指令
for (int i = 0; i < insnsCapacity; i++) {
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
byteCode[i * 2] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
byteCode[i * 2 + 1] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
outRandomAccessFile.writeShort(0);
}
instruction.setInstructionsData(byteCode);
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset);
//写出return语句
outRandomAccessFile.write(returnByteCodes);
return instruction;
}
private static Instruction extractMethod(Dex dex ,RandomAccessFile outRandomAccessFile,ClassDef classDef,ClassData.Method method)
throws Exception{
String returnTypeName = dex.typeNames().get(dex.protoIds().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getProtoIndex()).getReturnTypeIndex());
String methodName = dex.strings().get(dex.methodIds().get(method.getMethodIndex()).getNameIndex());
String className = dex.typeNames().get(classDef.getTypeIndex());
//native函数
if(method.getCodeOffset() == 0){
String log = String.format("method code offset is zero,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
Instruction instruction = new Instruction();
//16 = registers_size + ins_size + outs_size + tries_size + debug_info_off + insns_size
int insnsOffset = method.getCodeOffset() + 16;
Code code = dex.readCode(method);
//容错处理
if(code.getInstructions().length == 0){
String log = String.format("method has no code,name = %s.%s , returnType = %s",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName));
logger.warn(log);
return null;
}
int insnsCapacity = code.getInstructions().length;
//insns容量不足以存放return语句,跳过
byte[] returnByteCodes = getReturnByteCodes(returnTypeName);
if(insnsCapacity * 2 < returnByteCodes.length){
logger.warn("The capacity of insns is not enough to store the return statement. {}.{}() -> {} insnsCapacity = {}byte(s),returnByteCodes = {}byte(s)",
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(className),
methodName,
TypeUtils.getHumanizeTypeName(returnTypeName),
insnsCapacity * 2,
returnByteCodes.length);
return null;
}
instruction.setOffsetOfDex(insnsOffset);
//这里的MethodIndex对应method_ids区的索引
instruction.setMethodIndex(method.getMethodIndex());
//注意:这里是数组的大小
instruction.setInstructionDataSize(insnsCapacity * 2);
byte[] byteCode = new byte[insnsCapacity * 2];
//写入nop指令
for (int i = 0; i < insnsCapacity; i++) {
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
byteCode[i * 2] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
byteCode[i * 2 + 1] = outRandomAccessFile.readByte();
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset + (i * 2));
outRandomAccessFile.writeShort(0);
}
instruction.setInstructionsData(byteCode);
outRandomAccessFile.seek(insnsOffset);
//写出return语句
outRandomAccessFile.write(returnByteCodes);
return instruction;
}
extern "C" void _init(void) {
dpt_hook();
}
extern "C" void _init(void) {
dpt_hook();
}
void* MapFileAtAddressAddr = DobbySymbolResolver(GetArtLibPath(),MapFileAtAddress_Sym());
DobbyHook(MapFileAtAddressAddr, (void *) MapFileAtAddress28,(void **) &g_originMapFileAtAddress28);
void* MapFileAtAddressAddr = DobbySymbolResolver(GetArtLibPath(),MapFileAtAddress_Sym());
DobbyHook(MapFileAtAddressAddr, (void *) MapFileAtAddress28,(void **) &g_originMapFileAtAddress28);
void* MapFileAtAddress28(uint8_t* expected_ptr,
size_t byte_count,
int prot,
int flags,
int fd,
off_t start,
bool low_4gb,
bool reuse,
const char* filename,
std::string* error_msg){
int new_prot = (prot | PROT_WRITE);
if(nullptr != g_originMapFileAtAddress28) {
return g_originMapFileAtAddress28(expected_ptr,byte_count,new_prot,flags,fd,start,low_4gb,reuse,filename,error_msg);
}
}
void* MapFileAtAddress28(uint8_t* expected_ptr,
size_t byte_count,
int prot,
int flags,
int fd,
off_t start,
传播安全知识、拓宽行业人脉——看雪讲师团队等你加入!